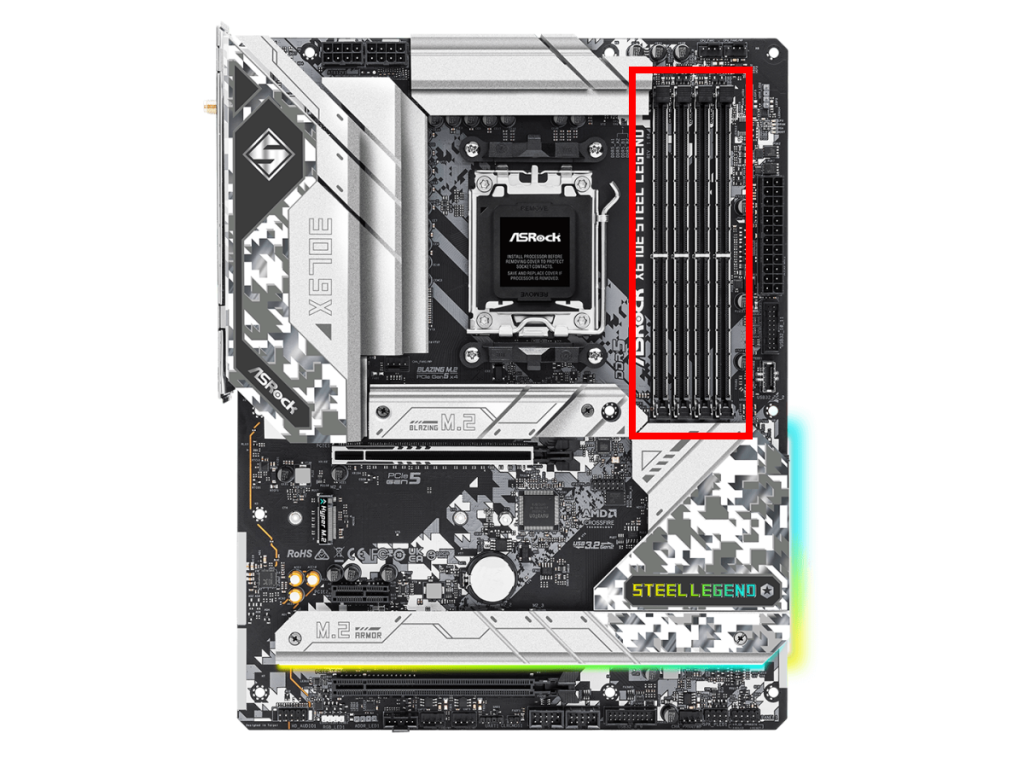
Memory is an essential component when using a computer, and it is a crucial part that directly affects the stability of a PC.
If there is enough memory capacity, it becomes more efficient to launch many applications or perform multiple tasks at the same time.
On the other hand, if inappropriate memory is chosen for the intended use, the PC may become slow or laggy, making it uncomfortable to use.
Also, when building a custom PC, it is necessary to select memory considering compatibility, such as whether the memory standard matches the motherboard.
Therefore, this article explains the knowledge and functions of memory required when planning a custom PC build, as well as how to choose memory from the perspectives of performance and compatibility.
- The most important performance factor is memory capacity
- Speed up with a dual-channel configuration
- Insufficient memory leads to an uncomfortable experience
- Check if the memory standard is compatible with the motherboard
- Pay attention to the number and capacity of memory modules the motherboard can support
- Be careful of interference between large air-cooled CPU coolers and memory with heat sinks
Basic knowledge, roles, and how to choose other PC parts from the perspectives of performance and compatibility are also explained, so please refer to them.
≫ Related article: PC Parts List and Explanation of Each PC Part [A Must-Read for Custom PC Beginners]
Select PC parts and online stores to instantly generate an estimate, check compatibility, and calculate power requirements. You can save up to five different builds, making it easy to try out multiple configurations.
≫ Tool:PC Parts Estimation & Compatibility Check Tool
Table of Contents
- 1 What is the Role of Memory?
- 2 Basic Knowledge of Memory
- 3 How to Choose Memory for a Custom PC [Performance]
- 4 How to Choose Memory for a Custom PC [Compatibility / Important]
- 5 Additional Knowledge about Memory
- 6 Frequently Asked Questions about Memory
- 7 Summary: It is Important to Choose the Appropriate Memory Capacity for the Intended Use!
What is the Role of Memory?
Memory is a component that temporarily stores data when a computer is working, and it acts as a bridge between the fast CPU and the slow storage (SSD/HDD), making data transfer more efficient.
![]() Ken
Ken
On a computer, many programs are running, including those used by the user and those running in the background.
Memory temporarily stores these programs and the data they use.
The larger the memory capacity, the more tasks can be performed at once.
The number of applications that can be launched increases, and multiple tasks can be executed simultaneously.
Therefore, for those who open many applications or use creative tasks such as image or video editing that tend to consume a lot of memory, it is better to have more memory capacity.
Performance guidelines for different memory capacities and recommended memory capacities for different purposes are explained later.
On the other hand, if there is not enough memory, the computer may slow down, temporarily freeze, or programs may not run properly.
Having experienced this situation myself, it becomes impossible to work properly and is very stressful, so choosing the right memory capacity is extremely important.
Basic Knowledge of Memory
Before explaining how to choose memory, this section covers basic knowledge such as how to read memory model numbers and performance guidelines for different uses.
Let’s explain these points in detail.
How to Read Memory Model Numbers (Understanding Performance)
Memory has model numbers, and by looking at them, it is possible to roughly understand their performance.
| Standard | Defines technical characteristics and performance such as memory compatibility, speed, size, and power consumption. Must match the memory slot standard of the motherboard. |
|---|---|
| Data Transfer Speed | Refers to the data transfer speed of memory, indicating how fast data can be read and written. |
| Capacity | Memory capacity. The most important factor for performance. |
| Number of Modules | The number of memory modules, often sold in sets of 1, 2, or 4. The number must fit within the memory slots of the motherboard. For faster data transfer, it is better to have a number that allows for a dual-channel configuration. |
Capacity and data transfer speed relate to performance, while standard and number of modules relate to compatibility, which will be explained in detail later.
About Memory Shortage
If the original memory capacity is small or if many applications are running and memory consumption is high, memory shortage may occur.
When memory shortage happens, the following may occur:
- When launching an application, a memory shortage warning appears and the application cannot run.
- The response speed of applications becomes slow, causing lag and making it difficult to work comfortably.
- Applications start up slowly.
In such cases, it is necessary to close other running applications to reduce memory usage before launching new ones.
Simply closing and reopening applications takes time, and if you want to work while referring to other applications, it may not be possible.
For example, playing a game while viewing strategy information in a browser, or entering data into Excel while looking up information in a browser.
There may be applications that are always used together for certain tasks, but depending on the memory capacity, even those applications may not be able to be displayed.
If this happens, work efficiency will obviously decrease, so it is best to avoid this situation.
To avoid work restrictions and stress caused by memory shortage, it is necessary to choose a PC with the appropriate memory capacity for the intended use.
By the way, the cause of lag due to memory shortage is memory swapping (paging).
When memory is insufficient, data in memory is temporarily moved to storage (swap file, page file).
This functions as part of the memory, but since the data transfer speed of storage is much slower than memory, the overall performance of the PC drops significantly.
Even when memory is insufficient, the system tries to manage memory to keep applications running.
However, the speed of memory and storage varies by product, but storage is about 1/10 to 1/100 the speed of memory.
Such slow data transfers cause processing to be interrupted due to data wait times.
From the CPU’s perspective, which processes various tasks based on data, if data is too slow, it cannot proceed to the next process and ends up waiting.
As a result, this appears as lag in application operation on the screen.
In this way, memory capacity is important for comfortable PC operation.
How to Choose Memory for a Custom PC [Performance]
This section explains how to choose memory focusing on performance and functionality.
Let’s explain these points in detail.
Memory performance consists of two factors: capacity and data transfer speed, but memory capacity is overwhelmingly more important.
In terms of importance, capacity: 9, data transfer speed: 1; memory capacity is crucial.
In any case, it is essential to choose memory with enough capacity for the intended use.
If there is still budget left for memory, then consider data transfer speed as well.
![]() Ken
Ken
Based on user selections in the Custom PC Tool, statistical data is created and explained by popularity ranking, price range, and specifications.
≫ Related article: Popular Recommended Memory Ranking and Selection Rate by Specification [Statistical Data]
Memory Capacity [Most Important]
Memory capacity is the amount of data that can be temporarily stored; the larger it is, the more tasks can be performed at once.
For example, it allows many applications to be launched or creative apps such as 3D games and video editing that use a lot of memory to be used comfortably.
When explaining PC parts, memory is often compared to the size of a desk.
If the desk is large, there is more space to place necessary items (computer, documents, calculator, various things), making it easier to work.
However, if the desk is small, it is necessary to organize limited space, such as putting away textbooks before opening reference books.
This is not efficient and can be stressful.
Here is a rough performance guideline by commonly used memory capacities:
| Memory Capacity | Performance Guideline | |
|---|---|---|
| High-end (High Performance) | 32GB or more | For professional creative use, data analysis, or programming such as AI learning. |
| Mid-range (High Performance) | 16GB | The mainstream capacity for gaming PCs and creative PCs. For gaming, 16GB is sufficient, but for creative work, which tends to use more memory, at least 16GB is recommended. For business use, if 10–20 applications are run simultaneously, 16GB is optimal. |
| 8GB | The current mainstream capacity. Comfortable for everyday use such as web browsing and video viewing, business tasks like Word, Excel, email, and programming. | |
| Low-end (Low Performance) | 4GB | For light tasks such as web surfing and video viewing. The number of applications that can be run simultaneously is small, so this is not a recommended memory capacity. |
Here are the recommended memory capacities by usage:
| Usage | Memory Capacity |
|---|---|
| Everyday Use (Web/Video/Shopping, etc.) | 8GB |
| Gaming | 16GB |
| Video Editing | 16GB / 32GB / 64GB |
| Business | 8GB / 16GB |
| Programming | 16GB / 32GB / 64GB |
| Trading (Stocks/FX/Cryptocurrency) | 8GB |
| AI/Deep Learning | 16GB / 32GB / 64GB |
| For College Students | 8GB / 16GB |
Even for the same purpose, the required memory capacity changes depending on what you want to do.
For example, for video editing, 16GB is sufficient for simple editing of home videos or FHD videos for YouTube, such as adding captions or cuts.
However, for editing 4K videos or performing heavy edits such as changing the color tone of the entire video or using many effects, 32GB or 64GB may be required.
In this way, the required memory capacity changes depending on the extent of the tasks. For more detailed explanations, refer to the links in the “Usage” column of the table.
The current mainstream is 8GB or 16GB, and for gaming or creative PCs, 16GB or more is recommended.
For standard PCs for everyday or business use, both 8GB and 16GB are options.
As time goes on, the standard memory capacity increases, and as of 2024, it is shifting from 8GB to 16GB.
For standard PCs, 8GB was mainstream two or three years ago, but recently, 8GB and 16GB are about half and half. In the future, 16GB may become the standard.
![]() Ken
Ken
For everyday or business use, 8GB is sufficient for light use. However, if you use various applications for a single task or prefer to keep many applications open to save time, 16GB is recommended.
I am the latter type and usually have about 10–20 applications open while working. When I used 8GB, memory usage was maxed out with about 10 applications, and performance slowed down.
Therefore, if you often have 10–20 or more applications open, 16GB is better.
The applications I use include browsers, Excel, notes, programming development tools, and email clients, with multiple instances of Excel and notes open. The memory used varies greatly depending on the application and workload, so use this as a guideline only.
In contrast, 4GB is too little, and memory runs out after opening just one or two applications, so it is not recommended.
When a PC is started, the OS uses memory. For Windows 10, about 2GB is used, so with 4GB of memory, only 2GB is left for other uses.
With this, it is almost impossible to run multiple applications, so at least 8GB is necessary, and 16GB is definitely better if the budget allows.
Data Transfer Speed
Data transfer speed is the speed at which data is transferred between the CPU and memory or between memory and storage.
The faster this speed, the faster data can be transferred, improving the overall processing speed of the PC.
However, due to the influence of other parts, even if a high-speed memory is chosen, it is rare to feel a significant speed increase.
Therefore, data transfer speed is not a major concern; capacity is overwhelmingly more important. Even in PC spec sheets, only memory capacity is often listed, showing how important capacity is.
Also, the memory slot on the motherboard must support the speed. If a motherboard with a lower speed than the memory is chosen, data will be transferred at the lower speed. If intentionally using high-speed memory, check the supported speed of the motherboard as well.
Dual Channel Memory Configuration
Dual channel is a technology that speeds up data processing by installing two memory modules of the same standard and capacity as a pair.
There are also triple channel (three modules) and quad channel (four modules), but these are only supported by high-end motherboards, so dual channel is mainstream.
It is rare to feel a speed increase, but depending on the environment and benchmark software, performance may improve by about 5–10%.
Therefore, data transfer speed can change depending on the memory configuration.
For example, to have 16GB of memory, there are two options:
- One 16GB memory module
- Two 8GB memory modules
Between these two, using two 8GB modules is faster due to the dual channel configuration.
≫ Related article: What is Dual Channel Memory? Double the Speed and Bandwidth with Two Modules!
How to Choose Memory for a Custom PC [Compatibility / Important]
This section explains how to choose memory focusing on compatibility.
If memory that is not compatible is chosen, it may not physically fit, so be sure to check.
Let’s explain these points in detail.
Is the Memory Standard Compatible with the Motherboard?
The memory standard differs in shape, so it must be compatible with the memory slot standard of the motherboard.
If the memory and motherboard standards are mismatched, the memory cannot be inserted, so do not make this mistake.
There are module standards and memory standards that indicate physical shape.
The two module standards are:
- “DIMM” for desktop PCs
- “SO-DIMM” for laptops

DIMM (for desktop PCs)
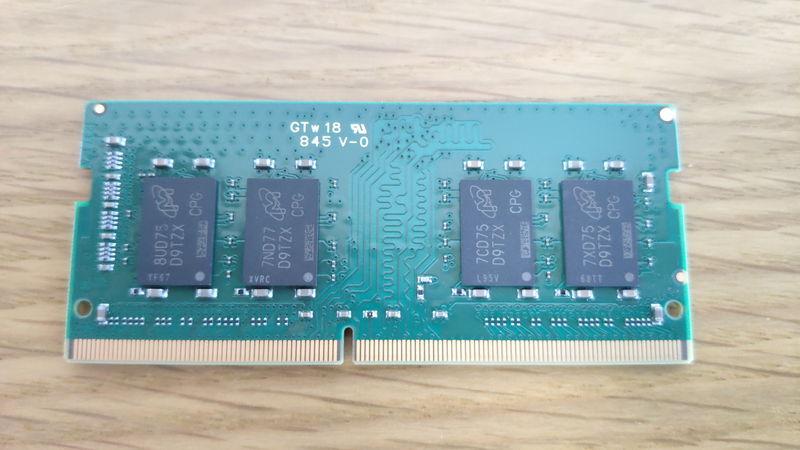

SO-DIMM (for laptops)
As you can see, the sizes are very different, and laptop memory is about half the length and smaller.
For custom PCs, desktop PCs are standard, so DIMM is used.
For laptops, use SO-DIMM when upgrading memory.
The currently used memory standards are:
- DDR5 SDRAM
- DDR4 SDRAM
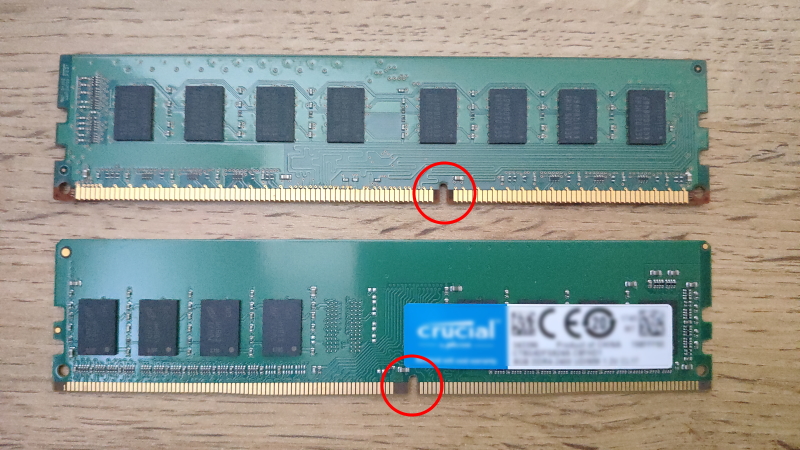
Top: DDR3, Bottom: DDR4
Memory modules have notches, and the position of these notches differs.
Because the shape differs by module and memory standard, check which standards the motherboard memory slots support.
≫ Related article: Explanation of Memory Standards, Module Standards, and Speed Standards for Custom PCs! Latest Mainstream Standards!
Can the Number of Memory Modules Fit on the Motherboard?
The number of memory modules that can be installed depends on the number of slots on the motherboard.
For consumer motherboards, 2 or 4 slots are common, but some server/workstation motherboards have 8, 12, 16, or 24 slots.
Motherboards with Mini-ITX or MicroATX standards often have 2 slots, while MicroATX, ATX, and Extended ATX often have 4 slots.
With a 2-slot motherboard and 2 memory modules, upgrading memory requires replacing the original modules, but with 4 slots, the original memory can be reused for upgrades.
Consider future upgrades when choosing the number of memory slots on the motherboard.
Is the Memory Capacity Within the Motherboard’s Maximum Supported Capacity?
The maximum memory capacity that can be installed is determined by the motherboard’s supported maximum memory capacity.
In other words, memory capacity must be within the motherboard’s maximum supported memory.
However, the maximum memory capacity of motherboards is often 64, 128, or 192GB, which is much larger than the typical amount installed, so it is not usually a concern.
Does the Memory Interfere with the Air-Cooled CPU Cooler?
When choosing memory, it is also important to check for physical interference with the CPU cooler.
If using a large aftermarket air-cooled CPU cooler and memory with a heat sink, there is a possibility that they may physically interfere and cannot be assembled.
With large air-cooled CPU coolers, the heat sink or fan may extend over the memory slots.
Also, memory with heat sinks is taller than normal memory, and depending on the height, it may exceed the height of the CPU cooler’s heat sink.
Therefore, these two factors may cause interference in the worst case.
The tricky part is that the detailed dimensions of memory height and air-cooled CPU coolers are rarely listed in the specifications, so it is difficult to determine interference before purchase.
Therefore, if you are concerned, it is recommended to choose memory without a heat sink.
With stock coolers, all-in-one liquid coolers, or small heat sink/fan CPU coolers, interference with memory with heat sinks is unlikely.
≫ Related article: About Memory Heat Sinks: Roles, Benefits, and Points to Note When Choosing
Additional Knowledge about Memory
This section explains knowledge about memory that is not as important as performance or compatibility but is still good to know.
Let’s explain these points in detail.
About ECC Function in Memory
ECC (Error Correcting Code) is a function that detects and automatically corrects data errors.
It is often used in servers and workstations where continuous operation and data accuracy are extremely important.
Therefore, it is basically unnecessary for custom PCs, and ECC memory tends to be expensive, so non-ECC memory is generally used.
Also, to use ECC, the motherboard must support ECC, and such motherboards are also more expensive.
Additionally, there is a slight performance decrease due to ECC, so it is not needed for general PCs.
ECC is unnecessary for custom PCs, but it is interesting to know how important systems are supported, so refer to the related article if you want to learn more.
≫ Related article: What is ECC Memory? Detection and Correction of Data Errors
About Registered Memory
Registered memory is memory that has a register to stabilize signals on the memory module.
The register temporarily holds data signals between the memory and memory controller and adjusts timing, improving system reliability and stability and reducing errors.
This function is used in high-load environments such as servers and workstations that require large amounts of memory and high data integrity.
Therefore, it is not necessary for general custom PCs.
Registered memory also requires a compatible motherboard, causes slight delays due to the register, and is generally expensive, so it is not suitable for custom PCs.
Like ECC, it is unnecessary for custom PCs, but it is interesting knowledge, so please check the related article.
≫ Related article: What is Registered Memory? Load Reduction by Register
About XMP Profile in Memory
XMP (eXtreme Memory Profile) is a memory performance setting specification developed by Intel that allows easy optimization of memory operation settings.
Normally, complex manual adjustments are required, but with XMP, memory speed, timing, and voltage can be automatically optimized.
However, to use XMP, both the CPU and motherboard must support XMP.
![]() Ken
Ken
Also, enabling XMP may increase memory voltage, so attention to cooling is necessary.
≫ Related article: What are Memory XMP and EXPO? Explanation of Memory Settings and Disadvantages
About Memory Timing and Latency
Memory timing is a parameter that determines the speed at which memory accesses data, with CL (CAS latency) being the most common value.
This value indicates the time it takes for memory to respond to a CPU request and send data; the shorter this time, the faster data can be processed, improving overall system responsiveness.
For games and high-load applications, choosing memory with low latency can provide smoother operation.
However, when it comes to memory speed, including timing and latency, capacity is more important, so there is no need to worry excessively.
≫ Related article: What is Memory Timing? Explanation of Performance Impact, How to Check, and How to Set
Frequently Asked Questions about Memory
This section explains frequently asked questions and doubts about memory.
Difference Between Memory and Storage
Memory is used for temporary data storage and is directly involved in the tasks the computer is currently performing, temporarily holding data and programs needed by the CPU.
“Temporarily” means that data linked to a program is stored in memory only while the program is running, and all data in memory is erased when the computer is turned off.
On the other hand, storage is for long-term data storage, where files and programs are saved.
Of course, data is not lost when the power is turned off, so the OS, games, and user-created files are saved in storage.
Although the storage period is different, both memory and storage are parts that store data, so
Why not transfer data directly from storage?
If it is only temporary, is memory even necessary?
You may wonder.
The reason this is not possible is that the data transfer speed of storage is very slow compared to the CPU.
It takes too long for the CPU to get data from storage, causing the CPU to wait and lowering the overall performance of the PC.
To compensate for this speed difference, memory acts as a buffer between the fast CPU and slow storage (SSD/HDD), making data transfer more efficient.
By temporarily storing data retrieved from storage in memory, data can be transferred quickly from memory on subsequent accesses.
Even with NVMe SSDs, which are considered fast among storage devices, there is a significant speed difference compared to memory.
With PCI Express Gen4, the read speed is about 7.0GB per second.
In contrast, memory data transfer speed varies by standard, but is about 20–50GB per second.
Compared to Gen4 NVMe SSDs, memory is 3–7 times faster, which may not seem like much, but with SATA SSDs (about 600MB per second), it is about 30–80 times faster, and with HDDs (about 150MB per second), it is about 130–330 times faster.
≫ Related article: Easy-to-Understand Explanation of the Difference Between Memory and Storage [Memory is a Cushion]
Summary: It is Important to Choose the Appropriate Memory Capacity for the Intended Use!
Memory is a component that temporarily stores data when a computer is working, and it acts as a bridge between the fast CPU and the slow storage (SSD/HDD), making data transfer more efficient.
For custom PCs, memory capacity is the most important factor for performance.
The required memory capacity changes depending on the intended use and the extent of the tasks, but if the capacity is incorrect, the PC will not run comfortably, so be careful.
Here is a summary of how to choose memory:
- The most important performance factor is memory capacity
- Speed up with a dual-channel configuration
- Insufficient memory leads to an uncomfortable experience
- Check if the memory standard is compatible with the motherboard
- Pay attention to the number and capacity of memory modules the motherboard can support
- Be careful of interference between large air-cooled CPU coolers and memory with heat sinks
Besides performance, compatibility must not be overlooked.
If the standard is wrong, the memory cannot be inserted into the motherboard, making assembly impossible.
If a replacement is needed, it will result in unnecessary extra expenses, so be sure to check the standard before purchasing.
Basic knowledge, roles, and how to choose other PC parts from the perspectives of performance and compatibility are also explained, so please refer to them.
≫ Related article: PC Parts List and Explanation of Each PC Part [A Must-Read for Custom PC Beginners]
Select PC parts and online stores to instantly generate an estimate, check compatibility, and calculate power requirements. You can save up to five different builds, making it easy to try out multiple configurations.
≫ Tool:PC Parts Estimation & Compatibility Check Tool
 ZisaLog: Beginner’s Guide to Building a Custom PC
ZisaLog: Beginner’s Guide to Building a Custom PC