Memory heat sinks play an important role in maintaining the stability and performance of a computer.
Basically, regular memory without a heat sink is sufficient, but for those who care about design, want to overclock, or use their PC in high-load environments, memory with a heat sink can be a good option for better cooling, system stability, and performance.
However, if the wrong type of memory with a heat sink is chosen, there is a risk of physical interference with the CPU cooler, making assembly impossible.
This article explains in detail the role, advantages, and disadvantages of memory heat sinks, including points to be careful about.
- Memory heat sinks improve cooling and stability
- Design features such as shape, color, and RGB functions are enhanced
- Memory with heat sinks is effective for overclocking and high-load environments
- For general use, memory without a heat sink is fine
- Large air-cooled CPU coolers may interfere with memory with heat sinks
- Memory with heat sinks tends to be more expensive than regular memory
- Aftermarket heat sinks exist, but design quality may be lacking
This article also explains how to choose memory from the perspective of basic knowledge, performance, and compatibility.
≫ Related article: How to Choose Memory for a Custom PC [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
Select PC parts and online stores to instantly generate an estimate, check compatibility, and calculate power requirements. You can save up to five different builds, making it easy to try out multiple configurations.
≫ Tool:PC Parts Estimation & Compatibility Check Tool
Table of Contents
What is a Memory Heat Sink?
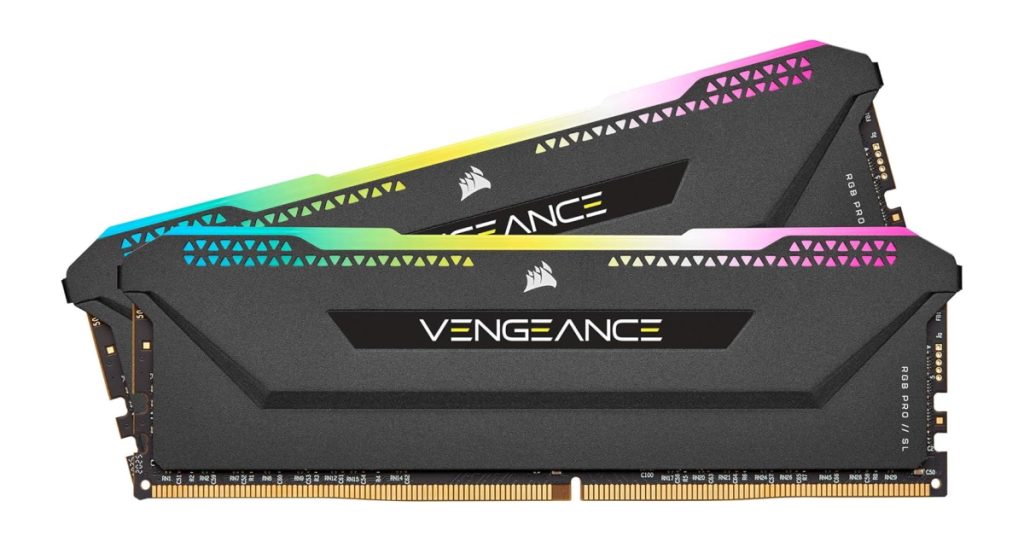

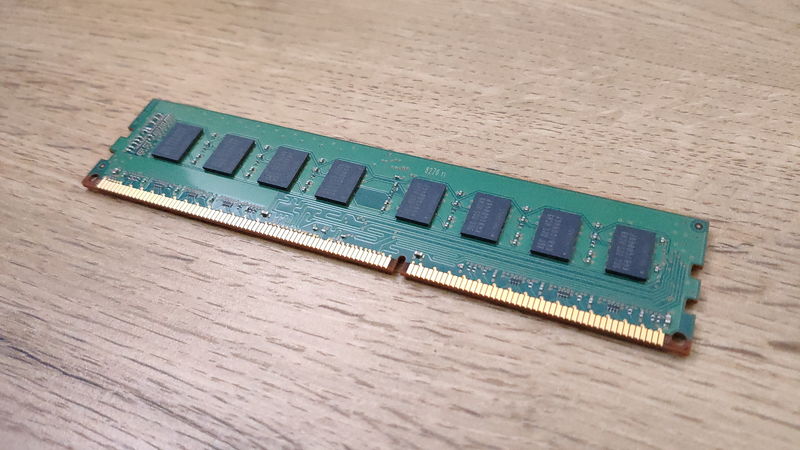
A memory heat sink is a metal cover attached to the memory module for heat dissipation.
It efficiently releases the heat generated by the memory chips to the outside, helping to keep the memory temperature low.
Heat sinks are mainly made of aluminum or copper, and their shapes and designs vary by product.
The metal heat spreader on the surface of the memory module is designed to efficiently lower the temperature of the memory.
When memory operates, it generates heat, and if this heat is not properly managed, performance may decrease or the lifespan may be shortened.
By attaching a metal heat sink to the memory module, heat can be effectively dissipated.
Since metal has high thermal conductivity, it quickly absorbs heat from the memory and releases it to the outside.
This helps keep memory operation stable and maintain high performance over a long period.
![]() Ken
Ken
Do Memory Modules Need Heat Sinks?
Whether a memory module needs a heat sink depends on its usage and environment.
For general use, memory does not generate much heat, so a heat sink is often unnecessary.
In my experience building mid-range and high-end PCs for daily use, business, 3D gaming, programming, and data analysis/AI learning, I have always used regular memory without heat sinks.
However, I have never experienced memory failure or a noticeable drop in memory performance.
Among these, AI learning was the most demanding, with both CPU and GPU usage exceeding 90% and running continuously for about six months, 24 hours a day. Even then, there were no problems with the memory or other parts.
AI learning frequently updates data in memory, so the read/write frequency was also high.
Therefore, even regular memory can withstand quite high loads, so there is no need to forcefully add a heat sink.
However, if overclocking the CPU or memory, or performing high-load tasks for long periods, it may be worth considering a heat sink for higher performance.
When memory is under heavy load, its temperature rises, so improving cooling performance can help maintain higher performance.
≫ Related article: What is Memory XMP/EXPO? Explanation of Memory Settings and Disadvantages
Advantages and Effects of Memory Heat Sinks
This section explains the advantages and effects of memory heat sinks.
Improved Heat Dissipation and Cooling Performance
With a heat sink attached, the heat generated by the memory is efficiently dispersed, preventing thermal runaway and instability due to rising temperatures.
The heat generated by memory during operation increases, especially under high load or overclocking.
Inside the memory are many IC (integrated circuit) chips, and when these operate simultaneously, the amount of heat increases and the memory temperature rises.
If the memory temperature is too high, data read/write errors become frequent, and problems such as freezing or blue screens are more likely to occur.
A memory heat sink directly contacts the surface of the IC chips, absorbing heat and spreading it throughout the heat sink.
Heat sinks are made of metals with high thermal conductivity, such as aluminum or copper, which effectively release heat to the outside.
As a result, the overall temperature of the memory can be lowered, allowing stable operation to be maintained.
Improved Performance
Attaching a heat sink to memory can improve performance.
The heat sink efficiently dissipates heat from the memory module, preventing overheating.
This allows the memory to continue operating stably even under high load, improving overall system performance.
Especially when overclocking or in environments requiring fast data processing, heat sinks can positively affect performance.
Enhanced Design
Memory heat sinks can improve the overall design of a custom PC.
There are heat sinks in various colors, shapes, and with RGB functions, so users can choose according to their PC case design.
This improves the unity and design of the entire PC, allowing for more unique customization.
If building a custom PC, users likely have specific performance and design preferences, so those who value design may definitely want to add a heat sink.
Improved Durability
Since the heat sink physically protects the memory chips and board, durability against external damage (pressure, vibration, etc.) is also improved.
On the memory module board, IC chips and capacitors are lined up, and these parts are vulnerable to vibration and impact.
Especially when installing or removing memory, holding the board or applying force can unintentionally damage components.
With a heat sink attached, the board and IC chips are protected from physical shocks, improving memory durability.
Especially with longer memory modules, if force is not applied evenly during installation, the board may twist, causing poor contact or disconnection.
Attaching a heat sink increases the strength of the entire board and reinforces areas prone to twisting.
Additionally, metal heat sinks can help prevent static electricity discharge.
Especially during handling, static electricity can damage IC chips or the board, so having a heat sink provides peace of mind.
Extended Lifespan
Attaching a heat sink to memory can extend its lifespan.
High temperatures accelerate the deterioration of electronic components, so proper temperature management leads to longer memory life.
This is especially effective when overclocking or performing high-load tasks, as temperatures are higher.
Disadvantages of Memory Heat Sinks
This section explains the disadvantages of memory heat sinks.
Physical Interference
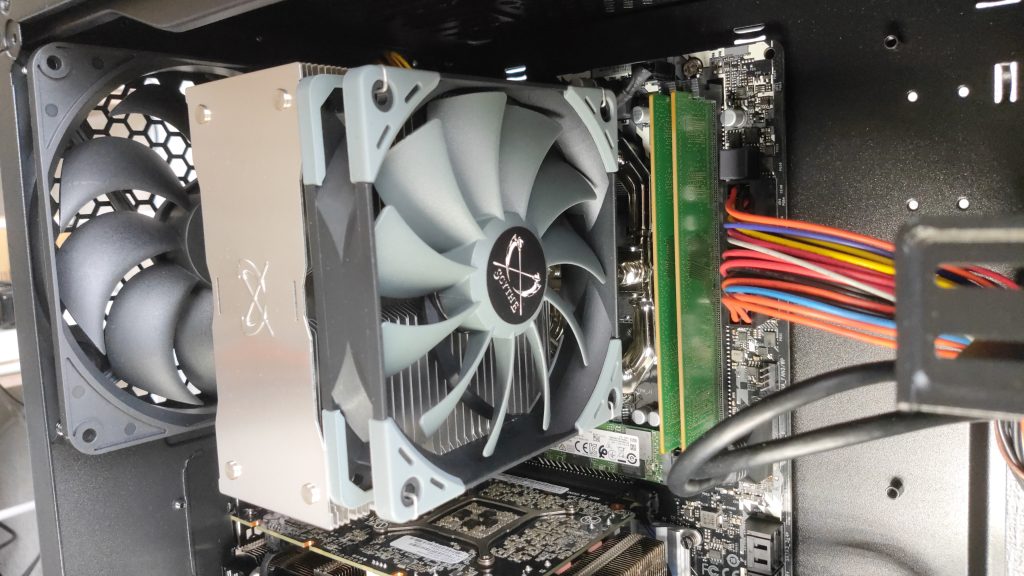

Memory heat sinks are taller than regular memory, so they may cause physical interference.
In the image, regular memory is used, and the CPU cooler does not overlap the memory slots, so there is no problem.
However, if the memory heat sink is tall and a large air-cooled CPU cooler is used, the bottom of the CPU cooler’s heat sink may interfere with the memory heat sink.
Even if there is no interference, the CPU cooler’s fan or heat pipes may be close to the memory slots, making installation more difficult.
When adding more memory, it may be necessary to remove the CPU cooler to access the memory slots, so this should be considered as well.
It would be ideal to check the dimensions of the CPU cooler and memory before purchasing, but unfortunately, this is not possible.
The required dimensions, such as the height of the memory, the distance from the memory slot to the CPU socket, and the height to the CPU cooler’s heat sink, are not specified in the specs.
Therefore, if there is concern about interference or having to repurchase parts, it is better to choose regular memory.
Price
Comparing the prices of memory with and without heat sinks, memory with heat sinks tends to be more expensive overall.
This is because an extra metal part is added, and if it has LED lighting, LED parts are also included, making it even more expensive.
Especially, high-quality heat sinks with excellent cooling and design tend to be more expensive.
Also, memory with heat sinks often has higher performance specs, such as faster data transfer speeds, so the price increases accordingly.
Therefore, for users who want to keep costs down, it may be difficult to choose memory with a heat sink.
If a heat sink is not necessary for the environment, the extra cost may be wasted.
Therefore, it is important to carefully consider the usage environment and necessity when purchasing.
Additional Information About Memory Heat Sinks
This section provides additional knowledge useful when choosing memory with a heat sink.
Check RGB Sync System for RGB Memory
When choosing memory with an RGB heat sink, check which sync system it supports to unify the lighting of the entire custom PC.
Many manufacturers provide dedicated software, allowing easy customization of lighting patterns and colors.
This makes it possible to adjust the PC’s appearance to personal preference.
If the sync system is not compatible, the memory lighting may not match other parts, or the software may not control it properly, affecting appearance and usability.
If only the memory lights up in a different color or pattern, the overall unity is lost, and the appearance becomes mismatched.
To achieve unified lighting, when setting up the PC’s lighting environment, it is necessary for the CPU cooler, memory, case fans, graphics card, and other RGB devices to support the same sync system.
For unified lighting effects, it is ideal to control everything on the same platform.
To ensure software compatibility, RGB memory control requires dedicated software, usually provided by the motherboard manufacturer (e.g., ASUS Aura Sync, MSI Mystic Light, Gigabyte RGB Fusion).
These software programs use different protocols, so if the software is not compatible, not all RGB functions can be controlled correctly.
If the sync system does not work properly, colors may be inconsistent or lighting may become unstable.
Therefore, when choosing memory with RGB functions, it is important to check if the motherboard and other devices support the same RGB sync system.
≫ Related article: Thorough Explanation of LED Lighting for Custom PCs
About Aftermarket Memory Heat Sinks
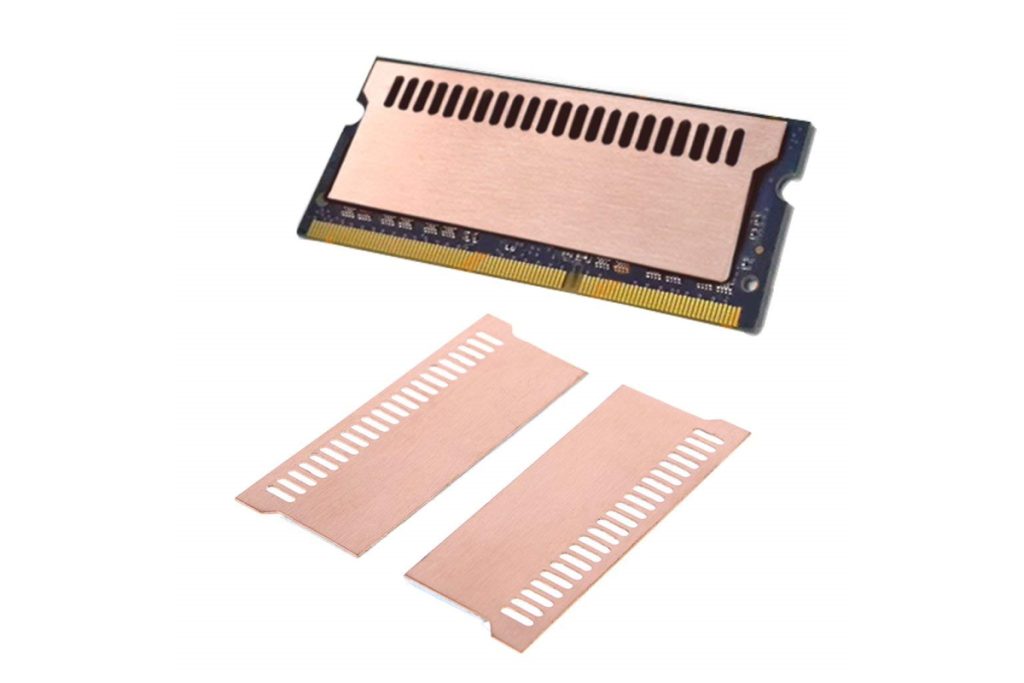


It is possible to add a heat sink to regular memory.
Searching on Amazon for “ Memory Heatsink ” shows that, while not many, metal heat sink plates are available for sale.
Therefore, by purchasing and attaching a heat sink separately, regular memory can be upgraded with a heat sink.
However, while it is possible, aftermarket heat sinks usually involve attaching a metal plate or finned heat sink, so design quality may be lacking, and those seeking a cool appearance may not find it suitable.
When choosing a heat sink, consider the size, shape, and material.
Make sure the height does not interfere with the CPU cooler, and that thick heat sinks do not interfere with adjacent memory modules.
That said, many custom PC users care about design, but aftermarket heat sinks may not be ideal for appearance.
Summary: No Need to Add One Unless Desired for Appearance!
This article explained the role, advantages, and disadvantages of memory heat sinks.
Here is a summary of the key points.
- Memory heat sinks improve cooling and stability
- Design features such as shape, color, and RGB functions are enhanced
- Memory with heat sinks is effective for overclocking and high-load environments
- For general use, memory without a heat sink is fine
- Large air-cooled CPU coolers may interfere with memory with heat sinks
- Memory with heat sinks tends to be more expensive than regular memory
- Aftermarket heat sinks exist, but design quality may be lacking
Memory with heat sinks can improve performance and lifespan, but is not always necessary for every environment.
For general use, memory without a heat sink is usually sufficient, but it is effective for overclocking or high-load tasks.
Memory with heat sinks is also attractive for users who want to enhance the appearance of their PC, and it can affect the overall design of a custom PC.
However, there are disadvantages such as physical interference and higher cost, so it is important to consider carefully before purchasing.
This article also explains how to choose memory from the perspective of basic knowledge, performance, and compatibility.
≫ Related article: How to Choose Memory for a Custom PC [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
Select PC parts and online stores to instantly generate an estimate, check compatibility, and calculate power requirements. You can save up to five different builds, making it easy to try out multiple configurations.
≫ Tool:PC Parts Estimation & Compatibility Check Tool
 ZisaLog: Beginner’s Guide to Building a Custom PC
ZisaLog: Beginner’s Guide to Building a Custom PC