To build a custom PC, 12 different parts are required.
To choose the right parts, it is important to first understand what kinds of PC parts exist, their roles, and how to select them.
This article provides a simple explanation of the types and roles of PC parts, and whether they are essential or optional for purchase.
Select PC parts and online stores to instantly generate an estimate, check compatibility, and calculate power requirements. You can save up to five different builds, making it easy to try out multiple configurations.
≫ Tool:PC Parts Estimation & Compatibility Check Tool
Table of Contents
List of Custom PC Parts
First, here is an introduction to the types of PC parts, along with a brief explanation and whether each part is essential to purchase.
Most of these parts are essential, but depending on the purpose and build, some parts may not need to be installed or purchased.
| No | Name | Required for Build | Required for Purchase | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | OS | Required | Required | Software needed to operate and manage the computer. *Although it is software and not a physical part, it is included here because it is necessary. |
| 2 | CPU | Required | Required | The part responsible for all calculations inside the computer. [Important] Has a major impact on overall PC performance. |
| 3 | CPU Cooler | Required | Optional | Part for cooling the CPU, which gets very hot. *Installation is required, but if using the cooler included with the CPU, purchase is not necessary. |
| 4 | Memory | Required | Required | Part for temporarily storing data when the computer is working. [Important] Has a major impact on overall PC performance. |
| 5 | Motherboard | Required | Required | The base part for connecting all other components. |
| 6 | Graphics Card (GPU) | Optional | Optional | Part responsible for graphics processing. Required for uses that need high graphics performance, such as 3D games or 3D CG. [Important] Has a major impact on overall PC performance. |
| 7 | Storage (SSD/HDD) | Required | Required | Part for long-term data storage. [Important] Has a major impact on overall PC performance. |
| 8 | Power Supply Unit | Required | Required | Part for supplying power to other components. |
| 9 | PC Case | Required | Required | Part for housing and physically protecting other components. The case is also the face of the PC, so choose a design that suits personal taste. |
| 10 | PC Case Fan | Required | Optional | Fan installed in the PC case to improve cooling. *Installation is required, but if the case includes fans, purchase is not necessary. |
| 11 | Optical Drive | Optional | Optional | Part for reading and writing media such as CDs and DVDs. |
| 12 | Expansion Card | Optional | Optional | Part for adding functions or ports, such as Wi-Fi/Bluetooth cards, sound cards, RAID cards, etc. |
Among these parts, especially the CPU, memory, graphics card, and storage greatly affect the overall performance of the PC.
If parts that do not match the intended use are chosen, work may not be comfortable, or the PC may not be usable for the intended purpose, so be careful.
Also, the priority of PC parts is explained, so please refer to it.
≫ Related article: [Custom PC] About the Priority of Choosing PC Parts [CPU/GPU First]
In addition, there are supplementary parts such as GPU support brackets and power cable extension/conversion cables, so prepare them as needed.
OS

OS (Operating System) is the software required to operate the computer and use applications.
It is also called basic software and manages the entire system inside the computer, runs applications, and determines the priority of running processes, among other things.
Without this OS, it is not possible to open folders or files or run applications as usual, so it is essential for operating a computer.
Common operating systems for computers include Windows, macOS, and Linux, but for custom PCs, Windows OS is usually chosen.
*macOS is only used on Apple computers and is not sold separately.
*Linux is a free OS, but its functions are minimal and many applications are not compatible, so it is not recommended unless the user understands these limitations.
≫ Related article: How to Choose an OS for a Custom PC [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
CPU

CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the part responsible for all calculations inside the computer.
This includes not only simple numerical calculations, but also logical operations, data transfer and management, instruction execution, and input/output control.
Since the CPU handles all processing, the performance of the CPU almost determines the processing speed of the computer, so it is important to choose carefully.
A CPU with enough performance for the intended use should be selected.
There are various CPUs with different performance and prices, but the main choices for PC CPUs are Intel and AMD.
Here is a simple summary of the brands, grades, performance, and uses of each company:
| Intel | AMD | Performance Guide | |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-end (High Performance) | Core i9 | Ryzen 9 | For uses that require high performance, professional use. – Heavy 3D games, game streaming/broadcasting, competitive gaming – Professional video editing – Data analysis – 3D modeling |
| Core i7 | Ryzen 7 | ||
| Mid-High (Upper Mid Performance) | Core i5 | Ryzen 5 | Cost-effective processing power for a wide range of users from beginners to intermediate. – 3D games, game streaming, casual gaming – Semi-professional video editing (YouTube, etc.) – Image/photo editing – Programming – Business use, Office (Word, Excel, PowerPoint) |
| Mid-Range (Mid Performance) | Core i3 | Ryzen 3 | For relatively light tasks and uses. – 2D games, light 3D games – Home video editing (simple cuts, less editing) – Light image/photo editing – Web browsing – Video viewing |
| Low-end (Low Performance) | Celeron | – | Only for light tasks, not recommended for beginners. – Web browsing – Video viewing – Simple Office work |
| Pentium | Athlon |
Prices vary depending on performance, but it is important to choose the best one for the intended use.
For example, for heavy tasks like gaming or video editing, a high-performance CPU should be chosen, but for light tasks like document creation or web browsing, a lower performance CPU is sufficient.
For everyday or business use, Intel Core i5 or AMD Ryzen 5 is recommended. For high-performance needs like 3D gaming or video editing, Intel Core i7 or AMD Ryzen 7 is a good choice.
Adjust based on comfort, total cost, and budget.
Also, when choosing a CPU, check compatibility with the motherboard. If the CPU socket does not match, it cannot be installed on the motherboard.
≫ Related article: How to Choose a CPU for a Custom PC [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
CPU Cooler
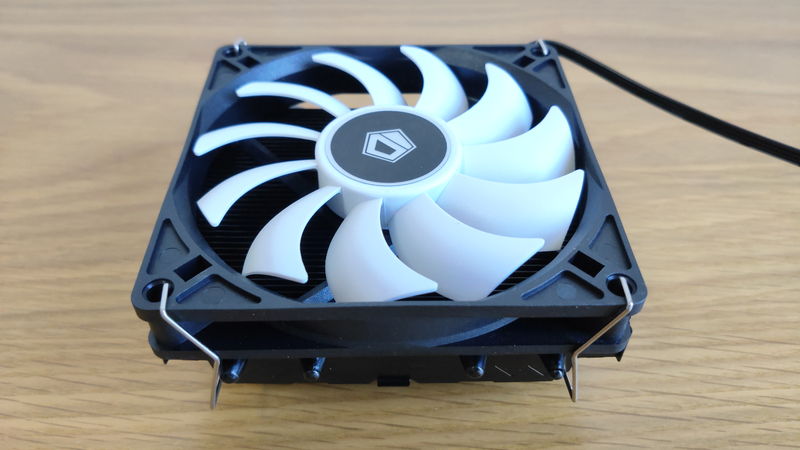

CPU Cooler is a part that efficiently cools the heat generated by the CPU to maintain its performance for a long time.
The CPU can reach temperatures above 80°C under heavy load, so dedicated cooling is necessary, which is the role of the CPU cooler.
A CPU cooler must be installed, but some CPUs come with a cooler, so purchasing one is not always necessary.
There are mainly three types of CPU coolers:
- Air coolers
- All-in-one liquid coolers
- Custom liquid coolers
Air coolers use fans and heat sinks to dissipate heat, while liquid coolers circulate liquid to transfer heat to a radiator for cooling.
Among these, air coolers and all-in-one liquid coolers are mainstream. Custom liquid coolers require building pipes and are not recommended for beginners due to the technical skill, effort, and risk of leaks.
CPU coolers include “retail coolers” (stock coolers) that come with the CPU and “aftermarket coolers” purchased separately.
High-performance CPUs often do not include a stock cooler, so an aftermarket cooler is needed in that case.
Even if a stock cooler is included, some people buy an aftermarket cooler for better cooling or quieter operation.
When choosing, it is important to select a product with cooling capacity suitable for the CPU’s TDP (Thermal Design Power).
Choosing the right CPU cooler maximizes custom PC performance and allows comfortable use for a long time.
≫ Related article: How to Choose a CPU Cooler for a Custom PC [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
Memory
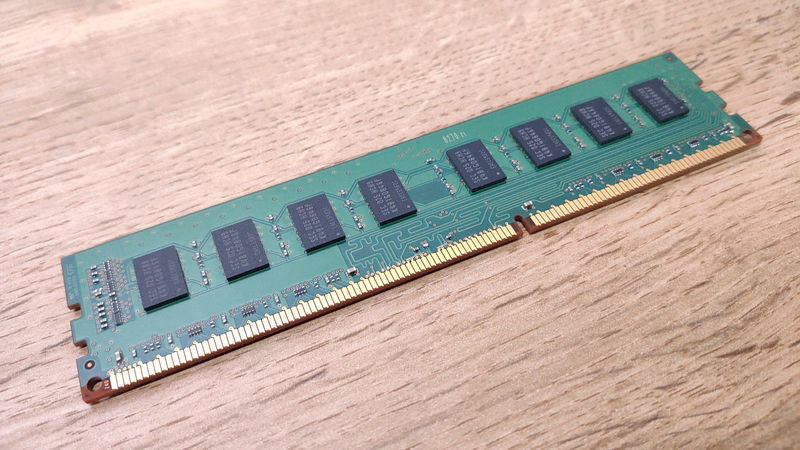
Memory is a part that temporarily stores data when the computer performs multiple tasks at the same time.
Generally, the larger the memory capacity, the more programs can run smoothly.
The most important specification for memory is capacity. Here are some general guidelines:
| Memory Capacity | Performance Guide | |
|---|---|---|
| High-end (High Performance) | 32GB or more | For uses that require high performance, professional use. – Live streaming of heavy 3D games – Professional video editing – Data analysis |
| Mid-High (Upper Mid Performance) | 16GB (Recommended) | For everyday use, gaming, and creative tasks. This is becoming the mainstream capacity and is recommended for new builds. – 3D games, game streaming/broadcasting – Semi-professional video editing (YouTube, etc.) – Image/photo editing – Programming – Light tasks and business use with 10-20 apps open at once |
| Mid-Range (Mid Performance) | 8GB | For relatively light tasks and uses. Still mainstream, but will become less common in the future. – 2D games, browser games – Home video editing (simple cuts, less editing) – Light image/photo editing – Web browsing – Video viewing |
| Low-end (Low Performance) | 4GB (Not Recommended) | Only for light tasks, not recommended for beginners. – Web browsing – Video viewing |
When building a custom PC, it is important to choose the right memory capacity and speed based on budget and usage.
There are memory standards such as DDR4 and DDR5, so check that the motherboard supports the memory standard.
≫ Related article: How to Choose Memory for a Custom PC [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
Motherboard
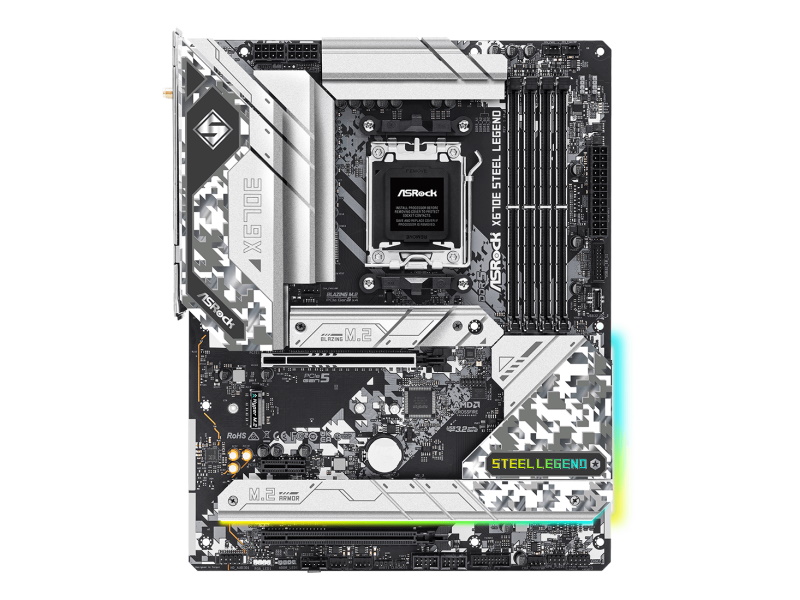

Motherboard is the base part for connecting all other components such as CPU, memory, and graphics card.
Depending on the product, the CPU socket type, memory, M.2 SSD, PCI Express slot count, and SATA connectors for SSDs and HDDs are determined.
Therefore, the number of parts that can be installed (expandability) changes, so consider how many parts will be installed and whether future upgrades are planned when choosing a motherboard.
Also, check if there are enough USB ports and video outputs on the back panel, and if the motherboard has connectors for front USB 3.0 ports on the PC case.
Motherboard size standards include ATX, Micro-ATX, and Mini-ITX. Choose according to the PC case to be used.
The larger the motherboard, the more parts can be installed and the greater the expandability, but a larger PC case is needed.
If choosing a small PC case, be sure to check if the motherboard size is compatible.
≫ Related article: How to Choose a Motherboard for a Custom PC [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
Graphics Card (GPU)
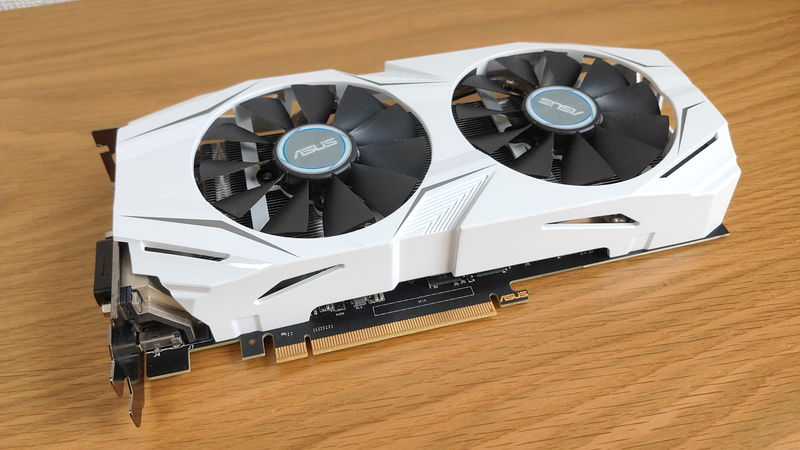

Graphics Card (GPU) is the part that handles graphics and video output processing in the computer.
If using a CPU with integrated graphics (iGPU), the CPU can handle graphics and video output, so a graphics card is not required.
However, for uses that require high graphics performance, such as 3D games or 3D CG, a separate graphics card is necessary.
There are various graphics cards with different performance and prices, but the main choices are NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel.
Here is a simple summary of the brands, grades, performance, and uses of each company:
| NVIDIA | AMD | Intel | Performance Guide | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-end (High Performance) | RTX 4090, RTX 4080, RTX 3090, RTX 4070, RTX 3080 | RX 6900 XT, RX 6800 XT | – | For uses that require high performance, professional use. – Playing heavy 3D games in 4K or high FPS, game streaming/broadcasting, competitive gaming – Professional video editing – AI learning and image generation using large amounts of data – Data analysis – High-definition, large-scale 3D modeling |
| Mid-High (Upper Mid Performance) | RTX 3070, RTX 4060 | RX 6800, RX 6700 XT | – | Cost-effective processing power for a wide range of users. RTX 4060 is popular for its value. – Playing 3D games in 4K or high FPS, game streaming/broadcasting, competitive gaming – Professional video editing – AI learning and image generation – Data analysis – Large-scale 3D modeling |
| Mid-Range (Mid Performance) | RTX 4050, RTX 3060 | RX 6700, RX 6600 XT | – | Cost-effective processing power for a wide range of users. – FHD 3D games, game streaming, casual gaming – Semi-professional video editing (YouTube, etc.) – AI learning and image generation for study – Data analysis – 3D modeling |
| Mid-Low (Lower Mid Performance) | RTX 3050, GTX 1660, GTX 1650 | RX 6500 XT, RX 6500 | Arc A770, Arc A750, Arc A580 | For relatively light tasks and uses. RTX 3050 is good for affordable 3D gaming. – FHD 3D games, game streaming, casual gaming (about 60 FPS at FHD and max settings for heavy games) – Semi-professional video editing (YouTube, etc.) – AI learning and image generation for study – Simple 3D modeling |
| Low-end (Low Performance) | – | Radeon Graphics | Iris Xe, UHD Graphics | For uses that do not require high graphics performance. These are integrated GPUs in CPUs, so only basic video output is possible. – Light 2D games, browser games – Home video editing (simple cuts, less editing) – Everyday use (web browsing, video viewing) – Business use, Office (Word, Excel, PowerPoint) – Programming |
When choosing a graphics card, make sure it physically fits in the PC case by checking the supported graphics card length.
Also, since the graphics card consumes the most power among PC parts, check the power supply unit’s capacity and number of cables.
≫ Related article: How to Choose a Graphics Card for a Custom PC [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
Storage (SSD/HDD)
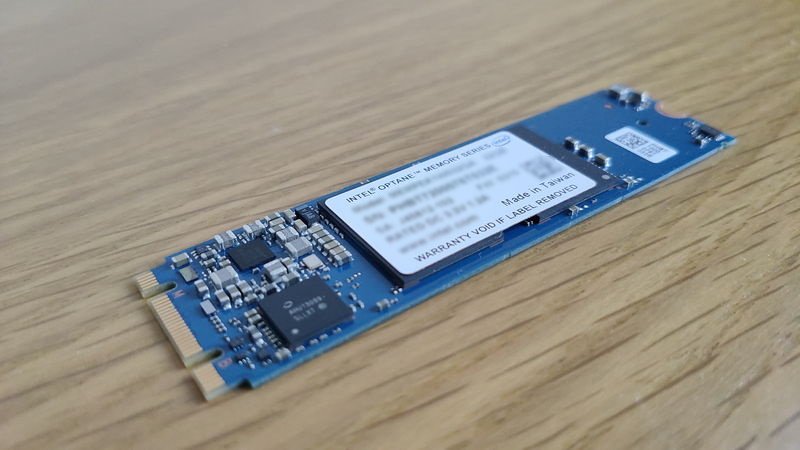

Storage (SSD/HDD) is a part for storing data long-term.
The main types are SSD (Solid State Drive) and HDD (Hard Disk Drive).
There are also two types of SSDs: NVMe SSD and SATA SSD, which differ in data transfer speed.
Choose the type, capacity, speed, and number of drives according to the intended use.
Here is a table summarizing the features of each type:
| Type | Common Capacities | Data Transfer Speed | Price per Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|
| NVMe SSD (Gen4) | 256GB, 512GB, 1TB, 2TB | 6,000–7,000MB/s | High |
| NVMe SSD (Gen3) | 256GB, 512GB, 1TB, 2TB | 2,300–3,500MB/s | High |
| SATA SSD | 256GB, 512GB, 1TB, 2TB | 450–550MB/s | Normal |
| HDD | 1TB, 2TB, 4TB, 8TB | 130–150MB/s | Low |
SSD is known for fast read/write speeds and is often used to speed up OS and app startup and game loading times.
On the other hand, HDD is slower but has large capacity, making it suitable for storing large files.
For example, use an SSD for fast data access like gaming or video editing, and an HDD for storing large numbers of photos or videos. Combining SSD and HDD allows for a balance of speed and capacity.
≫ Related article: How to Choose Storage (SSD/HDD) for a Custom PC [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
Power Supply Unit
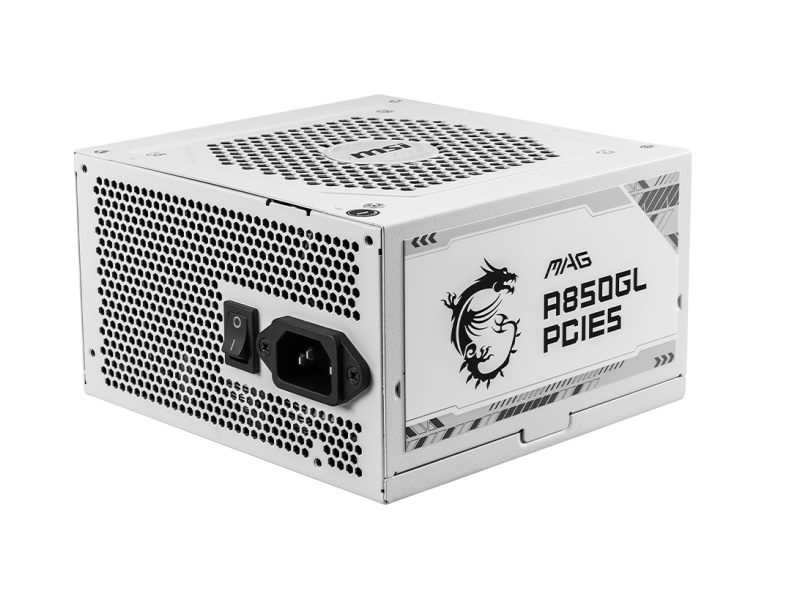

Power Supply Unit is a part that supplies stable power to the entire system (all parts).
The most important point is the power capacity. If it is insufficient, the system may become unstable or not start at all.
Calculate the optimal power capacity based on the power consumption of all parts. Ideally, total power consumption × 1.8.
It is best to have extra capacity to ensure stable power supply even when all parts are at maximum output.
Power supplies with 80 PLUS certification are efficient and can help save on electricity bills.
Also, power supplies come with various types of cables. Check how many of each type are needed for the build before choosing.
≫ Related article: How to Choose a Power Supply Unit for a Custom PC [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
PC Case
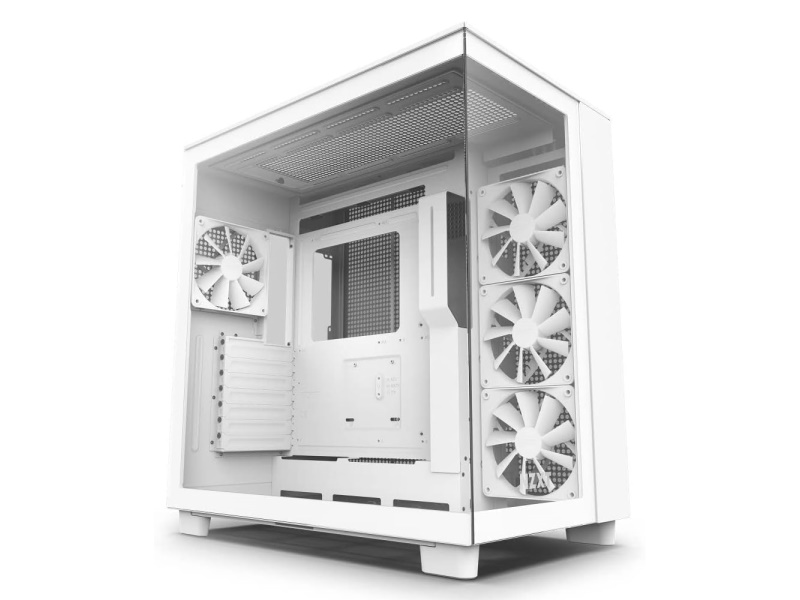

PC Case is a part for housing other components such as the CPU, memory, motherboard, graphics card, and power supply, and physically protects these parts.
Besides protection, the case is also the face of the PC, so color, design, tempered glass for viewing the inside, and LED lighting allow for personalization.
When buying a pre-built PC, the choice of cases is limited, but with a custom PC, the range of options is much wider.
Being able to build a PC to personal taste is one of the best things about custom PCs.
For users who want high expandability, a full tower case is suitable. For those who want to save space, a mini tower or slim case is preferred.
However, choosing a compact case means more restrictions on size, making part selection and assembly more difficult.
≫ Related article: How to Choose a PC Case for a Custom PC [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
PC Case Fan
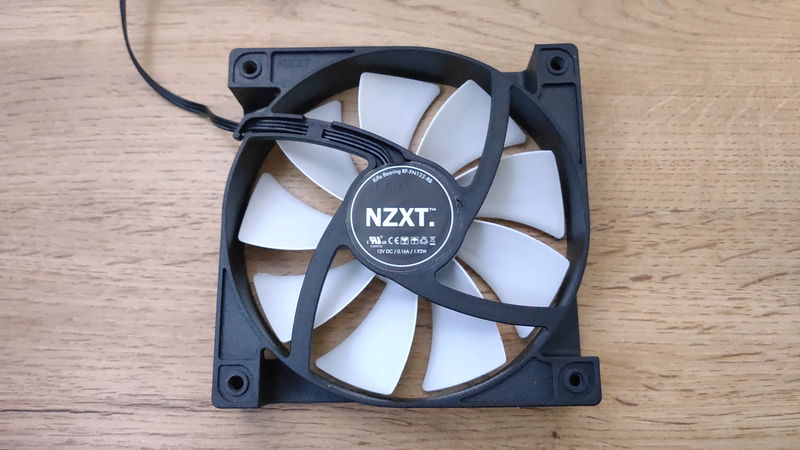

PC Case Fan is a part that removes heat from inside the PC and brings in fresh air to keep high-heat parts like the CPU and GPU at proper temperatures.
Lowering the internal temperature is essential for maintaining performance and extending hardware lifespan.
A case fan must be installed, but some PC cases include one or two fans, so purchasing extra fans is not always necessary.
Choose based on fan size, speed, noise level (quietness), whether the fan speed is automatically controlled by temperature, and design features like LED lighting and color.
Most PC cases come with one or two fans, so the number of additional fans to buy depends on the situation.
- Use only the included case fans
- Add more fans in addition to the included ones
- Replace all included fans with separately purchased ones
Also, the size, number, and position (front, rear, top, bottom) of fans that can be installed depend on the PC case, so check this as well.
Fan sizes generally range from 80mm to 200mm, but 120mm and 140mm are mainstream.
Larger fans can move the same amount of air at lower speeds, making them quieter.
≫ Related article: How to Choose a PC Case Fan for a Custom PC [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
Optical Drive
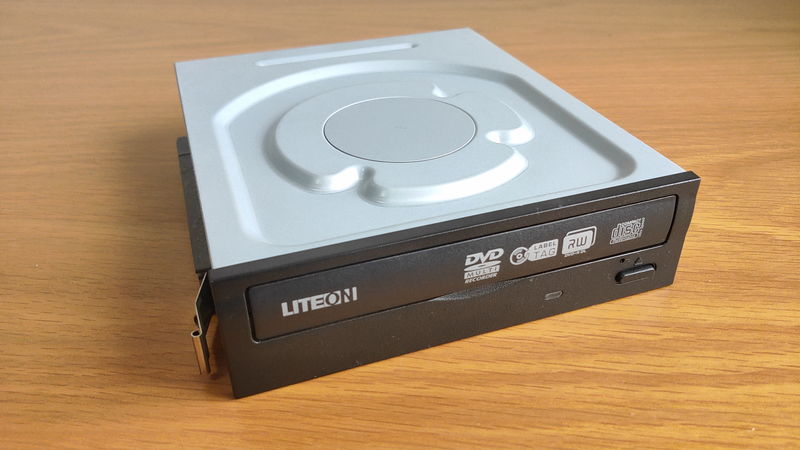

Optical Drive is a part for reading and writing optical media such as CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs.
This part is optional, so those who do not use media do not need it.
Recently, with the spread of online video streaming, USB memory, and cloud storage, optical drives are used less often.
In the past, OS installation was often done from DVD, so optical drives were included for that purpose. However, now OS installation can be done with a USB memory stick, so optical drives are rarely used.
To install an optical drive, a 5.25-inch bay is needed in the PC case, but many modern cases do not have a 5.25-inch bay, so check if one is needed.
Optical drives come in internal and external types. Internal drives are installed in the case and connected via SATA to the motherboard. External drives connect via USB and are portable, making them convenient for use with multiple PCs. Personally, external types are recommended for their versatility.
Also, some optical drives support only certain media types (CD, DVD, Blu-ray), and some are read-only, so choose according to how it will be used.
≫ Related article: How to Choose an Optical Drive for a Custom PC [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
Expansion Card
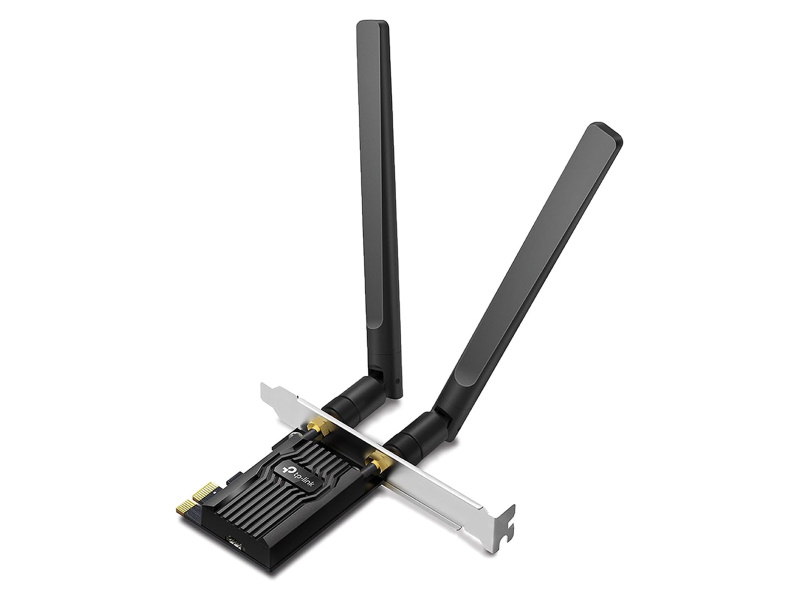

Expansion Card (Interface Card) is a part for adding functions or ports, installed in the motherboard’s PCI Express slot.
Expansion cards are not required, but can make the PC more convenient or add features. Consider purchasing if needed for the intended use.
Types of expansion cards include:
- Sound card
- Ethernet card (network card)
- Wi-Fi/Bluetooth card
- Capture card
- USB/Thunderbolt port expansion card
- M.2/SATA connector expansion card
- RAID card
- TV tuner card
![]() Ken
Ken
≫ Related article: How to Choose an Expansion Card for a Custom PC [Types / Compatibility]
Summary: Make Sure to Learn the Basics and How to Choose Each Part!
When building a custom PC, at least basic knowledge of the 12 types of parts such as CPU, memory, motherboard, graphics card, and storage (SSD/HDD) is necessary.
This article gave a simple explanation because there are many parts, but for more details, refer to the individual articles about each PC part.
Many parts are essential, but depending on the build and intended use, some parts may not need to be purchased. Make sure to understand when a part is needed and when it is not.
Also, the CPU, memory, graphics card, and storage have a major impact on the basic performance of the PC. If parts that do not match the intended use are chosen, work may not be comfortable, or the PC may not be usable for the intended purpose, so be careful.
Select PC parts and online stores to instantly generate an estimate, check compatibility, and calculate power requirements. You can save up to five different builds, making it easy to try out multiple configurations.
≫ Tool:PC Parts Estimation & Compatibility Check Tool
 ZisaLog: Beginner’s Guide to Building a Custom PC
ZisaLog: Beginner’s Guide to Building a Custom PC 



