This article explains what a motherboard chipset is, its role, and what is determined by the chipset.
Each chipset has different specifications, such as socket shape, USB standards, maximum number of ports, PCI Express version, maximum number of lanes, and support for CPU or memory overclocking.
Because of this, if the wrong parts are selected, it may not be possible to install all components or use the desired features.
That said, for most standard PC builds, almost any chipset will work, so there is no need to worry too much.
If overclocking the CPU or memory, or building a RAID setup is required, it is important to check compatibility, as not all chipsets support these features.
- The chipset manages communication between parts on the motherboard.
- Since 2008, systems have shifted to a CPU and PCH structure, with the northbridge integrated into the CPU.
- Each chipset supports different CPU generations, overclocking, USB ports, maximum display outputs, SATA connectors, PCIe standards and lanes, and RAID configurations.
- Both Intel and AMD offer chipset grades, and it is basic to choose according to the intended use.
- However, it is fine to choose any grade based on budget and required features.
- There is no performance difference between chipsets, but higher grades offer better motherboard features, maintenance, and durability.
- When selecting parts, check the motherboard specifications rather than just the chipset specs
This article also explains how to choose a motherboard based on its standards, part names, performance, and compatibility.
≫ Related article: How to Choose a Custom PC Motherboard [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
Select PC parts and online stores to instantly generate an estimate, check compatibility, and calculate power requirements. You can save up to five different builds, making it easy to try out multiple configurations.
≫ Tool:PC Parts Estimation & Compatibility Check Tool
Table of Contents
What is a Motherboard Chipset?
This section explains the role, structure, performance differences, and compatibility of chipsets in detail.
The Role of the Chipset
The role of the chipset is to act as a bridge to allow various parts on the motherboard to communicate and work together.
Specifically, it coordinates the efficient cooperation of main parts such as the CPU, memory, storage, and graphics card.
For example, when the CPU reads or writes data to memory, the chipset manages the data flow and ensures smooth communication.
The chipset also handles communication with external devices such as USB ports and network connections.
This optimizes overall system performance and allows users to work comfortably.
Chipset Structure
The chipset structure is divided into the CPU and PCH (Platform Controller Hub).
Before 2008, motherboards commonly had two chipsets: the “northbridge” and the “southbridge.”
Each chipset was physically located in different places on the motherboard and handled tasks according to its role.
Since this also relates to the CPU and PCH, the northbridge and southbridge will be explained first.
Northbridge
The northbridge, also called the Memory Controller Hub, directly connects the CPU to high-speed devices such as memory and graphics cards.
By managing high-speed communication between the CPU, memory, and graphics card, data transfer speeds increase and system responsiveness improves, resulting in better performance.
Because it needs to work closely with the CPU and other high-speed parts, the northbridge is located near the center of the motherboard, close to the CPU.
Due to the heavy load, it is often cooled with a heatsink or fan.
Southbridge
The southbridge, also called the I/O Controller Hub, handles communication with relatively low-speed peripherals such as USB ports, audio devices, network interfaces, and storage.
Since high-speed processing is not required compared to the CPU, memory, and graphics card, it is placed farther from the CPU.
The southbridge rarely communicates directly with the CPU or memory, instead communicating indirectly through the northbridge.
This helps improve overall system efficiency.
Transition to CPU + PCH Chipset Structure
Previously, chipsets consisted of the northbridge and southbridge, but since around 2008, the structure shifted to the CPU and PCH (Platform Controller Hub).
Because the northbridge required high-speed processing, it was placed physically close to the CPU for maximum speed.
However, even when close to the CPU, using the northbridge as an intermediary caused time lags in communication with other parts.
To solve this, the northbridge was integrated into the CPU, and the southbridge was replaced by the PCH.
The northbridge was abolished, and its functions were integrated into the CPU.
This integration allows memory and graphics cards to access the CPU directly, improving processing speed.
The southbridge’s functions were replaced by the PCH, which continues to manage input/output devices such as USB ports, audio devices, network interfaces, and storage.
Performance Differences Between Chipsets
Chipsets are divided by CPU manufacturer and further separated into several grades.
For example, Intel has the Z series, B series, and H series (details will be explained later).
Comparing some specifications of Intel 700 series Z790 and B760 chipsets:
| Z790 | B760 | |
|---|---|---|
| Supported CPUs | 14th Gen (Raptor Lake Refresh) 13th Gen (Raptor Lake) 12th Gen (Alder Lake) | |
| CPU Overclocking Support | ○ | × |
| Memory Overclocking Support | ○ | ○ |
| SATA 6.0Gb/s | 8 | 4 |
| Maximum USB Ports | 14 | 12 |
As shown, support for overclocking, the number of SATA connectors, and the maximum number of USB ports differ by chipset.
Other differences include the number of video outputs, PCI Express version and lanes, so it is important to check the specifications based on what is needed.
Also, even if the chipset supports certain features or port numbers, not all motherboards will provide all of them.
Even if the chipset defines a feature, the motherboard may not include it or may not have the maximum number of ports.
This is because some motherboard designs do not use all the features of the chipset, depending on the product concept or design philosophy.
Conversely, some motherboards add extra chips to increase functionality.
Therefore, when selecting parts, it is more common to check the motherboard specifications rather than just the chipset specs.
Also, there is no performance difference due to chipset specifications themselves, so if the same parts are used with a Z790 or B760 motherboard, performance will be the same.
However, differences in chipset or grade affect supported features and compatible parts, which can impact overall PC performance depending on the configuration.
Be Careful About Chipset Compatibility
Each chipset supports different standards and versions, so it is important to check compatibility when selecting parts.
For example, each chipset determines the CPU socket shape and generation, so it is necessary to choose a CPU and motherboard that match.
If they are not compatible, the CPU may not fit the motherboard, or even if it fits, it may not work.
Some chipset series (generations) may not support the latest interfaces or features.
For example, to use the latest PCI Express or NVMe SSD, a compatible chipset is required.
Version differences mainly affect data transfer speeds, so while installation may be possible, the speed will match the slower component.
Therefore, even if a high-speed NVMe SSD is purchased, if the motherboard does not support the latest standard, the full speed cannot be achieved.
As shown, chipset compatibility can prevent a custom PC from being assembled or from achieving maximum performance, so be sure to check carefully.
That said, it is more common to check the motherboard specifications rather than the chipset when confirming compatibility.
There are also tools that allow “estimation,” “compatibility check,” and “power calculation” just by selecting PC parts, so those who want to check compatibility should use them.
≫ Tool: Custom PC Parts Estimation & Compatibility Check Tool
About Chipset Grades (Alphabet)
Chipset grades can be identified by the alphabet in the chipset name.
For example, in “Z790,” the “Z” indicates the grade.
Each manufacturer designs series for different user groups and purposes, so by checking the grade, it is possible to know the target audience and features.
Most motherboard product names include the chipset name, so with experience, it is easy to identify by the product name.
About Intel Chipset Grades
| Grade | Example | Use (Target) | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Z | Z790 Z690 | High-end models For high-performance gaming and creators | ・Supports overclocking ・Many PCIe lanes and USB ports |
| H | H770 H670 | Mid-range models Mainstream use General, gaming, and creators | ・No overclocking support ・Standard feature set |
| B | B760 B660 | Entry models For office or light users | ・No overclocking support ・Standard feature set ・Cost performance focused |
| Q | Q670 | For business For companies and enterprises | ・Enhanced management features for businesses (vPro support) ・Rich security and remote management features |
| W | W790 | For workstations For professional PCs | ・High reliability, stability, and expandability ・Supports ECC memory ・Rich professional features ・Many PCIe lanes and memory support |
For personal custom PCs, “Z,” “H,” or “B” are most commonly used.
For high-performance gaming or creative PCs, “Z” is often chosen, while “H” or “B” are used for cost-effective builds, but there is no strict rule.
“Z” motherboards are high-end and expensive, so even for high-performance PCs, “H” or “B” may be used. If overclocking (only possible with “Z”) is not needed, there is no need to choose it, and the decision can be based on budget.
As mentioned earlier, there is no performance difference due to the chipset itself, but high-end motherboards often have extra features, such as reinforced PCI Express slots for heavy GPUs or BIOS upgrade buttons.
Therefore, if extra features are desired, “Z” may be a good choice.
About AMD Chipset Grades
| Grade | Example | Use (Target) | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| X | X670 X570 | High-end models For high-performance gaming and creators | ・Supports overclocking ・Many PCIe lanes and USB ports |
| B | B550 B450 | Mid-range models Mainstream use General, gaming, and creators | ・Partial overclocking support ・Standard feature set ・Cost performance focused ・Balanced PC builds |
| A | A520 A320 | Entry models For office or light users | ・No overclocking support ・Basic features only |
AMD does not have grades specialized for business, enterprise, or workstation use.
For high-performance gaming or creative PCs, “X” is often chosen, while “B” or “A” are used for cost-effective builds, but there is no strict rule.
This approach is similar to Intel chipsets.
Differences in Chipset Specifications
This section explains the various specification differences between chipsets.
CPU Socket Shape and Generation
Each chipset generation supports different CPU generations.
As a result, the CPU socket shape on the motherboard also changes, so be sure to match the CPU and motherboard.
However, this can usually be checked from the CPU and motherboard specifications, so it is rare to check the chipset specs directly.
Overclocking Support
Overclocking (OC) means increasing the clock frequency of the CPU or memory above the standard value.
This improves PC processing power, especially for gaming or heavy workloads.
Whether CPU and memory overclocking is supported depends on the chipset. Some chipsets support only memory OC but not CPU OC, so those who want to overclock should check carefully.
Generally, higher-grade chipsets support overclocking, while others do not.
PCI Express
PCI Express (PCIe) is an interface for connecting expansion cards such as graphics cards, network cards, and NVMe SSDs.
Chipset specifications determine the PCIe standard, version, configuration (x1, x4, etc.), and maximum number of lanes.
However, the actual configuration and maximum number of lanes depend on the motherboard, so it is better to check the motherboard specs.
The most important thing to check is the PCI Express version.
If using the latest NVMe SSD, the latest PCI Express version is needed to get maximum data transfer speed.
For example, if the NVMe SSD supports PCI Express Gen 5.0 but the motherboard only supports Gen 4.0, the speed will be limited to Gen 4.0, and the SSD’s full speed cannot be used.
Storage Interface
The chipset determines the SATA port standard and maximum number of connections.
Most recent motherboards use SATA 6.0 Gb/s, so the standard is not a concern.
As for the maximum number of connections, most builds use only one or two SATA SSDs or HDDs, so it is not usually an issue. However, if four, six, or eight SATA connectors are needed, it should be checked.
RAID Configuration
RAID is a technology that combines multiple storage devices to improve data redundancy and performance, mainly for performance, data protection, and availability.
Each chipset differs in whether it supports RAID and which RAID levels are supported for PCIe and SATA.
For example, Intel’s “B” series does not support RAID at all.
“Z” series supports RAID levels 0, 1, 5 for PCIe and 0, 1, 5, 10 for SATA.
Workstation “W” series supports RAID levels 0, 1, 5, 10 for PCIe and 0, 1, 5, 10 for SATA.
As shown, whether RAID is supported and which levels are available differ by chipset, so check if RAID is needed.
USB Ports
The maximum number of USB ports varies by standard:
- USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 (20G) ports
- USB 3.2 Gen 2×1 (10G) ports
- USB 3.2 Gen 1×1 (5G) ports
- USB 2.0
However, most motherboards do not provide the maximum number of USB ports specified by the chipset, so it is common to check the motherboard’s USB port specs when selecting parts.
For general use, such as connecting a mouse, keyboard, or USB memory, there are usually enough ports, so there is little need to worry.
Network
Ethernet and Wi-Fi standards vary by chipset.
For example, many recent chipsets support Wi-Fi 6 and 2.5GbE (Gigabit Ethernet).
Older chipsets may not support these latest standards, resulting in lower network speed or stability.
Video Output
The maximum number of supported video outputs differs by chipset.
Most recent chipsets support up to four displays.
For more multi-display setups, a graphics card is needed.
How to Check the Motherboard Chipset
This section introduces how to check the motherboard chipset.
How to Check the Chipset on Your PC
To check the chipset used in your PC, use software that displays hardware information.
For example, CPU-Z and Speccy are both free to use.
With CPU-Z
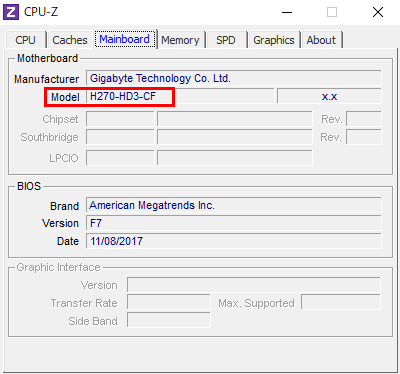
Check the [Mainboard] tab under Chipset.
In my case, the Chipset section is grayed out, possibly because my PC is old, but the chipset can be identified from part of the Model field.
With Speccy
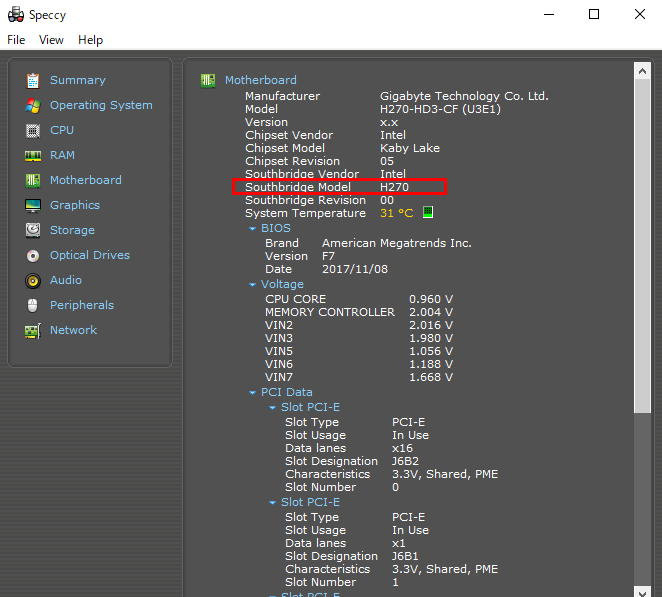
With Speccy, the Southbridge Model section under [Motherboard] in the left menu shows the chipset.
Checking from Motherboard Specifications
When selecting parts for a custom PC, the chipset may be a concern.
In that case, check the product name or official page specifications for the motherboard.
For example, the ASUS TUF GAMING B760M-PLUS II motherboard includes “B760” in the product name, indicating the chipset.
Most product names include the chipset.
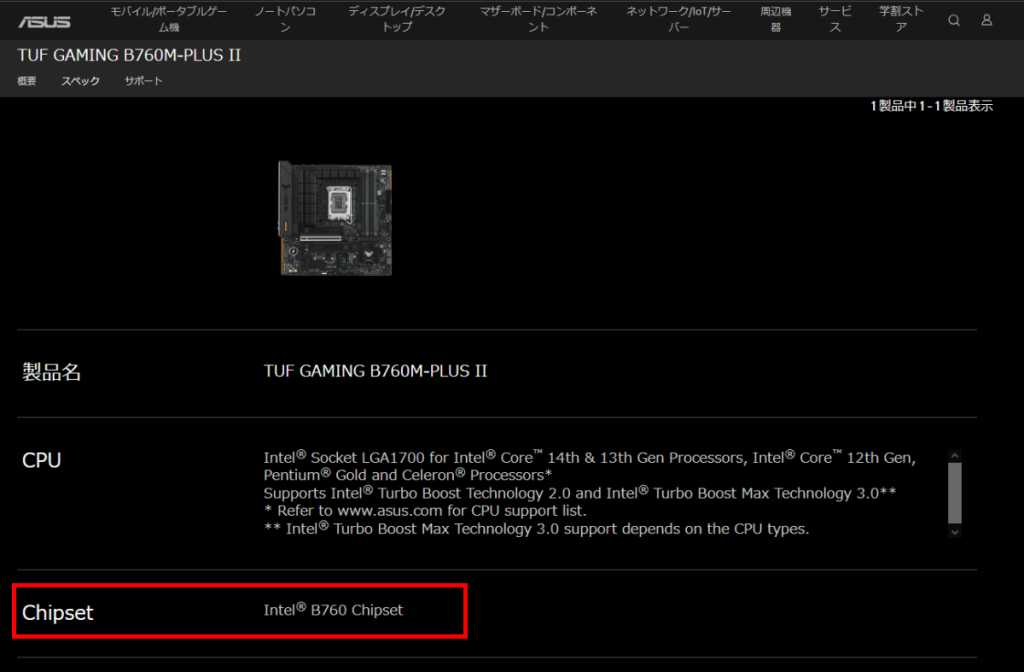
The official product page also lists the chipset in the specifications.
If it is unclear which part of the product name is the chipset, check the product page.
Summary: Choose the Right Chipset for Your Custom PC Build!
This article has explained the basics of chipsets, differences in series, grades, and specifications, using tables for clarity.
Here is a summary of the key points.
- The chipset manages communication between parts on the motherboard.
- Since 2008, systems have shifted to a CPU and PCH structure, with the northbridge integrated into the CPU.
- Each chipset supports different CPU generations, overclocking, USB ports, maximum display outputs, SATA connectors, PCIe standards and lanes, and RAID configurations.
- Both Intel and AMD offer chipset grades, and it is basic to choose according to the intended use.
- However, it is fine to choose any grade based on budget and required features.
- There is no performance difference between chipsets, but higher grades offer better motherboard features, maintenance, and durability.
- When selecting parts, check the motherboard specifications rather than just the chipset specs
For standard part configurations and general use, the chipset does not make much difference.
However, if connecting the latest NVMe SSD, overclocking the CPU or memory, or building a RAID setup, be sure to check the chipset and motherboard specifications carefully.
This article also explains how to choose a motherboard based on its standards, part names, performance, and compatibility.
≫ Related article: How to Choose a Custom PC Motherboard [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
Select PC parts and online stores to instantly generate an estimate, check compatibility, and calculate power requirements. You can save up to five different builds, making it easy to try out multiple configurations.
≫ Tool:PC Parts Estimation & Compatibility Check Tool
 ZisaLog: Beginner’s Guide to Building a Custom PC
ZisaLog: Beginner’s Guide to Building a Custom PC 



