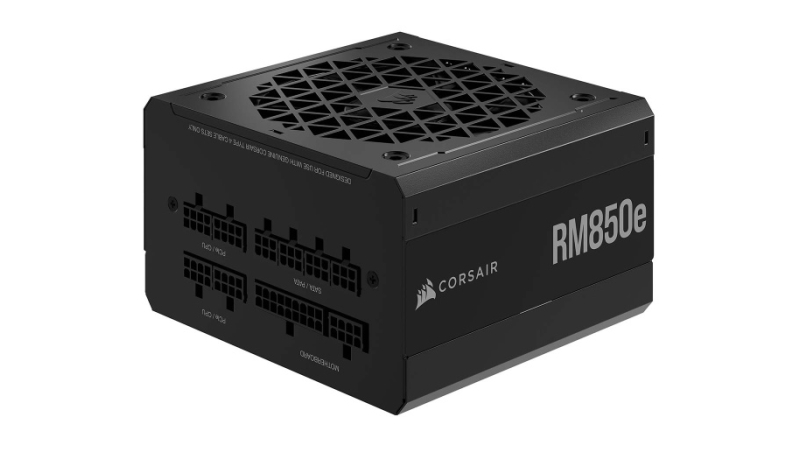
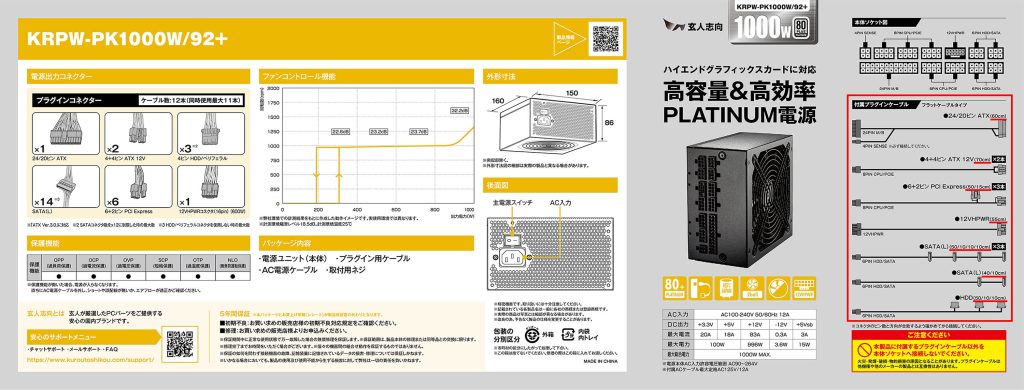
Power supply units have various types of cables, so it is necessary to check the types and number of power cables needed according to the PC parts configuration and select the power supply unit accordingly.
For this reason, it is important to know which cable is used for which part. Without this knowledge, it is not possible to choose a power supply unit that matches the configuration. This article will explain about the cables of power supply units.
If there are enough types and numbers of cables for the parts configuration, there is no problem. However, if not, it may be necessary to buy a new power supply unit.
- Select a power supply unit with the types and number of cables suitable for the parts configuration
- Cheap power supply units × large parts configuration may result in cables being too short
- If the cable is too short, extension cables can be used as a last resort
- If future expansion is possible, choose a unit with extra capacity
This article also explains the basics of power supply unit standards and cables, as well as how to choose from the perspective of performance and compatibility.
≫ Related article: How to Choose a Custom PC Power Supply Unit [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
Select PC parts and online stores to instantly generate an estimate, check compatibility, and calculate power requirements. You can save up to five different builds, making it easy to try out multiple configurations.≫ Tool:PC Parts Estimation & Compatibility Check Tool
Table of Contents
About Power Supply Unit Cables
Power supply unit cables play an important role in supplying power to each part inside a custom PC.
First, let’s learn the basic knowledge about cables.
Types of Cables
There are the following types of power supply unit cables.
- Main cable
- CPU auxiliary power cable
- PCI Express cable
- 12VHPWR cable
- SATA cable
- Peripheral cable
- FDD cable
Each cable connects to different parts, so it is necessary to check if the required cables are available according to the parts configuration when choosing a power supply unit.
The usage of each cable will be explained later, but if this is mistaken, it may be necessary to buy a new power supply unit.
That said, in most cases, the necessary types of cables are included, so there is not much need to worry.
Peripheral connectors and FDD connectors are often not included, as they are used for old standard parts.
Therefore, if these connectors or cables are needed, be sure to check the specifications of the power supply unit.
Number of Connectors and Cables
Even if all types of power supply unit cables are included, the number of connectors and cables needed will change depending on the parts configuration.
For main cables, only one is usually needed, but for other cables, it is necessary to check the required number according to the parts configuration.
Especially for PCI Express cables and SATA cables, the required number can vary greatly depending on the parts configuration, so this is important to check.
Cable Length
The length of power supply unit cables is fixed for each product.
In most cases, the cables are long enough to connect from the power supply unit to each part, but sometimes they may not reach.
This is especially likely to happen when using a cheap power supply unit with a large case or motherboard.
Cheap power supply units tend to have shorter cables to reduce costs.
Also, with large parts such as full tower cases or Extended ATX motherboards, the distance between parts becomes longer.
When these two factors overlap, cable length shortages are more likely to occur.
To address this, basically avoid such parts configurations, or supplement with extension cable .
The cable information is often written in the specifications of the power supply unit, but the actual distance between the power supply unit and the parts cannot be known until assembly.
Therefore, it is possible to choose cables as long as possible, but it is not possible to know exactly how long is enough, so in the end, if the cable is not long enough, extension cables will be needed.
Future Expandability
If planning to add more storage in the future, it is necessary to choose a power supply unit with the required types and number of cables, considering the final parts configuration.
Even if there is no plan to expand at first, it is also good to choose a unit with extra cables for possible future expansion.
With the current mainstream parts configuration, even a general power supply unit should allow for the addition of storage or optical drives without any problem.
However, if planning to use a graphics card or old standard parts, be sure to check in advance if the necessary connectors are available.
One of the strengths of custom PCs is the ability to freely customize even after assembly if there is knowledge and skill.
Therefore, it is recommended to choose a power supply unit with extra types and numbers of cables so that expansion is possible when needed.
Types of Power Supply Unit Cables and Connectors
There are various types of power supply unit cables.
Each cable is used for a specific purpose, and it is important to connect them properly.
First, the images and features of each connector are summarized below, followed by detailed explanations.
| Type of Connector | Image | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Main Connector (20+4 pin) |  | ・Supplies power to the motherboard ・Can be used as 20-pin or 24-pin ・Currently used as 24-pin ・Usually only one cable |
| CPU Auxiliary Power Connector (4+4 pin) |  | ・Supplies additional power to the CPU ・Can be used as 4-pin or 8-pin ・Essential for high-performance CPUs ・Usually 1 or 2 cables included |
| PCI Express Connector (6+2 pin) |  | ・Mainly supplies extra power to the GPU ・Can be used as 6-pin or 8-pin ・Supplies power to PCI Express slots ・Often 1-3 cables connected to GPU |
| 12VHPWR Connector (12+4 pin) |  | ・Supplies extra power to the latest high-performance GPUs ・High power supply capacity (up to 600W) ・4-pin signal pins for optimization |
| SATA Power Connector |  | ・Supplies power to SSDs, HDDs, and optical drives ・One cable usually has 2-3 connectors |
| Peripheral Power Connector |  | ・Supplies power to old IDE standard parts ・3-pin or 4-pin ・One cable usually has 2-3 connectors ・Used for fans or LEDs ・Rarely used today |
| FDD Power Connector | – | ・Supplies power to floppy disk drives ・Rarely used today |
Main Connector (20+4 pin)
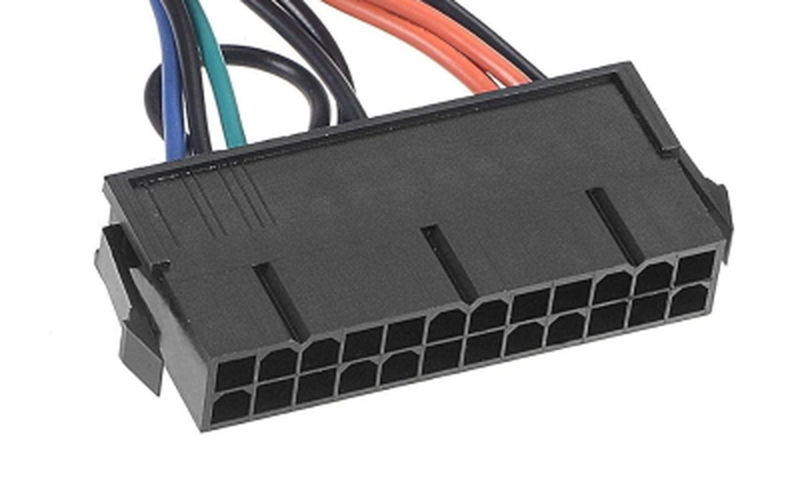
The main connector (20+4 pin) is the main cable that supplies power from the power supply unit to the motherboard.
This connector is divided into a 20-pin and a 4-pin part, so it can be used for both old 20-pin motherboards and new 24-pin motherboards.
The 20-pin part supplies basic power, and the 4-pin part is used to supply additional power.
This expands compatibility and allows connection to various motherboards.
However, the 20-pin is for motherboards from around the year 2000, so recent motherboards almost never use 20-pin.
Therefore, some power supply units use a single 24-pin connector without separation.
During the transition from 20-pin to 24-pin, there was a period when both needed to be supported, so the 20+4 pin form was created.
Other connectors may also be split for similar reasons, and the specifications may say “20+4 pin” to indicate this.
≫ Related article: How to Choose a Custom PC Motherboard [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
CPU Auxiliary Power Connector (4+4 pin)
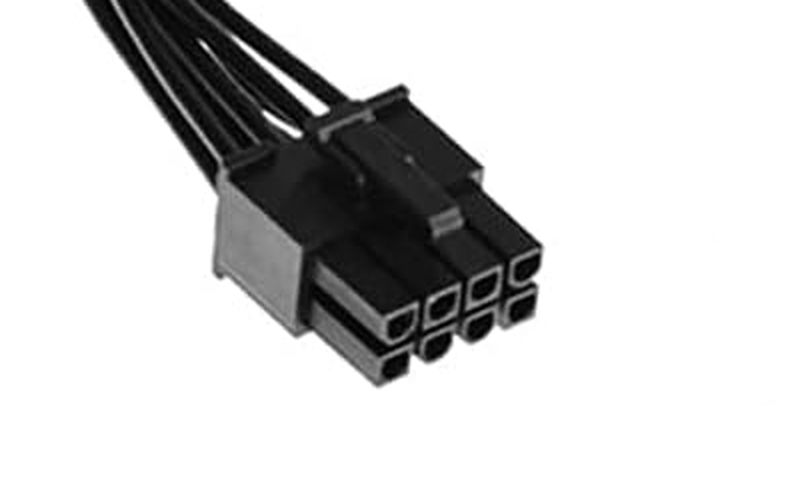

The CPU auxiliary power connector (4+4 pin) is a cable that supplies power to the CPU.
This is also split into 4+4 pins, but like the main connector, it is almost always used as 8-pin today.
Originally, 8-pin connectors became common on server motherboards, but now even general motherboards use 8-pin.
This was originally used to supply extra power for high-performance CPUs when the main connector was not enough.
However, since modern CPUs are much more powerful and consume more power, auxiliary power is used in most cases.
≫ Related article: How to Choose a Custom PC CPU [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
PCI Express Connector (6+2 pin)
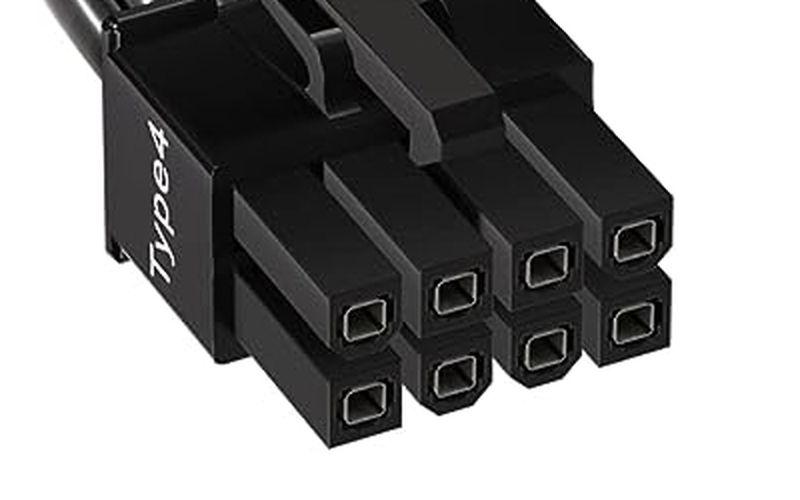

The PCI Express connector (6+2 pin) is a cable mainly used to supply power to graphics cards.
Besides graphics cards, it is also used to supply extra power to high-power expansion cards.
The PCI Express slot also supplies power (x16 slot: up to 75W), but for high-power parts like graphics cards, the slot alone is not enough, so the PCI Express connector is used for additional power.
This connector is split into 6-pin and 2-pin parts, so it can be used as 6-pin or 8-pin as needed.
6-pin supplies 75W, 8-pin supplies 150W, so it can support high-performance graphics cards.
Recently, graphics cards have become even more powerful and consume more power, so it is common to connect 2 or 3 PCI Express cables, and a new connector called 12VHPWR has also appeared.
≫ Related article: How to Choose a Custom PC Graphics Card [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
12VHPWR Connector (12+4 pin)
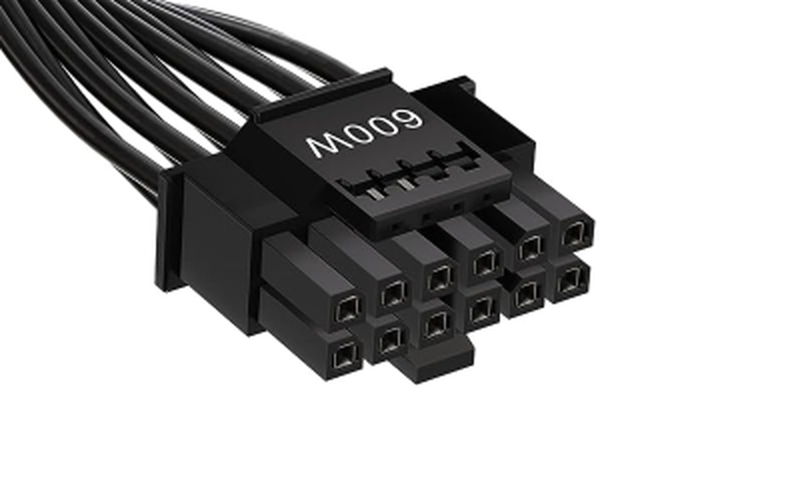

The 12VHPWR connector (12+4 pin) is a relatively new type of connector, designed to support the latest high-performance graphics cards.
This connector was introduced as part of the PCI Express 4.0/5.0 standard, and can safely supply more power than the previous 6-pin or 8-pin connectors, making it suitable for high-end graphics cards with high power consumption.
It first appeared with NVIDIA GeForce RTX 30 series, and is widely used from the RTX 40 series.
The 12VHPWR connector has 12 pins for power supply and 4 pins (signal pins) for data communication.
The signal pins provide functions such as monitoring how much power the GPU is actually using and communication between the power supply unit and GPU.
This optimizes power management and enables more stable power supply.
When checking how many cables are needed for a graphics card’s auxiliary power, it is often written as 12VHPWR or 16-pin.
12VHPWR is easy to understand, but 16-pin can be confusing, so remember that 16-pin = 12VHPWR.
Also, when using this connector, both the power supply unit and graphics card must support it, so check compatibility in advance.
High-performance graphics cards tend to consume more power, so it is common to use 2 or 3 PCI Express connectors, but the 12VHPWR connector can handle large amounts of power with just one cable.
As graphics cards have become more powerful and require more power, the number of PCI Express connectors needed has increased, so the 12VHPWR connector was introduced.
If there are too many cables, the graphics card needs more ports, which takes up space on the board and circuits.
While the 6-pin PCI Express connector supplies 75W and the 8-pin supplies 150W, the 12VHPWR connector supports 150W, 300W, 450W, and 600W.
Although the standard supports all four, since the 12VHPWR connector was introduced to address the shortage of 150W PCI Express connectors, it is often used for 300W or more.
Even with the same 12VHPWR connector, the power supplied can differ, so consider how much power is needed from the PCI Express x16 slot (75W) and how much from the 12VHPWR connector when choosing.
SATA (Serial ATA) Connector
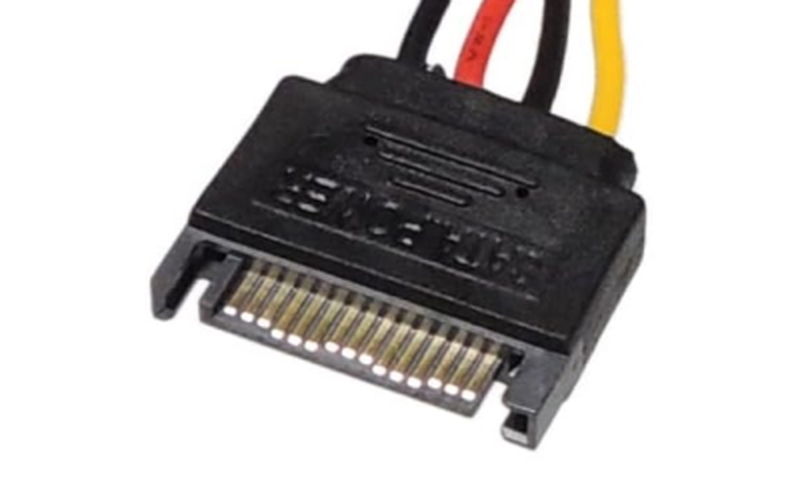

The SATA (Serial ATA) connector is mainly used to supply power to SATA standard parts such as SSDs (*), HDDs, and optical drives.
The connector has 15 pins and can supply 3.3V, 5V, and 12V, so it is flexible for various parts.
*M.2 SSDs connect directly to the motherboard and do not need a power cable.
One connector is needed for each part, so choose a power supply unit with enough SATA connectors for the number of storage devices (SATA SSDs, HDDs) to be installed in the custom PC.
For example, if using 2 SSDs and 3 HDDs, at least 5 SATA connectors are needed.
However, considering the possibility of adding more storage in the future, it is recommended to choose a power supply unit with extra connectors.
![]() Ken
Ken
SATA power cables from the power supply unit usually have multiple connectors, so one cable can supply power to several devices.
This reduces the number of cables and makes effective use of internal space.
≫ Related article: How to Choose Custom PC Storage (SSD/HDD) [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
Peripheral Connector
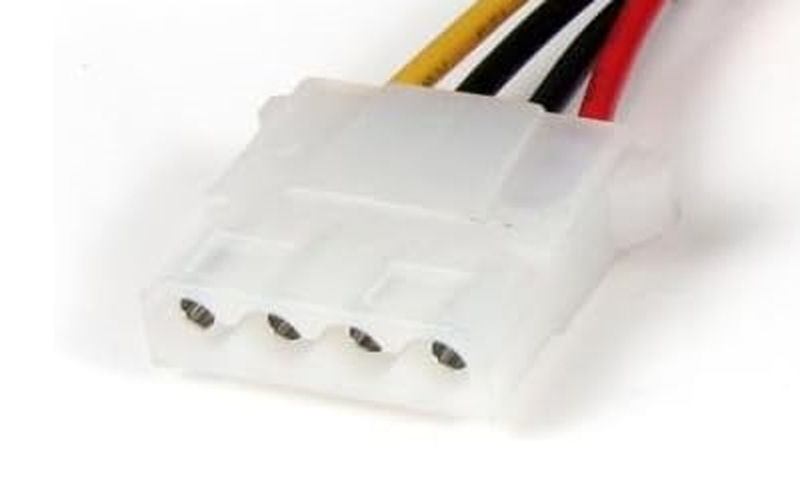

The peripheral connector is mainly a cable used to supply power to old HDDs and optical drives, but it is basically not used anymore.
Recent HDDs and optical drives use the SATA standard and SATA cables, but this cable is used for IDE standard parts.
IDE is an old connection standard used before SATA became common.
It was once commonly used for many devices, but now SATA connectors are the mainstream, so usage has decreased.
It is still sometimes used with a conversion connector to supply power to fans, but this is rare.
Even so, many modern power supply units still include peripheral power connectors to support old parts.
FDD Connector
The FDD connector is a cable that supplies power to floppy disk drives (FDD).
Floppy disk drives were once installed in many computers, but they are rarely used today.
Therefore, most modern power supply units do not include FDD power connectors.
The FDD power connector is a small 4-pin connector, smaller than other power connectors.
This connector may be needed when using old computers or specific old parts, but for most users, it is not important.
Summary: Understand the Types and Number of Cables Needed from the Parts Configuration!
This article explained the basic knowledge about power supply unit cables and connectors, their features and roles, and which parts they connect to.
Here are the key points again.
- Select a power supply unit with the types and number of cables suitable for the parts configuration
- Cheap power supply units × large parts configuration may result in cables being too short
- If the cable is too short, extension cables can be used as a last resort
- If future expansion is possible, choose a unit with extra capacity
There are various types of cables, so it is necessary to check the types and number of power cables needed according to the parts configuration and select the power supply unit accordingly.
For this reason, it is important to know which cable is used for which part. Without this knowledge, it is not possible to choose a power supply unit that matches the configuration.
If a mistake is made, it may be necessary to buy a new unit costing around 10,000 yen, so be careful when choosing.
This article also explains the basics of power supply unit standards and cables, as well as how to choose from the perspective of performance and compatibility.
≫ Related article: How to Choose a Custom PC Power Supply Unit [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
Select PC parts and online stores to instantly generate an estimate, check compatibility, and calculate power requirements. You can save up to five different builds, making it easy to try out multiple configurations.
≫ Tool:PC Parts Estimation & Compatibility Check Tool
 ZisaLog: Beginner’s Guide to Building a Custom PC
ZisaLog: Beginner’s Guide to Building a Custom PC