Memory ECC function is a feature that detects and corrects data errors in memory.
Mainly, this function is used in servers and workstations where high data reliability is required, and it is not often used in custom-built PCs or general consumer computers.
- ECC function is a technology that detects and corrects memory data errors
- Data errors can occur due to electromagnetic waves, radiation, or aging of parts
- If a computer is used for 8 hours a day, about 3.6 errors can occur
- ECC is a function aimed at improving system reliability
- Mainly used in servers, workstations, mission-critical applications, and scientific computing
- Data errors could change a bank balance of 8,488,608 yen to 100,000 yen?
- Not used for everyday tasks, gaming, or video editing
- More expensive per capacity and slower than regular memory
The article also explains how to choose memory from the perspective of standards, performance, and compatibility.
≫ Related article: How to Choose Memory for Custom PCs [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
Select PC parts and online stores to instantly generate an estimate, check compatibility, and calculate power requirements. You can save up to five different builds, making it easy to try out multiple configurations.
≫ Tool:PC Parts Estimation & Compatibility Check Tool
Table of Contents
- 1 What is the ECC Function in Memory?
- 1.1 How Memory Data Error Detection and Correction Works
- 1.2 Function Used When High Data Reliability is Needed
- 1.3 Not Used in Custom PCs or Consumer Computers
- 1.4 ECC Memory is More Expensive Than Regular Memory
- 1.5 What Happens When a Data Error Occurs?
- 1.6 Why Do Data Errors Occur?
- 1.7 How Often Do Data Errors Occur?
- 2 Conditions and Hardware Requirements for Using ECC Memory
- 3 Frequently Asked Questions About ECC Memory
- 4 Summary: ECC Improves Data Reliability, But Not Needed for Most People
What is the ECC Function in Memory?
This section explains how the ECC function works, why data errors occur, and other related questions.
How Memory Data Error Detection and Correction Works
ECC (Error-Correcting Code) is a function that detects and corrects bit-flipped data errors.
A bit flip refers to a phenomenon in digital data where the value of a bit in memory changes unintentionally.
Specifically, it means the value of a bit changes from “0” to “1” or from “1” to “0”.
Such bit flips affect the reliability and accuracy of data, making them a significant issue especially in hardware like memory and CPUs.
Regular memory only has data bits for storing data, but ECC memory adds parity bits to check data integrity.
With this, single-bit errors (where only 1 bit is wrong) can be detected and corrected, and double-bit errors (where 2 bits are wrong) can be detected.
The number of parity bits added to ECC memory depends on the memory’s capacity and design, but generally, 7 to 12 bits are added for every 64 bits of data.
This allows automatic correction of single-bit errors and detection of double-bit errors.
More complex ECC implementations are designed to detect and correct even more bit errors.
The error correction capability of ECC memory increases with the number of additional bits, allowing for more advanced error detection and correction.
Function Used When High Data Reliability is Needed
Memory with ECC function is used when a system requires high reliability.
On the other hand, it is generally not used in custom-built PCs or consumer computers.
Especially in servers, workstations, scientific computing, and mission-critical applications, data accuracy is extremely important.
Mission-critical refers to the degree of importance in business operations, where service outages or malfunctions can lead to issues affecting human life or cause significant economic or reputational damage.
For example, if an error occurs while a server is processing large amounts of data, the reliability of the entire system may be compromised, but using ECC memory can reduce that risk.
In scientific computing, where calculation accuracy is required, ECC memory is also recommended.
More specifically, it is used for bank deposit data, data centers, payment systems, and similar applications.
When handling money or customer data, data corruption must never occur.
Even a single bit flip can change an amount to a very large or very small number.
For example, if there is a deposit of 100,000 yen, it is represented in binary as “0000 0001 1000 0110 1010 0000”.
*In actual financial systems, more complex encoding is used, but this is a simple example.
If the most significant bit (the leftmost bit) flips from “0000 0001 1000 0110 1010 0000″ to “1000 0001 1000 0110 1010 0000″,
then the 100,000 yen data becomes 8,488,608 yen.
It might be nice if the amount increases, but it could also decrease, and in any case, nobody wants to deposit money in a bank where the numbers keep changing.
This kind of bit flip can be fatal in real banking systems.
Since accurate calculation of amounts is required, even a one-bit error can cause large discrepancies, leading to incorrect billing or deposits, and many other problems.
For these reasons, financial institutions usually use ECC memory and highly reliable storage to ensure data integrity and reliability.
Not Used in Custom PCs or Consumer Computers
ECC memory is rarely used in custom-built PCs or consumer computers due to cost, performance, and necessity.
For general use, non-ECC memory provides enough performance and reliability.
Also, ECC memory is slower, which can reduce performance.
Especially for gaming, memory speed is important, so ECC memory is not suitable for general use.
In other words, unless reliability is absolutely necessary even at the cost of performance and higher memory prices, there is no need to use ECC memory.
ECC Memory is More Expensive Than Regular Memory
ECC memory is more expensive per capacity than regular non-ECC memory.
For example, 64GB (32GB×2) of non-ECC memory costs about 20,000 yen (or about 40,000 yen with heatsinks or LEDs), but the same capacity of ECC memory costs about 50,000 yen.
Because ECC improves system reliability and stability, it requires additional circuits and chips, and the manufacturing process is more complex, which increases the cost.
Therefore, ECC memory is valuable for systems that prioritize reliability, but for general use, it is often considered to have poor cost performance.
What Happens When a Data Error Occurs?
If a bit flip data error occurs in regular non-ECC memory, continuing calculations or processing as is may cause apps or the computer to crash or forcibly shut down.
Since the location of the bit flip is random, depending on the importance of the data at that location, the system may continue to work without issue, or it may crash.
For personal computers, simply restarting is enough, but for servers, scientific computing, or financial systems, restarting is not so easy, so ECC memory is needed.
Why Do Data Errors Occur?
The main reason for data errors is that bits in memory are affected by external factors, causing bit flips.
These bit flips can be caused by cosmic radiation (cosmic rays, solar radiation), electromagnetic waves, voltage stress, temperature changes, environmental factors, or aging of parts.
Memory bits have a state of 0 or 1, but these external factors can change their state.
![]() Ken
Ken
If the cause is environmental or aging, it can be handled by improving the environment or replacing parts, but cosmic radiation and electromagnetic waves cannot be prevented, so ECC is useful for detecting and correcting errors when they occur.
How Often Do Data Errors Occur?
Data errors occur more frequently than expected, about 3.6 times per day.
When using a computer, apps rarely crash, and even if they do, it is hard to know if it was caused by a bit flip, so it may seem like errors are rare.
According to a Google paper that measured errors in millions of DIMM memories over two and a half years, each memory module experiences about 4,000 correctable errors per year on average.
However, DIMMs that have experienced errors are 13 to 228 times more likely to experience another error in the same month compared to DIMMs with no errors, so the average varies greatly.
In other words, some memory modules have high error rates, while others have low rates.
If we use the average of 4,000 times, that’s about 11 times per day, and since server memory operates 24 hours a day, for those who use a computer about 8 hours a day, about 3.6 errors occur.
So, errors occur more frequently than expected.
From reading this paper, I realized that my own computer had memory-related issues, probably due to accumulated errors from aging.
In my case, I used a Surface Pro 6 for 8 to 12 hours a day for about 5 years, and around the fourth year, memory-related issues started to appear.
I usually put the computer to sleep instead of shutting it down after daily use, but in the fourth year, memory errors started to occur after two days or so.
Probably, the memory had aged, and using it for long periods caused errors to accumulate, resulting in noticeable problems.
Even though errors occur daily, if there are only one or two, there is little impact.
After that, shutting down every day to refresh the memory data stopped the errors from occurring.
However, this shows that not only servers and workstations, but also regular computers are affected.
Conditions and Hardware Requirements for Using ECC Memory
ECC memory is not needed for general use, but here are the necessary conditions and hardware requirements if you want to use it.
The Memory Must Support ECC
First of all, the memory itself must support ECC.
Check the memory’s specifications to see if it supports ECC.
Also, “ECC” is usually written in the model number, so it is easy to identify.
The Motherboard Chipset Must Support ECC
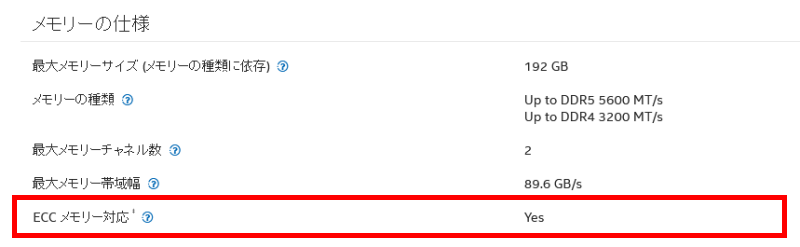
Besides the memory, the motherboard chipset must also support ECC.
Server and workstation motherboards often have ECC-compatible chipsets, but general desktop motherboards often do not.
Therefore, when introducing ECC memory, it is important to check the motherboard specifications to see if the chipset supports ECC.
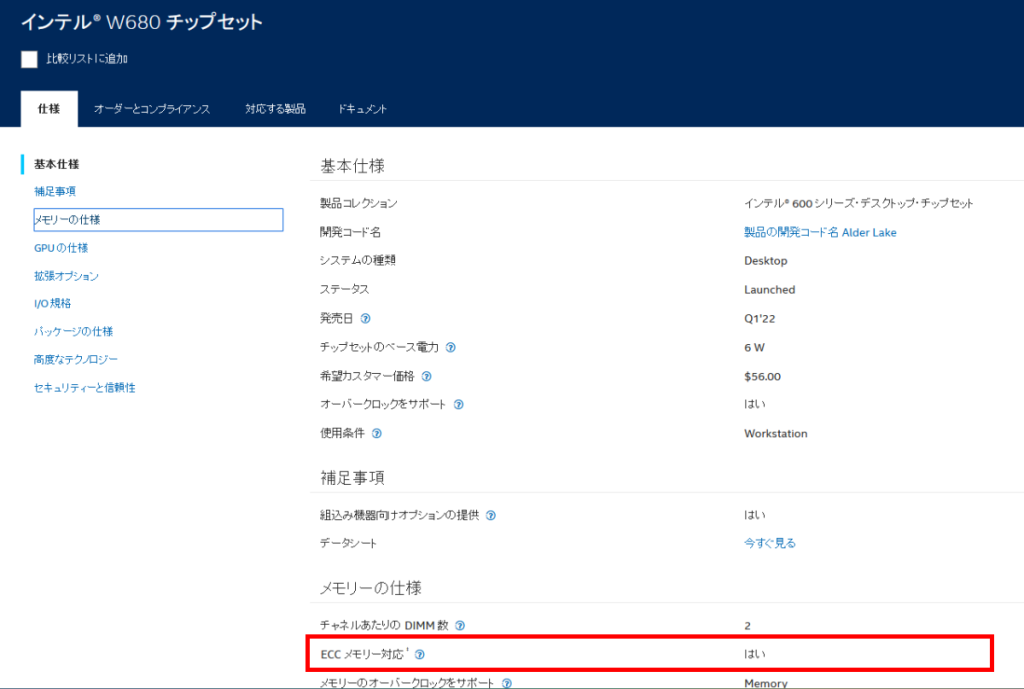
For example, searching for “Intel Chipset W680” will bring up the chipset specification page.
Check the memory specifications section to see if ECC memory is supported.
The CPU Must Support ECC
Finally, the CPU must also support ECC.
Similarly, check the CPU’s specification sheet to confirm.
For example, the “Intel Core i9 14900K” memory specifications include an item for ECC memory support.
Frequently Asked Questions About ECC Memory
This section explains frequently asked questions about ECC memory.
How to Check if Memory Supports ECC
There are several ways to check if memory supports ECC.
- Check the memory model number or specifications
- Check BIOS or UEFI settings
- Check the memory chips
Memory modules usually have model numbers or specifications written on them, which can be checked to determine ECC support.
If “ECC” or “Error-Correcting Code” is written in the model number, the memory supports ECC.
If the model number is listed, searching for it will bring up the specifications, where you can check for ECC support.
Next, you can check the system’s BIOS or UEFI settings.
Many motherboards that support ECC memory have an option to enable ECC in the BIOS or UEFI settings.
Checking this setting will show if the system supports ECC memory.
Another way is to check the memory chips themselves.
ECC memory usually has extra chips for error detection and correction, so it often has more chips than non-ECC memory.
Non-ECC memory usually has chips arranged regularly, with the number of chips matching the capacity.


On the other hand, ECC memory often has more chips or chips arranged irregularly.
However, this is not always the case, so it is best to check the model number or BIOS.
Mixing ECC and Non-ECC Memory
It is not recommended to mix ECC and non-ECC memory.
Even if the motherboard supports it, there is no compatibility, so mixing them may prevent the computer from booting.
Motherboard manufacturers also generally do not guarantee operation when mixing ECC and non-ECC memory, so it is best not to use both together.
Even if the system works with mixed memory, if data is stored in non-ECC memory, errors cannot be detected or corrected, so overall system reliability does not improve.
Therefore, if you want to use ECC, make sure all memory modules support ECC.
ECC Function in Storage (SSD/HDD)
If bit flip data errors can occur in memory due to various factors, you may wonder if the same can happen in storage (SSD/HDD) where data is saved.
In fact, storage can also experience data errors, affecting the memory cells or magnetic material on the disk where data is stored.
SSDs use NAND flash memory to store data.
Flash memory cells hold data using electric charge, making them susceptible to radiation.
If radiation hits a flash memory cell, the charge may change by mistake, causing a bit flip.
HDDs record data on magnetic disks.
Magnetic disks have a relatively low risk of direct bit flips from radiation, but under very strong magnetic fields or certain environmental conditions, data may experience magnetic reversal.
However, this is very rare in normal use.
So, do SSDs and HDDs have ECC functions? Basically, they do.
However, it depends on the product and application.
Consumer SSDs and HDDs usually have basic ECC functions to detect and correct errors that occur during data writing and reading.
Enterprise SSDs and HDDs for data centers and businesses have more advanced ECC functions.
This allows higher reliability even for mission-critical applications.
However, some low-cost or special-purpose storage devices (such as USB memory or SD cards) may not have ECC functions to reduce costs.
Thus, not only memory but also storage has various measures to protect data.
Summary: ECC Improves Data Reliability, But Not Needed for Most People
The ECC function in memory detects and corrects data errors, and is mainly used in servers, workstations, and scientific computing where data reliability and mission-critical applications are important.
However, for general use, such high data reliability is not needed, and ECC memory is expensive and may reduce performance due to error detection and correction, so it is basically not used.
Here are the key points again.
- ECC function is a technology that detects and corrects memory data errors
- Data errors can occur due to electromagnetic waves, radiation, or aging of parts
- If a computer is used for 8 hours a day, about 3.6 errors can occur
- ECC is a function aimed at improving system reliability
- Mainly used in servers, workstations, mission-critical applications, and scientific computing
- Data errors could change a bank balance of 8,488,608 yen to 100,000 yen?
- Not used for everyday tasks, gaming, or video editing
- More expensive per capacity and slower than regular memory
Not only memory but also storage has ECC functions, showing how important data in the world is protected.
The article also explains how to choose memory from the perspective of standards, performance, and compatibility.
≫ Related article: How to Choose Memory for Custom PCs [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
Select PC parts and online stores to instantly generate an estimate, check compatibility, and calculate power requirements. You can save up to five different builds, making it easy to try out multiple configurations.
≫ Tool:PC Parts Estimation & Compatibility Check Tool
 ZisaLog: Beginner’s Guide to Building a Custom PC
ZisaLog: Beginner’s Guide to Building a Custom PC