The rotation speed of an HDD is a value that indicates how many times the platter rotates per minute, and it is a specification related to data read and write speeds.
Currently, SSDs are the mainstream, and opportunities to use HDDs as the main storage have decreased.
However, HDDs still have certain needs, such as for backup, storing large amounts of data, or when prioritizing cost.
For this reason, choosing the right rotation speed model according to the intended use is important to balance performance and stability.
This article explains how the rotation speed of an HDD affects performance, heat generation, and power consumption, and describes the features and suitable uses for each major rotation speed.
- The rotation speed of an HDD indicates how many times the platter rotates per minute (unit: RPM)
- Rotation speed affects read/write speed and performance
- Common HDDs are mainly 5400RPM and 7200RPM
- Higher rotation speed increases access speed, but also increases noise and heat
- Speed differences due to rotation speed are only comparisons within HDDs
- SSDs are overwhelmingly faster than HDDs and are the current mainstream storage
- HDDs are suitable for backup and large-capacity storage
- Rotation speed can be checked from product specifications or tools
- Some HDDs have undisclosed or variable rotation speeds
This article also explains basic knowledge about storage standards and mainstream storage configurations, as well as how to choose from the perspective of performance and compatibility.
≫ Related article: How to Choose Storage (SSD/HDD) for Custom PCs [Performance / Functionality / Compatibility]
Select PC parts and online stores to instantly generate an estimate, check compatibility, and calculate power requirements. You can save up to five different builds, making it easy to try out multiple configurations.
≫ Tool:PC Parts Estimation & Compatibility Check Tool
Table of Contents
What is HDD Rotation Speed?
This section explains HDD rotation speed, touching briefly on the structure and mechanism of HDDs.
About the Structure and Mechanism of HDDs
To understand HDD rotation speed, it is important to first know the structure and mechanism of HDDs.
An HDD is a storage device that records data on a disk-shaped recording medium called a platter (disk).
A single HDD may have multiple platters, and these are rotated at a constant speed by a central motor.
![]() Ken
Ken
On the surface of these rotating platters, a magnetic head moves with a tiny gap to read and write data.
The magnetic head itself can only move left and right, so it cannot access the entire platter as is. By rotating the platter itself, data can be read and written across the whole platter.
![]() Ken
Ken
The Number of Rotations per Minute of the Platter
HDD rotation speed is the value that shows how many times the platter rotates per minute and is expressed in RPM (Revolutions Per Minute).
RPM is a unit widely used not only for HDDs but also for various machines involving rotational motion.
This rotation speed affects the read/write speed and access speed of the HDD.
Generally, HDDs often have rotation speeds of 5400RPM or 7200RPM, which determines the data read/write speed.
The higher the rotation speed, the faster the data access speed tends to be, but power consumption and heat generation also increase.
For example, 7200RPM is common for desktop PCs, while 5400RPM is often chosen for laptops or when prioritizing power saving.
The features of each mainstream rotation speed will be explained later.
Types of HDD Rotation Speeds
Let’s take a closer look at the characteristics and uses of different HDD rotation speeds.
First, here is a summary of the features by mainstream rotation speed.
| Rotation Speed | Main Uses | Features | Read/Write Speed | Noise | Heat | Power Consumption | Lifespan | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5400 RPM | ・Laptop PCs ・External HDDs ・Power-saving PCs | Quiet, low heat, low speed | Low speed About 80–100 MB/s | Very quiet | Low | Low | Long | Cheap |
| 7200 RPM | ・General use ・Desktop PCs ・Custom PCs | Balanced, highly versatile | Medium speed About 100–160 MB/s | Slightly audible | Medium | Medium | Standard | Medium |
| 10000 RPM | ・Servers ・Workstations ・High-performance PCs | High speed, response-focused | High speed About 160–200 MB/s | Loud | High | High | Short | Expensive |
There are a few other rotation speeds, but they account for only about 2–3% of all products, so referring to the above speeds is sufficient.
Terms like “low speed” and “high speed” for read/write speed are only comparisons within HDDs. Compared to SSDs, HDDs are slower at all RPM levels.
Even SATA SSDs have 500MB/s, and NVMe SSDs can reach 2,000–12,000MB/s, so if speed is a priority, SSDs are recommended.
≫ Related article: How to Choose Storage (SSD/HDD) for Custom PCs [Performance / Functionality / Compatibility]
![]() Ken
Ken
Also, terms like “long” or “short” for lifespan depend on usage conditions, but higher rotation speeds tend to wear out parts faster.
However, high-quality enterprise models are sometimes designed for long life as an exception.
Rotation Speed: 5,400RPM
HDDs with 5,400RPM are designed with relatively low rotation speed and are mainly used in laptops, external HDDs, and PCs that prioritize power saving.
The main features of this rotation speed are excellent quietness and energy efficiency.
Because the platter rotation is suppressed, heat generation is also low, and the fan speed can be kept down, so the whole system operates quietly.
Also, because power consumption is low, it can be used stably in battery-powered mobile devices or environments that require long continuous operation.
In terms of performance, read/write speeds of about 80–100MB/s are common, and it is practical enough for everyday file storage, document work, and web browsing.
It is not designed for high performance, but its relatively low price and longer lifespan are valued for long-term use.
Rotation Speed: 7,200RPM
HDDs with 7,200RPM are currently the most commonly used models and are a standard choice with a good balance of performance and cost.
This rotation speed is widely used in desktop PCs, custom PCs, and business work environments, and has performance that can handle everything from daily use to slightly heavier tasks.
Because the platter rotation speed is higher than 5,400RPM, the data read/write speed is about 100–160MB/s, which is in the medium speed class.
Especially for handling large files such as videos and photos, unless speed is a top priority, it is comfortable to use.
However, as the rotation speed increases, heat and noise also increase slightly, so it is not ideal for environments that prioritize quietness or energy saving.
Still, it is often used as a balanced HDD with high cost performance and versatility.
Rotation Speed: 10,000RPM
HDDs with 10,000RPM are high-performance models that achieve excellent read/write speed and responsiveness due to their high rotation speed.
This class of HDD is often used in servers, workstations, and high-load business PCs, where data access speed directly affects work efficiency while still requiring large capacity. They are rarely seen in consumer PCs.
Because the platters rotate at high speed, read/write speeds can exceed 160–200MB/s, which is advantageous for processing large numbers of files in a short time or for applications that depend on disk I/O.
In fact, before SSDs became popular, 10,000RPM was the standard choice for the fastest HDDs.
On the other hand, the disadvantages of high-speed rotation include loud operating noise and increased vibration, so vibration-resistant design may be required.
Also, heat generation and power consumption are high, and because higher rotation speeds accelerate wear, the lifespan is generally shorter.
How to Check HDD Rotation Speed
This section explains how to check the rotation speed of an HDD.
Check in Product Specifications
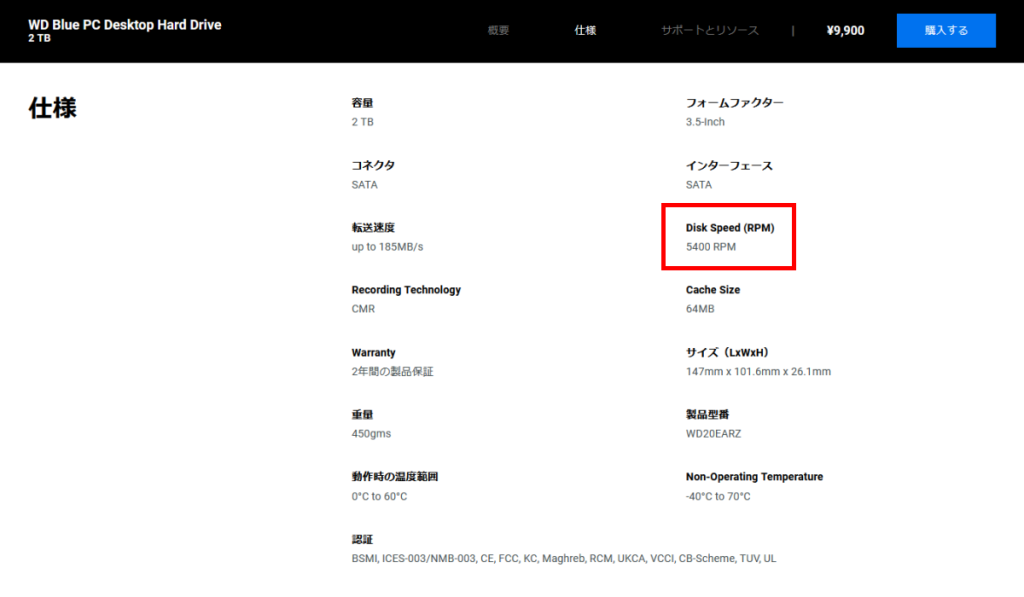
The rotation speed is written in the specifications on the HDD product page, so it can be checked there.
This method is useful if the HDD has not been purchased yet or if you want to look it up by model number.
Check with CrystalDiskInfo
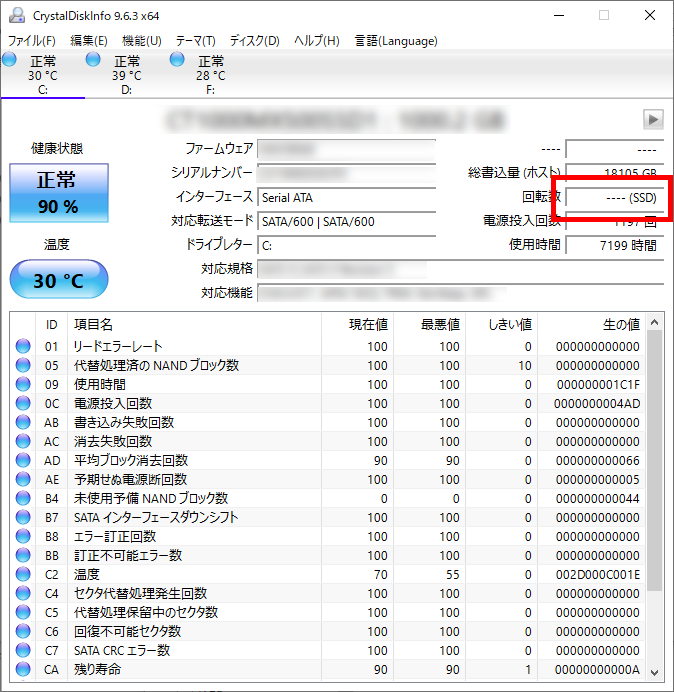
By using the free software CrystalDiskInfo, which allows checking storage information installed in a computer, the rotation speed of the HDD can be checked.
This is useful when the HDD is already installed, the model number is unknown, and it is troublesome to check the model number from the specification sheet or by opening the computer.
The image shows an SSD, so the rotation speed is not displayed, but if you check an HDD, the rotation speed will be shown here.
Some Products Do Not Disclose Rotation Speed
Two methods to check HDD rotation speed have been introduced, but some products do not have their rotation speed disclosed by the manufacturer.
Because I run a custom PC tool, I also have HDD specification information, but about 10% of 500 products have undisclosed rotation speed.
This is especially seen in certain manufacturers, server models, RAID, and models for recording purposes.
It may be displayed in CrystalDiskInfo, but the information is based on S.M.A.R.T., which records HDD information and status.
This information is also recorded by the manufacturer, so if the rotation speed is undisclosed, it is unlikely to be recorded, and basically cannot be obtained.
The reason for non-disclosure may be to maintain a competitive advantage by not revealing product specifications, for design reasons, or for marketing strategy, but the exact reason is unknown.
Some Models Have No Fixed Rotation Speed Due to Variable RPM Technology
Some HDDs use variable RPM technology, where the platter rotation speed changes depending on the situation.
For example, Western Digital’s “IntelliPower” is a typical example, where instead of a specific RPM being disclosed, the balance of power consumption, performance, and quietness is dynamically optimized.
For such HDDs, there is no fixed rotation speed by design, so the rotation speed may not be displayed in the product specifications or in CrystalDiskInfo.
This variable rotation speed is often seen in models that prioritize energy saving and quietness, and because they do not always operate at high speed, they are designed to reduce heat and noise and consider lifespan.
Summary: For Custom PCs and Desktop PCs, 7,200RPM is Recommended!
This article explained HDD rotation speed, the structure and mechanism of HDDs, and the features of different rotation speeds.
Here is a summary of the key points.
- The rotation speed of an HDD indicates how many times the platter rotates per minute (unit: RPM)
- Rotation speed affects read/write speed and performance
- Common HDDs are mainly 5400RPM and 7200RPM
- Higher rotation speed increases access speed, but also increases noise and heat
- Speed differences due to rotation speed are only comparisons within HDDs
- SSDs are overwhelmingly faster than HDDs and are the current mainstream storage
- HDDs are suitable for backup and large-capacity storage
- Rotation speed can be checked from product specifications or tools
- Some HDDs have undisclosed or variable rotation speeds
HDD rotation speed is a specification related to storage read/write performance, quietness, heat generation, and power consumption.
The higher the rotation speed, the better the access speed, but heat and noise also tend to increase, so it is important to choose according to the intended use.
Currently, SSDs are the mainstream storage, and HDDs are mainly used for storing large amounts of data or for backup.
For custom PCs or desktop PCs, a balanced 7,200RPM HDD is recommended.
This article also explains basic knowledge about storage standards and mainstream storage configurations, as well as how to choose from the perspective of performance and compatibility.
≫ Related article: How to Choose Storage (SSD/HDD) for Custom PCs [Performance / Functionality / Compatibility]
Select PC parts and online stores to instantly generate an estimate, check compatibility, and calculate power requirements. You can save up to five different builds, making it easy to try out multiple configurations.
≫ Tool:PC Parts Estimation & Compatibility Check Tool
 ZisaLog: Beginner’s Guide to Building a Custom PC
ZisaLog: Beginner’s Guide to Building a Custom PC 



