Thermal throttling is a function that automatically limits performance to prevent damage when parts become too hot.
When a computer is used for a long time under heavy load and the cooling performance is insufficient, components such as the CPU or GPU can become very hot, which may lead to part failure or a shorter lifespan.
This article explains in detail the basics of thermal throttling, which parts are affected, and measures to prevent thermal throttling.
- Thermal throttling is a function that limits performance when parts become too hot
- The purpose is to prevent part damage, system instability, and reduced lifespan due to high temperatures
- Mainly occurs in CPUs, GPUs, and NVMe SSDs
- Temporary performance drops and response delays may occur
- Improving cooling performance, including airflow, is the main countermeasure
- Maintenance such as CPU grease replacement and dust cleaning also affects cooling
- The occurrence of thermal throttling can be checked with monitoring tools
This site also explains the basic knowledge, roles, and how to choose other PC parts from the perspective of performance and compatibility, so please refer to them as well.
≫ Related article: PC Parts List and Explanation of Each PC Part [A Must-Read for Custom PC Beginners]
Select PC parts and online stores to instantly generate an estimate, check compatibility, and calculate power requirements. You can save up to five different builds, making it easy to try out multiple configurations.
≫ Tool:PC Parts Estimation & Compatibility Check Tool
Table of Contents
About Thermal Throttling
This section explains the basics, roles, and purposes of thermal throttling.
What is Thermal Throttling?
Thermal throttling is a function that temporarily lowers the clock frequency of parts such as the CPU to prevent further heat generation and protect the parts when they become too hot.
Clock frequency is an indicator of how many instructions a CPU or GPU can process per second, usually expressed in gigahertz (GHz).
The higher this number, the more instructions the CPU or GPU can process in a short time, which means higher processing performance and faster completion of tasks.
When this clock frequency is temporarily lowered, performance drops during that time.
Therefore, to prevent thermal throttling from occurring, it is common to ensure cooling performance that matches the performance and heat output of the parts.
For example, when performing high-load tasks such as 3D gaming or video editing for a long time on a computer, the temperature of the CPU and other parts can rise.
If this high temperature continues, it may lead to part failure or a shorter lifespan.
The system monitors the internal temperature, and automatically lowers performance according to the temperature to protect the parts.
The Role and Purpose of Thermal Throttling
The main roles and purposes of thermal throttling are as follows:
- Protection and Prevention of Part Damage
If the temperature rises too much, the semiconductors inside the CPU or GPU can be damaged, leading to long-term performance degradation or part failure. Thermal throttling reduces the risk of damage from high temperatures. - Improving Overall System Stability
If the temperature is too high, the system can become unstable or suddenly shut down, but this risk can be reduced. Although performance temporarily drops due to thermal throttling, the system remains stable and work can continue. - Extending Part Lifespan
If high temperatures continue, electronic components deteriorate more easily, leading to failures. However, by properly managing temperature with thermal throttling, the lifespan of parts is extended and the reliability of the parts and the entire computer is improved.
In this way, the role and purpose of thermal throttling is to protect the computer in terms of part damage and system stability.
Parts Where Thermal Throttling Occurs
Thermal throttling can occur in CPUs, GPUs, and NVMe SSDs.
When talking about thermal throttling in computers, it usually refers to the CPU, but GPUs and NVMe SSDs also have thermal throttling functions.
Thermal throttling is likely to occur in CPUs and GPUs when high load continues for a long time and cooling performance is insufficient, limiting performance by temporarily lowering the clock frequency to prevent further heat generation.
Thermal throttling can also occur in NVMe SSDs.
Especially during high-load data transfers or continuous writing, the controller chip inside the SSD can become hot, and its operation may be temporarily limited.
The Impact of Thermal Throttling on Performance
This section explains the impact of thermal throttling on performance.
Performance Degradation
When thermal throttling occurs, the CPU or GPU temporarily limits the clock frequency, and the NVMe SSD temporarily limits data transfer speed to prevent further temperature rise, resulting in decreased performance.
Processing speed slows down, and data transfer takes more time.
To get the maximum performance from the CPU, GPU, or NVMe SSD, more power is consumed, which generates heat in the process.
In other words, the higher the performance at that time, the more power is consumed and the more heat is generated, so limiting performance suppresses heat generation.
Unstable Frame Rate (Especially in 3D Games)
Due to thermal throttling, especially in 3D games that require high performance, FPS (frame rate) drops, causing stuttering and lag.
3D games require a lot of graphics processing, so the CPU and GPU are heavily loaded and tend to get hot, making thermal throttling more likely.
As a result, game operation becomes unstable and the gaming experience may be impaired.
To prevent this, it is effective to adjust game settings to reduce the load, but it is better to enhance cooling performance when selecting parts for the entire computer.
In the case of graphics cards, the number of fans is already fixed and cannot be customized, so basically, ensuring proper airflow throughout the computer is the countermeasure.
Response Delay
Due to thermal throttling, the performance of the CPU or GPU and the data transfer speed of the NVMe SSD decrease, which can cause slower response when the user operates the computer.
For example, launching software or loading games may be slower than usual.
Thermal throttling is more likely to occur in high-load situations, so in high-load tasks such as 3D games, video editing, 3D rendering, data analysis, or AI learning, this response delay may be more noticeable.
Unstable Operation Due to Fluctuating Clock Frequency
If the clock frequency frequently fluctuates according to temperature rises and falls, operation becomes unstable, and high-load processing or multitasking may not proceed smoothly.
If this unstable operation continues, not only does data processing and file saving take longer, but the risk of application crashes also increases.
Difficult to Maintain Long-Term Performance
If high-load work continues for a long time and cooling cannot keep up, thermal throttling will continue to occur.
As a result, work progress will be delayed and take more time, making it difficult to maintain long-term performance.
Factors That Cause Thermal Throttling
Let’s take a closer look at the various factors that cause thermal throttling.
Rising Part Temperatures
One of the main factors that cause thermal throttling is rising part temperatures.
Since thermal throttling is a function to prevent system instability or failure due to rising part temperatures, temperature rise is naturally a factor.
Especially in high-load situations such as 3D games, video editing, 3D rendering, data analysis, or AI learning, and when these continue for a long time, temperature rises and thermal throttling is more likely to occur.
Insufficient Cooling of Parts
Thermal throttling is also likely to occur if the cooling performance is not sufficient to properly cool the heated parts.
Especially under high load for a long time, as mentioned above, insufficient cooling will cause it.
Insufficient cooling performance can be due to using a CPU cooler that does not match the CPU’s heat output, not having enough case fans, or improper airflow inside the PC case.
Also, if the thermal grease that transfers heat from the CPU to the CPU cooler has deteriorated or is not applied properly, thermal throttling may occur.
For custom PCs, it is necessary to check whether the CPU cooler has sufficient cooling performance for the CPU’s performance and heat output when selecting parts.
Also, maintenance such as reapplying thermal grease every three years is important.
In addition, small PC cases with narrow spacing between parts can easily have poor airflow and require attention.
Since there are fewer air passages, it is necessary to carefully consider airflow when selecting and assembling parts.
Rising Room Temperature
When the room temperature rises, the computer’s temperature also rises, so higher cooling performance is required than usual.
If cooling performance is insufficient and high load continues for a long time, it can lead to thermal throttling.
Especially in summer, temperatures rise, so use an air conditioner as needed.
Dust Inside the PC Case
If dust accumulates inside the PC case, it can block airflow and reduce the efficiency of case fans and heat sinks, making it difficult to dissipate heat.
As a result, the CPU and GPU become hot, thermal throttling occurs, and performance drops.
Especially if the PC has not been cleaned for a long time or is placed on the floor, dust tends to accumulate.
Regularly cleaning the inside of the PC and removing dust helps maintain cooling performance and prevent thermal throttling.
≫ Related article: Thorough Explanation of Custom PC Cleaning Methods and Necessary Tools [With Photos]
Measures to Prevent Thermal Throttling
This section explains measures to prevent thermal throttling.
Some measures need to be taken when selecting or assembling parts, while others can be done after assembly, so even those who have already bought parts can refer to this.
Installing a High-Performance CPU Cooler
For the CPU, a CPU cooler with cooling performance that matches the CPU’s performance and heat output is necessary.
If the cooling performance is insufficient for the CPU, it will quickly become hot, or it may be fine for short periods of high load, but will become hot if used for a long time.
Specifically, check the TDP (Thermal Design Power) listed in the CPU specifications and the maximum TDP in the CPU cooler specifications.
If the CPU cooler’s value is higher, it has sufficient cooling performance.
Basically, the values are set with plenty of margin to handle various CPUs and high-load situations.
For more details, see the article on how to choose a CPU cooler with images.
≫ Related article: How to Choose a Custom PC CPU Cooler [Performance / Functionality / Compatibility]
![]() Ken
Ken
Adding Case Fans
Case fans are used to ensure airflow throughout the computer, but if there are too few or their performance is low, cooling will be insufficient.
If there are not enough case fans, the heat from each part, especially the CPU, GPU, and NVMe SSD, cannot be properly expelled from the case, resulting in higher part temperatures and leading to thermal throttling.
Basically, PC cases come with 2 or 3 case fans, and having at least these is sufficient.
If you want to further improve cooling performance, add more case fans.
Fan performance refers to the amount of airflow, which is determined by the size and rotation speed of the fan.
Larger fans can provide more airflow even at lower speeds, and higher speeds increase airflow even more.
The case fan sizes compatible with PC cases are 120mm and 140mm, so there should be no problem if you use these sizes.
Also, as long as the rotation speed is not extremely low, it should be fine.
There are no strict standards for the number, size, or speed of fans, but basically, as long as you install the fans that come with the PC case in the correct orientation and position, you can get sufficient airflow.
≫ Related article: How to Choose a Custom PC Case Fan [Performance / Functionality / Compatibility]
Replacing CPU Grease
CPU grease is applied between the CPU and CPU cooler to smoothly transfer heat from the CPU to the cooler.
When freshly applied, CPU grease is soft and viscous, allowing smooth heat transfer, but it gradually hardens and loses thermal conductivity as it ages, reducing cooling performance.
Especially if used continuously in high-temperature environments, hardening accelerates.
Depending on usage time, load, the type of grease, or the grease pre-applied to the CPU cooler, it is generally necessary to reapply every 3 to 5 years.
After assembly, record the CPU temperature at idle and under high load, and periodically check if the temperature has increased to determine when to reapply the grease.
![]() Ken
Ken
≫ Related article: Explaining the Role, Application, and Maintenance of CPU Grease [Custom PC]
Attaching a Heatsink to NVMe SSD
Attaching a heatsink to an NVMe SSD improves cooling performance.
Depending on the product, NVMe SSDs have high data transfer speeds and generate a lot of heat.
Especially when moving, copying, or continuously writing large amounts of data for a long time, they tend to get hot.
Therefore, many motherboards have M.2 slots with heatsinks, so choose such motherboards.
If the motherboard’s M.2 slot does not have a heatsink, you can also attach a separately sold heatsink for NVMe SSDs.
If the motherboard already has one, just attach it and it should be fine.
If not, monitor the temperature during data transfer, and if it exceeds about 60°C, consider attaching a heatsink.
Checking Airflow
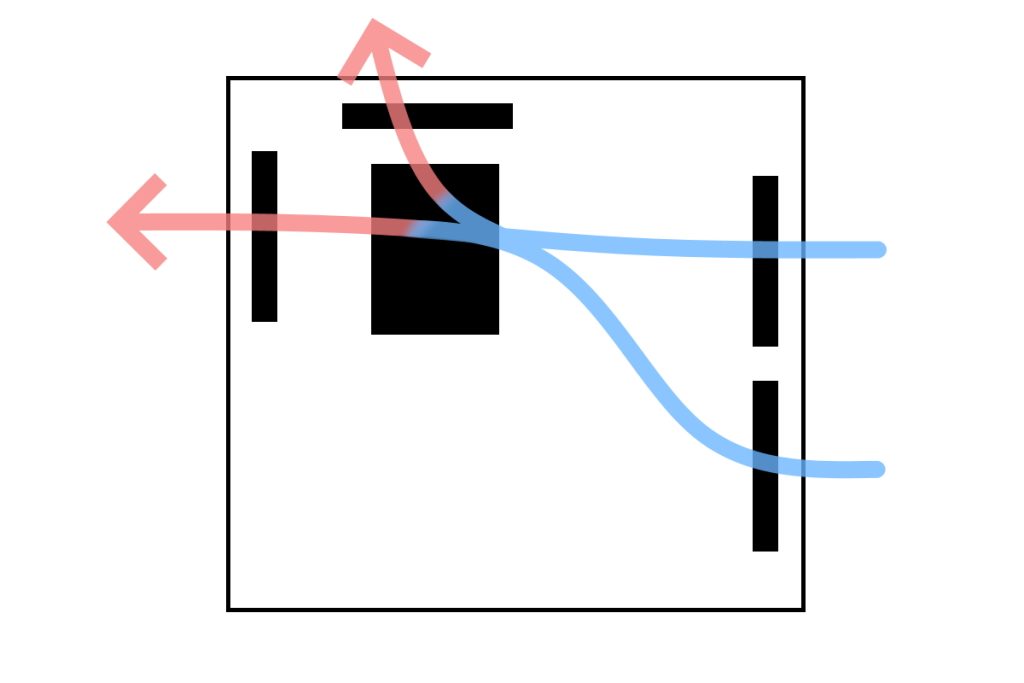
Check if the airflow inside the case is properly set up.
It is important that the computer as a whole is properly taking in and exhausting air, and that warm air is being expelled smoothly.
Sometimes, the orientation of the case fan or CPU cooler fan is reversed, or cables are not organized and block airflow, so be careful.
![]() Ken
Ken
≫ Related article: Basics of Custom PC Airflow and Efficient Cooling
Using a Larger PC Case with More Space
When considering airflow, small cases where parts are packed tightly are not ideal.
While they may be attractive in terms of design and compactness, it can be difficult to ensure cooling performance and airflow.
There are more things to consider than with regular cases, such as fewer case fans, strict CPU cooler height limits, and ensuring airflow, so the decision is a bit more difficult.
Therefore, for those building a custom PC for the first time, it is recommended to use at least a mini-tower case or larger.
≫ Related article: How to Choose a Custom PC Case [Performance / Functionality / Compatibility]
Cleaning the Computer
Dust accumulates when using a computer, so it needs to be cleaned every six months to a year.
Since computers take in air with fans, dust gets inside, and this dust can block airflow and reduce the performance of fans and heat sinks.
If cooling performance drops, the temperature of each part rises more easily, leading to thermal throttling.
Even if thermal throttling does not occur, overall performance will drop, so regular cleaning is necessary.
![]() Ken
Ken
Also, if too much dust accumulates, it can get into circuits or connectors, causing shorts, part failure, or even fire, so cleaning is necessary from that perspective as well.
≫ Related article: Thorough Explanation of Custom PC Cleaning Methods and Necessary Tools [With Photos]
Adjusting Room Temperature
If the room temperature is high, the temperature inside the computer also tends to rise, increasing the possibility of thermal throttling.
The countermeasure is simple: use an air conditioner to lower the room temperature.
If the room temperature reaches about 30°C, people will also need air conditioning, so keeping it in the high 20s should be fine.
How to Check for Thermal Throttling and Monitoring Tools
This section explains how to determine if thermal throttling is occurring and tools to monitor it.
CPU
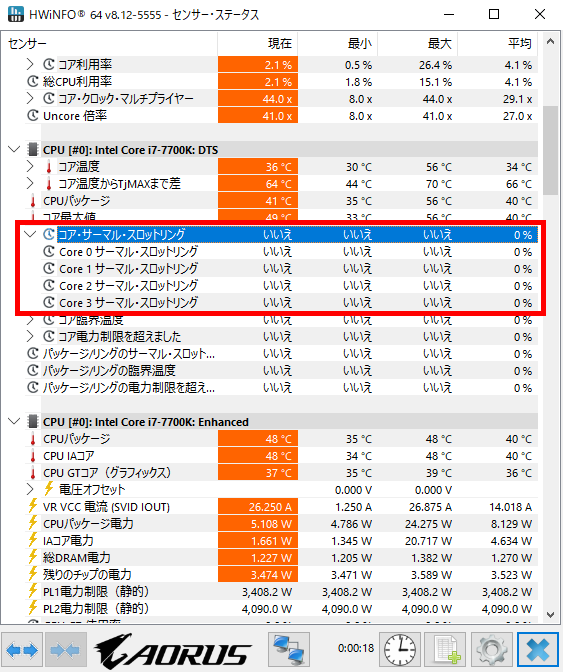
For the CPU, using a hardware monitoring tool called HWiNFO allows checking if thermal throttling is occurring.
HWiNFO displays the monitoring status of each part, and in the CPU section, in addition to usage and temperature, it shows whether thermal throttling has occurred.
The tool determines whether thermal throttling is occurring, making it easy to understand.
GPU
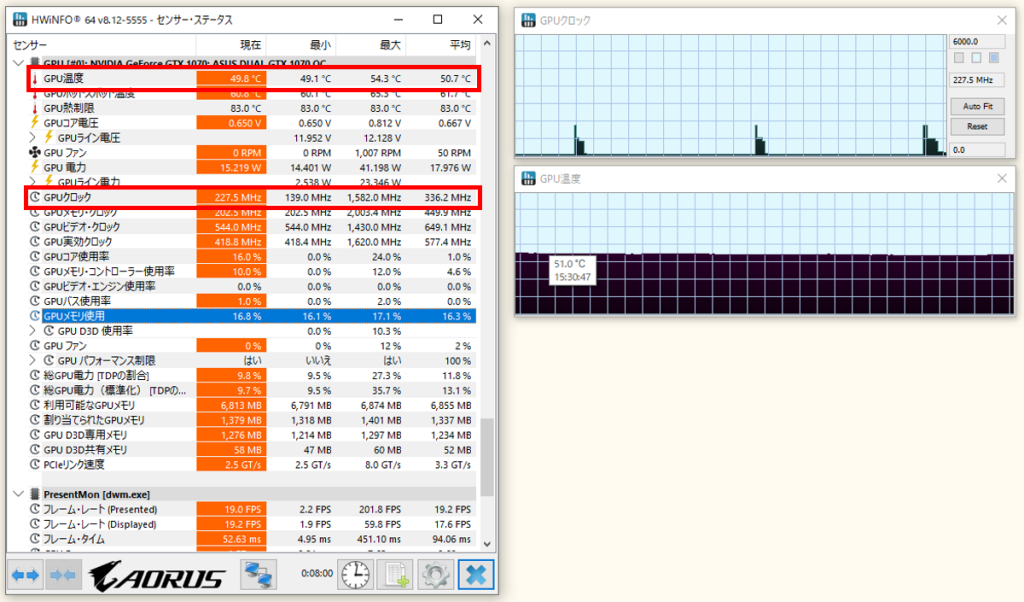
GPU information can also be checked with HWiNFO, but unlike the CPU, the tool does not determine thermal throttling.
Therefore, it is necessary to judge by looking at the GPU’s clock frequency and temperature graphs.
Double-click the item you want to see to display the graph.
There is no clear standard, but many GPUs are designed to trigger thermal throttling when the temperature exceeds 85–90°C.
If the clock frequency is high during high-load graphics processing and the temperature is also high, but the clock frequency suddenly drops, thermal throttling is likely occurring.
NVMe SSD
NVMe SSD temperature information can also be checked with HWiNFO, but it is necessary to judge for yourself whether thermal throttling is occurring.
NVMe SSDs, which have high-speed data processing capabilities, tend to accumulate heat, and are often designed to trigger thermal throttling when the temperature exceeds 70–80°C.
When this temperature is exceeded, performance drops and data transfer speed is limited.
Especially if data transfer speed suddenly drops during continuous reading or writing under high load, thermal throttling may be occurring.
A sudden drop in transfer speed or intermittent changes in write speed are signs that the SSD is trying to avoid overheating.
Therefore, monitor the temperature with HWiNFO and check whether data transfer speed is maintained using Task Manager or the dialog during data movement or copying.
Summary: Thermal Throttling is an Important Function to Protect Parts
This article explained in detail the basic knowledge and role of thermal throttling, the factors that cause it, its impact on performance, countermeasures, and monitoring methods.
Here is a summary of the key points:
- Thermal throttling is a function that limits performance when parts become too hot
- The purpose is to prevent part damage, system instability, and reduced lifespan due to high temperatures
- Mainly occurs in CPUs, GPUs, and NVMe SSDs
- Temporary performance drops and response delays may occur
- Improving cooling performance, including airflow, is the main countermeasure
- Maintenance such as CPU grease replacement and dust cleaning also affects cooling
- The occurrence of thermal throttling can be checked with monitoring tools
Thermal throttling is an important function to protect parts from becoming too hot.
Without this function, the temperature of each part could become dangerously high.
Having such safety features increases the overall reliability of the computer (meaning it can be used with peace of mind).
This site also explains the basic knowledge, roles, and how to choose other PC parts from the perspective of performance and compatibility, so please refer to them as well.
≫ Related article: PC Parts List and Explanation of Each PC Part [A Must-Read for Custom PC Beginners]
Select PC parts and online stores to instantly generate an estimate, check compatibility, and calculate power requirements. You can save up to five different builds, making it easy to try out multiple configurations.
≫ Tool:PC Parts Estimation & Compatibility Check Tool
 ZisaLog: Beginner’s Guide to Building a Custom PC
ZisaLog: Beginner’s Guide to Building a Custom PC 



