The auxiliary power supply for a graphics card is intended to provide the additional power required to keep high-performance graphics cards operating stably.
If you do not properly understand auxiliary power when planning your parts configuration, you may find that the power supply unit’s capacity is insufficient or that you lack the right type/number of cables, which means you’ll end up having to buy parts again.
Moreover, if adequate power cannot be supplied, the graphics card or the entire system may not function correctly and, in the worst case, it leads to system instability.
This article explains in detail the importance, types, and selection of auxiliary power for graphics cards.
- GPUs are powered by both the “PCIe slot” and “auxiliary power”
- Recent GPUs are underpowered by the PCIe slot alone (auxiliary power is essential)
- Auxiliary power connectors come in three types: 12VHPWR (16-pin) / 8-pin / 6-pin
- 12VHPWR is a high-output connector for the latest GPUs and can supply up to 600 W
- A 6+2-pin can be used as an 8-pin, making it a flexible auxiliary power connector
- When choosing a PSU, make sure it supports the required auxiliary connector types and counts
- Incorrect use of adapter cables can pose a risk of ignition or fire—exercise caution
We also explain basic knowledge such as how to read manufacturers and model names, performance benchmarks, and how to choose from performance and compatibility perspectives.
≫ Related article: How to Choose a Graphics Card for a Custom PC [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
Select PC parts and online stores to instantly generate an estimate, check compatibility, and calculate power requirements. You can save up to five different builds, making it easy to try out multiple configurations.
≫ Tool:PC Parts Estimation & Compatibility Check Tool
Table of Contents
What Is a Graphics Card’s Auxiliary Power?
Let’s look closely at how graphics cards are powered and why this is necessary.
About GPU Auxiliary Power
A GPU’s auxiliary power is meant to supply additional power required for a graphics card to operate stably.
Modern high-performance graphics cards often cannot get enough power from the motherboard alone, so they use auxiliary power connectors to supplement it.
In general, 6-pin or 8-pin PCI Express auxiliary power connectors are used, supplying power directly from the power supply unit through these connectors.
If adequate power is not delivered, the graphics card may not function correctly, performance may drop, or the system may become unstable.
Strictly speaking, for safety reasons the system shouldn’t even boot.
![]() Ken
Ken
Two Power Sources: “PCI Express Slot” and “Auxiliary Power”
A graphics card’s power is mainly provided by two methods: the PCI Express slot and auxiliary power.
First, the PCI Express slot on the motherboard supplies up to 75 W to the graphics card.
For graphics cards that don’t need much power, the PCI Express slot alone suffices without auxiliary power.
![]() Ken
Ken
However, many recent high-performance graphics cards require more than this and therefore need auxiliary power.
Auxiliary power is supplied directly from the PSU through 6-pin, 8-pin, or 12VHPWR (16-pin) power connectors.
A 6-pin connector can supply up to 75 W, and an 8-pin up to 150 W; depending on the card’s specifications, one or multiple auxiliary connectors may be required.
Thus, by combining the PCIe slot and auxiliary power, the graphics card secures the power it needs for stable operation.
Why Auxiliary Power Is Necessary
When installing a graphics card in a custom PC, “whether auxiliary power is needed” is a very important checkpoint.
Especially with recent high-performance GPUs, auxiliary power is practically a given.
So, why do graphics cards need auxiliary power?
- The PCI Express slot alone is insufficient
Graphics cards are typically mounted in a PCI Express x16 slot on the motherboard, but the slot can supply only up to 75 W.
This is the spec limit; any power beyond that must be supplied via another path. - The latest GPUs consume 200 W or more
As performance has improved, power consumption has increased significantly.
High-end models often have a TGP (Total Graphics Power) of 200–400 W or more, so the 75 W from the PCIe slot is nowhere near enough.
therefore supply power directly from the PSU via auxiliary connectors.
If power is insufficient, the following issues may occur:
- The screen goes black during gaming or 3D workloads
- Unstable frame rates or processes halting mid-operation
- Sudden restarts or forced shutdowns
- In the worst case, component failure or heat-related incidents
In fact, due to these safety concerns, many recent graphics cards are designed not to boot at all if auxiliary power isn’t connected.
In short, auxiliary power is essential for safe and comfortable operation of a graphics card.
Types of Auxiliary Power
Here we explain the types of auxiliary power connectors.
When planning parts for a custom PC, first check which type of PCI Express or 12VHPWR connector your graphics card requires.
Then select a power supply unit equipped with the required connector types and counts.
For more details, see how to choose a graphics card.
Also, you can use tools that check compatibility from specifications just by selecting parts—be sure to make use of them.
≫ Related article: How to Choose a Graphics Card for a Custom PC [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
≫ Related tool: Custom PC Parts Estimate & Compatibility Check Tool
12VHPWR (16-pin)
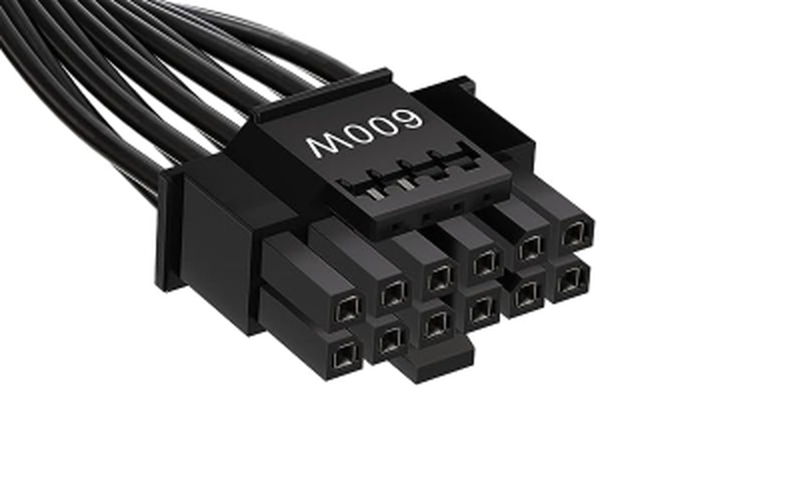

12VHPWR (16-pin) is a new auxiliary power connector designed to support the latest graphics cards.
started appearing around 2022.
This connector can deliver more power than conventional 8-pin or 6-pin connectors, with maximum power delivery set by spec at 600 W, 450 W, 300 W, and 150 W.
Although the standard supports these four levels, considering that it emerged to address the inadequacy of 150 W PCI Express connectors, in practice it is often implemented at 300 W or higher.
In particular, the 600 W capability provides ample power to fully leverage cutting-edge high-performance GPUs.
Behind the development of 12VHPWR is the rising power demand of modern graphics cards and other high-performance computing devices (such as workstations and AI-training machines).
With conventional PCI Express connectors (8-pin, 6-pin), it had become difficult to efficiently supply the power required by the latest high-end GPUs.
Notably, high-end models in NVIDIA’s GeForce RTX 40 and 50 series adopt the 12VHPWR connector.
Specifically, models like the RTX 3090, 4070, 4080, 4090, 5070, and 5080.
However, this does not mean every model in those series necessarily uses 12VHPWR; some use multiple PCI Express connectors.
Therefore, be sure to check the specifications for each product.
Another advantage is that, compared to connecting multiple PCI Express connectors, using a single 12VHPWR makes cable routing easier and allows more efficient use of internal case space.
6+2-pin
The 6+2-pin is one type of auxiliary (PCI Express) power connector used to supply power to a graphics card.
This connector is divided into a 6-pin and a 2-pin section and can be used as a combined 8-pin.
The 6+2-pin design provides flexibility, supporting cards that require only 6-pin as well as higher-performance cards that require 8-pin.
Typically, adding the 75 W from the PCIe slot to the 75 W from a 6-pin yields a total of 150 W.
An 8-pin can supply 150 W, for a total of 225 W.
However, if one connector is not enough, the graphics card side may provide two or three auxiliary connector sockets.
This enables stable operation even for graphics cards that need more power.
In particular, higher-power graphics cards from the RTX 20 series onward often require this 8-pin (6+2-pin) connector.
8-pin
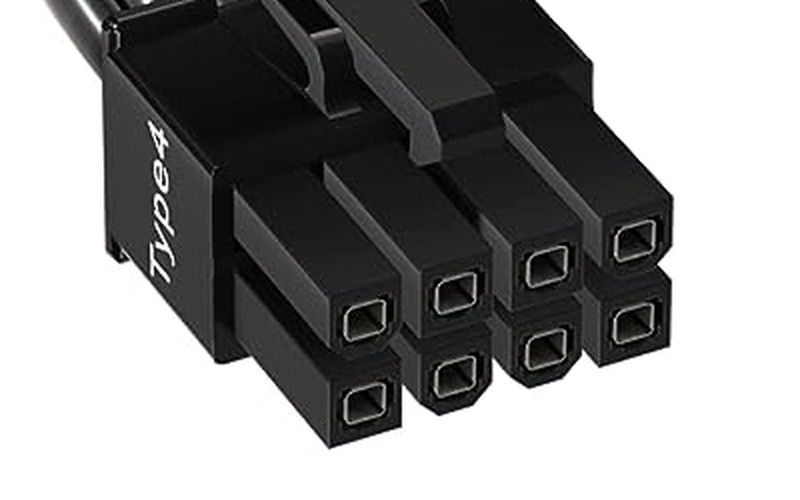

An 8-pin auxiliary power connector provides up to 150 watts.
Compared with a 6+2-pin, it is the same as using a 6+2-pin as an 8-pin, except that it simply cannot be split into 6-pin and 8-pin.
![]() Ken
Ken
While it lacks the flexibility of a 6+2-pin, most recent graphics cards require an 8-pin anyway, so it’s not really an issue.
However, note that in a small subset of RTX 3050 and 4060 products a 6-pin may be used, so be careful.
Therefore, check which auxiliary power connector is required for each graphics card product, and choose a PSU while confirming whether it includes that cable.
6-pin
A 6-pin auxiliary power connector provides up to 75 watts.
Combined with the 75 W provided by the PCI Express slot itself, a total of 150 W can be supplied.
However, very few recent graphics cards require a 6-pin auxiliary connector; since the RTX series, only a small subset of RTX 3050 and 4060 products use it.
Most graphics cards now require more power, typically multiple 8-pins or a single 12VHPWR (16-pin).
Therefore, use of 6-pins has become quite rare recently.
Points to Note When Choosing PC Parts
The parts relevant to a graphics card’s auxiliary power are the graphics card and the power supply unit; focusing on these, here are points to note when choosing parts.
Connector Types and Counts on the PSU
When choosing a PSU, you need one that matches the type and number of auxiliary power connectors required by the graphics card.
To that end, first check the auxiliary power connector specifications of the graphics card you selected.
The required type and count of auxiliary power connectors are fixed per product.
For example: one 12VHPWR, two 8-pins, or one 6-pin.
It is not the case that multiple different types are required together—basically it’s only one type.
Also, while 12VHPWR currently uses only a single cable, 8-pin and 6-pin may require multiple cables.
Once you know the required connector type and count for the graphics card, next check the PSU’s PCI Express and 12VHPWR specifications to ensure it has the necessary types and counts.
If you get the types or counts wrong, in the worst case you may have to repurchase the graphics card or the PSU, so check carefully in advance.
Whether 12VHPWR Is Supported and Its Power Delivery Capability
We’ve explained checking connector types and counts, but in practice most PSUs typically include around three to five 6+2-pin PCIe connectors, so selecting one is not that difficult and mistakes are unlikely.
Cheaper PSUs may include only one 6+2-pin, which can be insufficient for high-end GPUs (and often the overall capacity is insufficient as well), but generally they include enough 6+2-pins to cover a wide range.
However, if 12VHPWR is required, you must thoroughly check whether the PSU supports 12VHPWR.
As this connector has become common only recently, PSUs clearly differ between those that include it and those that do not; if you choose casually, you may end up with a PSU that lacks a 12VHPWR connector.
Therefore, rather than assuming “it’s common now so it must be included,” make sure to verify the PSU specifications.
Also, 12VHPWR has tiered maximum power delivery levels of 600 W, 450 W, 300 W, and 150 W.
Thus, after checking the TGP (Total Graphics Power) of the graphics card to be used—and including the maximum 75 W delivered by the PCIe slot—you need to confirm that the 12VHPWR wattage can supply enough power.
For example:
Example 1: RTX 4080
TGP: approx. 320 W
PCIe slot: 75 W
Required auxiliary power: approx. 245 W
⇒ 12VHPWR (300 W or higher) is OK
Example 2: RTX 4090
TGP: approx. 450 W
PCIe slot: 75 W
Required auxiliary power: approx. 375 W
⇒ 12VHPWR (450 W or higher) is OK
However, while you can tell whether a PSU supports 12VHPWR, its exact supported wattage is often not written in the specs.
That said, since 150 W equals one 8-pin and 300 W equals two 8-pins, it’s rare for a 12VHPWR connector to be 150 W or 300 W; in most cases it supports either 450 W or 600 W.
Notes on Using Adapter Cables or Adapters [Risk of Ignition/Fire]
There are cables that convert multiple PCI Express 8-pins into a 12VHPWR, so even if the graphics card requires 12VHPWR while the PSU supports only PCI Express 8-pins, you can handle it with a conversion cable.
Such adapter cables may be included with the PSU or may need to be purchased separately, so check the box contents.
However, when converting multiple PCI Express 8-pins to a 12VHPWR, you must pay attention to how you connect the cables.
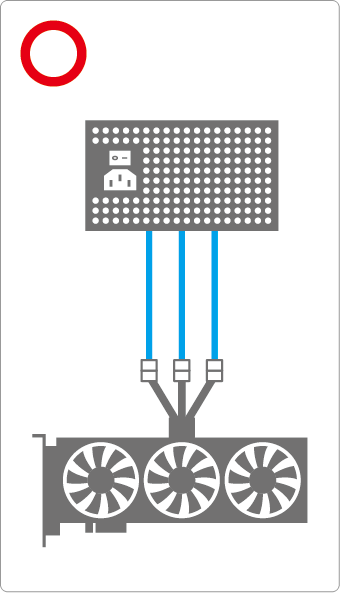
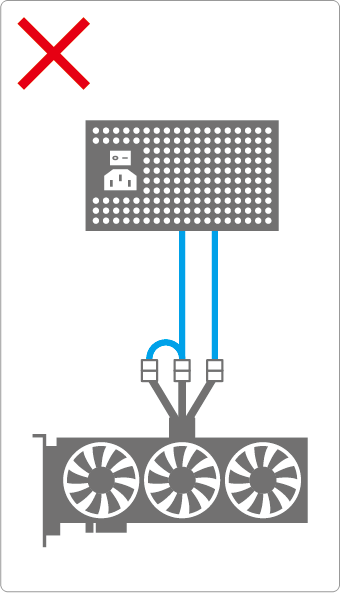
If, as shown in the right image, you connect only two plugs that branch from the same PSU cable line (※), excessive current will flow through a single cable.
※A cable from which two 8-pins branch out of one line
Such incorrect connections can cause the following problems:
- Abnormal heating or melting of the cable or connector area
- In the worst case, a risk of burning or fire
- Insufficient power under heavy load, causing GPU performance drops or sudden shutdowns
- The PSU’s protection features may trip, forcing a system restart
Because a 12VHPWR connector requires very high power, it is absolutely essential to connect the required number of 8-pin cables drawn individually from separate rails/outputs of the PSU.
This connection mistake is hard to spot visually, but power-delivery design directly impacts stability and safety, so never take it lightly.
![]() Ken
Ken
Also, if the GPU side requires three 8-pin connectors instead of a 12VHPWR, using two branched 8-pins from the same cable line (as in the right image) and one from a different line is likewise NG.
Basically, branched 8-pin cables are intended for graphics cards with modest power draw, not high-end, high-consumption GPUs.
Given the performance (and power) of recent graphics cards, it’s better to avoid using branched 8-pin cables.
Summary: For High-End GPUs, 12VHPWR Is Virtually Essential!
We have covered the basics of auxiliary power for graphics cards, connector types, and key points when choosing parts.
Here are the key points once again.
- GPUs are powered by both the “PCIe slot” and “auxiliary power”
- Recent GPUs are underpowered by the PCIe slot alone (auxiliary power is essential)
- Auxiliary power connectors come in three types: 12VHPWR (16-pin) / 8-pin / 6-pin
- 12VHPWR is a high-output connector for the latest GPUs and can supply up to 600 W
- A 6+2-pin can be used as an 8-pin, making it a flexible auxiliary power connector
- When choosing a PSU, make sure it supports the required auxiliary connector types and counts
- Incorrect use of adapter cables can pose a risk of ignition or fire—exercise caution
In recent years, as power consumption has increased for high-end graphics cards, traditional 8-pin and 6-pin auxiliary power has increasingly struggled to keep up.
In response, the “12VHPWR (16-pin)” connector has appeared and is becoming standard on GPUs from the RTX 40 series onward.
12VHPWR supports up to 600 W of power delivery, offering the advantages of a single-cable setup for easier routing and high power capacity.
On the other hand, many PSUs still don’t support it, so when selecting a PSU, always confirm the presence of the connector and the supported wattage.
Also, incorrect connections or misuse of adapter cables entail risks of overheating or burning, so safety considerations are crucial.
To use a high-end GPU comfortably and safely, you need the right understanding of auxiliary power and proper parts selection.
We also explain basic knowledge such as how to read manufacturers and model names, performance benchmarks, and how to choose from performance and compatibility perspectives.
≫ Related article: How to Choose a Graphics Card for a Custom PC [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
Select PC parts and online stores to instantly generate an estimate, check compatibility, and calculate power requirements. You can save up to five different builds, making it easy to try out multiple configurations.
≫ Tool:PC Parts Estimation & Compatibility Check Tool
 ZisaLog: Beginner’s Guide to Building a Custom PC
ZisaLog: Beginner’s Guide to Building a Custom PC 



