A power supply unit is a component that supplies power to each part of a computer. Unlike the CPU or GPU, it does not directly affect performance, so it can be difficult to understand. However, it is very important for keeping a PC running stably.
If the power supply unit is not suitable, the computer may become unstable, or in the worst case, it may not start or may shut down unexpectedly.
Also, if the size is different, it may not fit into the PC case at all.
This article explains the knowledge, features, performance, and compatibility of power supply units needed when building a custom PC, as well as how to choose the right one.
- Most power supply units are ATX or SFX standard
- Choose a power supply unit with a depth that fits the supported size of the PC case
- Select a power supply with enough capacity
- As a guideline, total power consumption of all parts × 1.8 times
- Check the types and number of power cables
- Modular (plug-in) types that allow cable removal are recommended
For other PC parts, basic knowledge, roles, and how to choose from the perspective of performance and compatibility are also explained, so please refer to them.
≫ Related article: PC Parts List and Explanation of Each PC Part [A Must-Read for Custom PC Beginners]
Select PC parts and online stores to instantly generate an estimate, check compatibility, and calculate power requirements. You can save up to five different builds, making it easy to try out multiple configurations.
≫ Tool:PC Parts Estimation & Compatibility Check Tool
Table of Contents
What is the Role of a Power Supply Unit?
A power supply unit converts the AC power from an outlet into DC power that a computer can use, and supplies power to each part such as the CPU, GPU, motherboard, and storage.
The most important point when choosing is the power capacity. If it is insufficient, the computer may become unstable, may not start, or may shut down during use.
Therefore, it is important to first calculate the required power capacity and choose a power supply unit with some margin above the total power consumption of the computer.
Also, since the types of cables needed for each part are different, the types and number of cables are also important points when choosing.
![]() Ken
Ken
Choosing a model with the efficient 80 PLUS certification can prevent wasted electricity and help reduce long-term costs.
In addition, it is necessary to consider the size and type of cooling fan, how easy it is to manage cables, quietness, and ease of assembly.
How to Choose a Power Supply Unit for a Custom PC [Performance]
This section explains how to choose a power supply unit focusing on performance and features.
Let’s explain these points in detail.
Based on user choices in the Custom PC Tool, statistical data is summarized on what is popular by ranking, price range, and specifications.
≫ Related article: Popular Power Supply Unit Rankings and Selection Rates by Specification [Statistics]
Power Capacity [Important]
To choose the power capacity of a power supply unit, add up the power consumption of each part and use a value with some margin as a guideline.
Specifically, 1.8 times the total power consumption of all parts is ideal.
By multiplying by 1.8, there will be enough margin even when all parts are under heavy load, and it can also handle future upgrades or sudden increases in power demand.
It also reduces the burden on the power supply unit.
To calculate the power capacity, it is necessary to know the power consumption of each part.
For CPU and GPU, it is listed in the product specifications, but for other parts, estimate using general guidelines.
Here is a summary of how to check the power consumption of the CPU and GPU, and the estimated power for each part.
For more details, see How to Calculate Power Supply Unit Capacity and Calculation Tools.
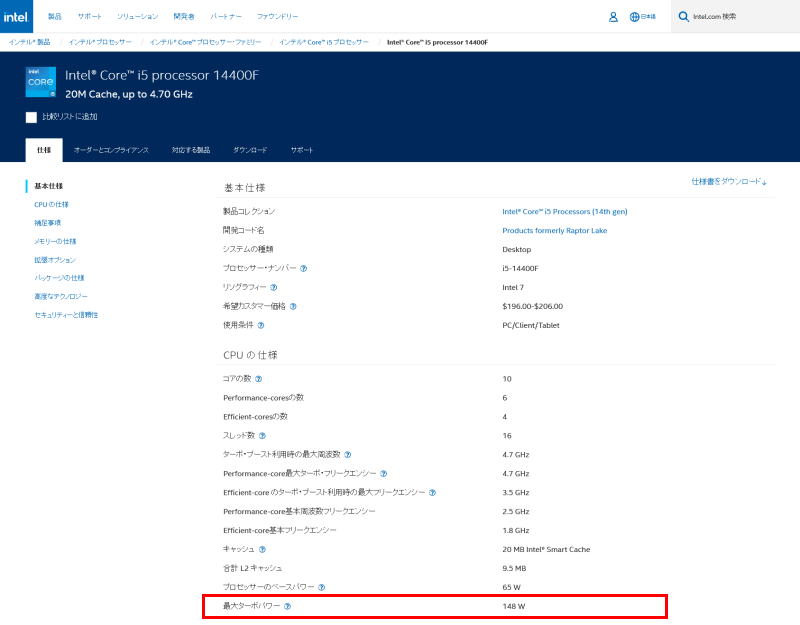
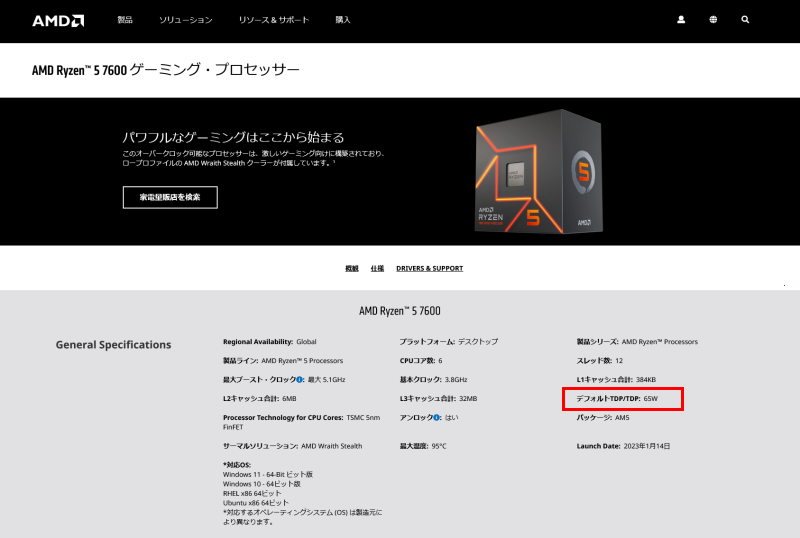
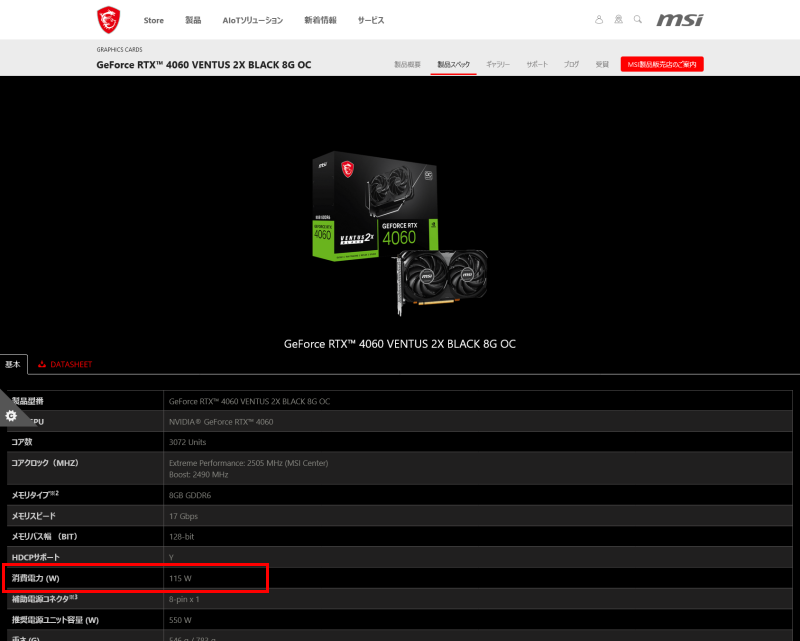
How to Check CPU and GPU Power Consumption
The power consumption of CPUs and GPUs varies by product, so check by model number and confirm from the official specification page.
Here are some sample locations where it is listed.
Estimated Power Consumption of Each Part
The estimated power consumption for each part is as follows.
| Part | Estimated Power |
|---|---|
| Memory | 5W |
| Motherboard | 30W |
| NVMe SSD | 25W |
| SATA SSD | 3W |
| HDD | 24W |
| Case fan | 3W |
| Optical drive | 25W |
These are estimates per unit, so if there are multiple memory modules, storage devices, or case fans, calculate for each one.
Even if all parts are at maximum output, it is important to choose a power supply unit with enough margin to provide stable power.
Detailed explanations on how to calculate power capacity, how to check CPU and GPU power, and why to multiply by 1.8 are provided.
≫ Related article: How to Calculate Power Supply Unit Capacity and Calculation Tools
A tool has also been created to check power capacity, estimates, and compatibility just by selecting parts, so please use it.
≫ Related article: Custom PC Parts Estimate and Compatibility Check Tool
80 PLUS Certification for Power Supply Units
80 PLUS certification is a system that shows the efficiency of a power supply unit, guaranteeing that the conversion efficiency meets certain standards for power consumption.
There are five levels of this certification: Bronze, Silver, Gold, Platinum, and Titanium. The higher the level, the better the efficiency.
| 80 PLUS Certification | Logo | Conversion Efficiency (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Load: 10% | Load: 20% | Load: 50% | Load: 100% | ||
| TITANIUM |  | 90% | 92% | 94% | 90% |
| PLATINUM |  | – | 90% | 92% | 89% |
| GOLD |  | – | 87% | 90% | 87% |
| SILVER |  | – | 85% | 88% | 85% |
| BRONZE |  | – | 82% | 85% | 82% |
| STANDARD |  | – | 80% | 80% | 80% |
Power supply units with high efficiency reduce unnecessary power consumption and heat, which affects stable PC operation and electricity savings in the long run.
Especially for gaming PCs or servers that require high loads, a highly efficient power supply unit is better.
However, the higher the certification level, the higher the price tends to be, so it is important to choose based on purpose and budget.
Even if the main unit price is higher and the certification level is higher, it is difficult to save enough electricity to make up for the cost, so from a power-saving perspective, it is not necessary to focus too much on this.
80 PLUS certification is commonly used for power supply units, but there are also ETA and LAMBDA certifications.
ETA, like 80 PLUS, shows energy efficiency, and LAMBDA evaluates noise levels.
≫ Related article: What is Power Supply Unit Certification? Best Grades Explained [80PLUS/ETA/LAMBDA]
Modular (Plug-in) Support
Some power supply units are modular types that allow only the necessary cables to be attached.
Including non-removable types, there are three patterns:
- Full modular (all cables removable)
- Semi-modular (main connectors fixed, others removable)
- Non-modular (all cables fixed)
Full modular allows all cables to be removed, semi-modular allows removal except for main connectors.
The big advantage of modular types is that there is no need to store unnecessary cables, and they do not get in the way during work.
With non-modular types, unused cables must be stored inside the PC case, which is often a tight fit.
Sometimes cables must be bent forcibly, which is not good for the cables. While unused cables may seem unimportant, storage upgrades such as adding more drives are common, and you may need those cables later, so it is better not to treat them roughly.
Also, during assembly, upgrades, or cleaning, unnecessary cables can get in the way and reduce work efficiency, especially since power supply cables are often thick and stiff, making them hard to move aside.
Therefore, using a modular type can solve these problems. Modular power supply units are a few hundred to a thousand yen more expensive than non-modular types, but the value is worth it.
For more details on the advantages and disadvantages, please refer to the following.
≫ Related article: What is a Modular Power Supply Unit? Features, Advantages, and Disadvantages Explained
Semi-Fanless Function
The semi-fanless function is an important feature for improving the quietness of a power supply unit.
Power supply units with this function stop or slow down the fan at low loads, greatly reducing noise.
When under normal or heavy load, the fan operates as usual, so it is the same as a regular power supply unit, but it is much quieter during idle or light tasks.
![]() Ken
Ken
However, power supply units with this function tend to be more expensive than those without, so it is necessary to consider the balance with your budget.
Also, the temperature range and load conditions for the semi-fanless function vary by power supply unit, so check the specifications before purchasing to see if it suits your environment.
≫ Related article: What is Semi-Fanless? Improving Quietness at Low Loads
How to Choose a Power Supply Unit for a Custom PC [Compatibility / Important]
This section explains how to choose a power supply unit focusing on compatibility.
If you choose a power supply unit that is not compatible, it may not physically fit, so be sure to check.
Let’s explain these points in detail.
Power Supply Unit Standards

ATX Standard

SFX Standard

SFX-L Standard
Power supply unit standards define the size, shape, and features of power supply units, so compatibility with the PC case must be checked.
If you get the standard wrong, the power supply unit may not fit in the case or the screw holes may not align.
There are about eight types of power supply unit standards, but the most commonly used are ATX, SFX, and SFX-L.
![]() Ken
Ken
For example, ATX cases usually support ATX power supply units, but smaller cases like MicroATX or Mini-ITX may require SFX or SFX-L power supply units.
Each standard has a general body size. For example, the ATX size is as follows:
Width: 150mm
Depth: 125–220mm
Height: 86mm
If it is ATX standard, the width and height are always the same, so if the PC case supports ATX, it will fit.
However, the depth varies, and higher capacity or more feature-rich power supply units tend to be longer.
≫ Related article: What are Power Supply Unit Standards? Features, Sizes, and Points to Note When Choosing
Power Supply Unit Size (Depth)
Not only should the power supply unit and PC case standards match, but the depth should also be checked.
As mentioned earlier, ATX power supply units range from 125 to 220mm in depth, so check if it fits in the PC case.
PC cases list the supported power supply unit size in mm, so choose one within that size.
Also, unused power supply cables must be stored inside the PC case, so if the size is just right, there may not be enough space.
Therefore, choose a power supply unit and PC case with some margin, or choose a modular power supply unit that allows cable removal.
Types and Number of Power Supply Unit Cables
Power supply unit cables come in various types, so choose a power supply unit while checking the types and number of cables needed for your parts configuration.
Therefore, it is necessary to know which cable is used for which part.
Here is a summary of the types of cables.
| Connector Type | Image | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Main Connector (20+4 pin) |  | • Supplies power to the motherboard • Can be used as 20-pin or 24-pin • Now used as 24-pin • Usually only one |
| CPU Auxiliary Power Connector (4+4 pin) |  | • Supplies extra power to the CPU • Can be used as 4-pin or 8-pin • Essential for high-performance CPUs • Usually one or two included |
| PCI Express Connector (6+2 pin) |  | • Mainly supplies extra power to the GPU • Can be used as 6-pin or 8-pin • Supplies power to PCI Express slots • Often 1–3 cables for GPUs |
| 12VHPWR Connector (12+4 pin) |  | • Supplies extra power to the latest high-performance GPUs • High power supply capability (up to 600W) • 4-pin signal pins for optimization |
| SATA Power Connector |  | • Supplies power to SSDs, HDDs, and optical drives • 2–3 connectors per cable |
| Peripheral Power Connector |  | • Supplies power to old IDE parts • 3-pin or 4-pin • 2–3 connectors per cable • Used for fans and LEDs • Rarely used now |
| FDD Power Connector | – | • Supplies power to floppy disk drives • Rarely used now |
Basic knowledge and details about each cable and connector for power supply units are explained.
≫ Related article: About Types of Power Supply Unit Cables
Additional Knowledge about Power Supply Units
This section explains knowledge about power supply units that is not as important as performance or compatibility, but is still good to know.
Let’s explain these points in detail.
Protection Circuits in Power Supply Units
Power supply units are equipped with protection circuits to protect the unit itself and connected parts from various abnormal conditions.
Choosing a power supply unit with these protection features is important for maintaining PC stability and long-term reliability.
There are various types of protection circuits.
| Protection Circuit | Overview | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Over Power Protection (OPP) | Stops operation if the power supply exceeds its maximum output. | Prevents overheating or failure of the power supply or parts. |
| Over Current Protection (OCP) | Cuts off the circuit if excessive current flows. | Protects parts from short circuits or overload risks. |
| Over Voltage Protection (OVP) | Cuts off power if the voltage exceeds the set limit. | Prevents damage to parts from overvoltage. |
| Under Voltage Protection (UVP) | Stops operation if voltage falls below a certain standard. | Prevents data loss or part failure from low voltage. |
| Short Circuit Protection (SCP) | Immediately cuts off power if a short circuit occurs. | Protects parts from sudden current increases due to shorts. |
| Over Temperature Protection (OTP) | Automatically stops operation if the power supply overheats. | Prevents damage to internal components and ensures safety. |
| No Load Operation Protection (NLO) | Operates safely even when no load is connected. | Prevents abnormal voltage/current and extends power supply life. |
| Surge/Inrush Current Protection (SIP) | Protects against sudden current changes or surge voltage. | Protects internal circuits and parts from inrush current or lightning surges. |
For more basic knowledge and detailed examples about protection circuits in power supply units, please refer to the following.
≫ Related article: About Protection Circuits in Power Supply Units
Warranty Period of Power Supply Units
Power supply units have warranty periods, which vary widely from 1 to 10 years depending on the product and price range.
Here is a general trend:
Under 10,000 yen: 1–3 years
Over 10,000 yen: 7–10 years
Although there is a warranty period, power supply failures are rare, so 1 year is too short, but if it is 3 years or more, there is not much need to be particular.
I have used two 玄人志向の電源ユニット Amazonで見る 楽天で見る Yahoo!ショッピングで見る power supply units under 10,000 yen with 3-year warranties (500W and 600W) for about 5 years, and they are still working fine.
In terms of load, I use them for 8–10 hours a day for work, which is longer than most people.
For about 2 of those 5 years, I ran AI learning programs 24 hours a day, with CPU and GPU loads over 90%, which is a harsh environment.
Even after 5 years in this situation, they are still fine, so unless there is an initial defect, you probably will not need the warranty for normal use.
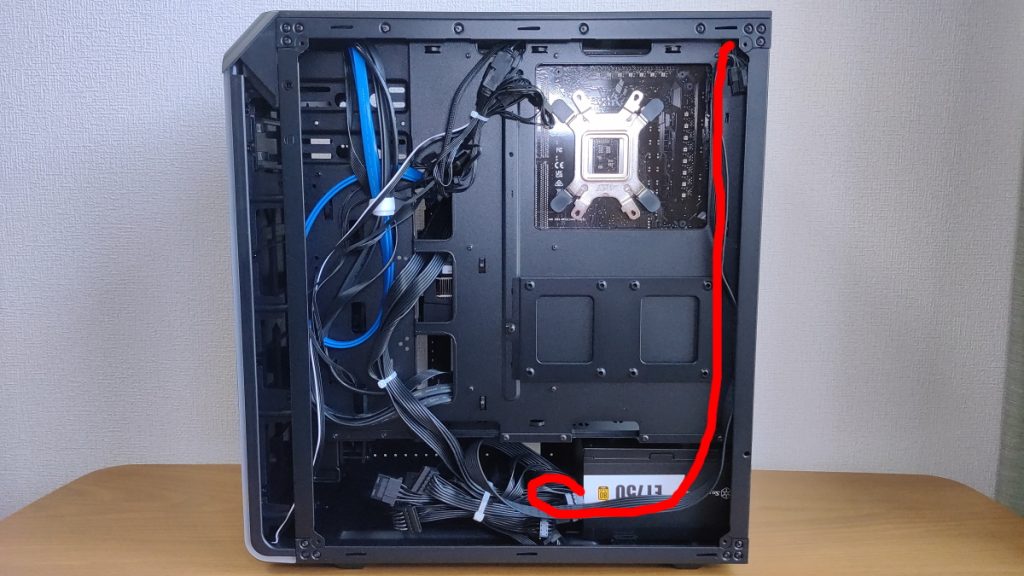
If Power Supply Unit Cables Are Not Long Enough
Depending on the length of the power supply unit cables, the size of the PC case, the structure of cable routing, and the size of the motherboard (ATX or larger), the cables may not reach.
In that case, purchase a extension cable extension cable or replace the power supply unit.
However, since replacement is expensive, first check if you can use an extension cable.
Extension cables are sold as sets or individually, so check which cables need to be extended before choosing.
Depending on the case layout, the cable that usually needs the most length is the ATX 12V / EPS 12V connector (4+4 pin) for CPU power.
This cable is often just barely long enough.
If the power supply unit is at the bottom of the case, the cable goes through the back, up to the top, then comes out to the front near the CPU power connector on the motherboard, and then folds back to connect.
Because of the folding, more length is needed, so depending on the case height and hole position, it may be just barely enough or not enough.
If that happens, do not panic and just buy an extension cable.
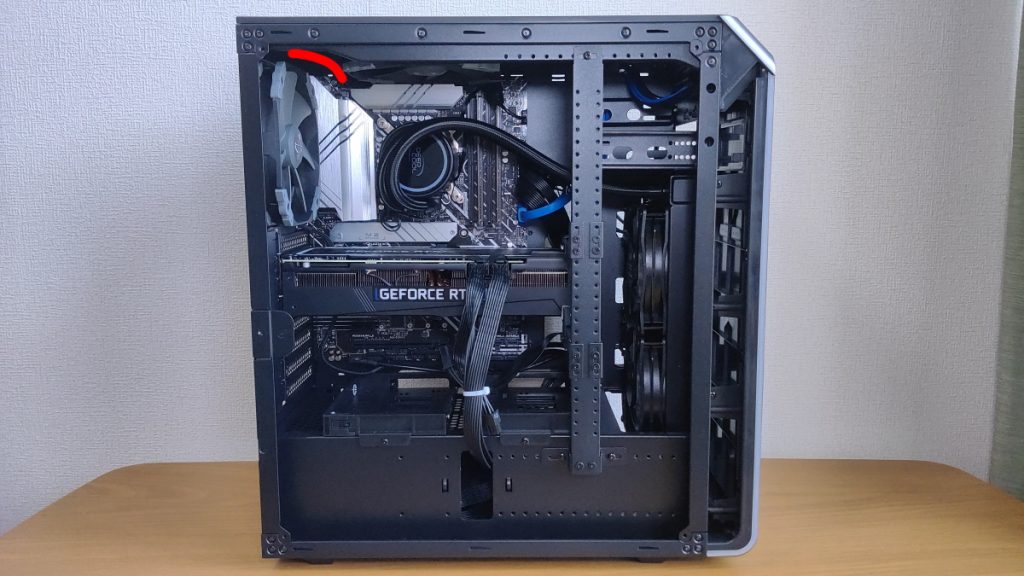
Power Supply Unit Orientation
The orientation and placement of the power supply unit depend on the structure of the PC case.
Generally, the power supply unit is installed at the bottom of the case with the fan facing outward (downward).
This arrangement improves cooling efficiency by bringing in fresh air from outside the case and prevents internal heat from affecting the power supply unit.
On the other hand, some cases have the power supply unit at the top or require the fan to face inward (upward), but in that case, pay attention to airflow and cooling.
Basically, the orientation is determined by the PC case, but some cases support both orientations.
≫ Related article: About Power Supply Unit Orientation and Placement [Custom PC]
About 105°C Capacitors in Power Supply Units
Power supply units contain capacitors that store and release electricity. Usually, 85°C capacitors are used.
However, high-quality power supply units use 105°C capacitors, which can withstand higher temperatures than usual.
These are suitable for high-load (high-temperature) uses such as 3D gaming, video editing, AI learning, and workstations.
About 50–60% of power supply units support 105°C capacitors, so you can choose while meeting other desired features, and your options will not be limited.
Other advantages, disadvantages, and recommended uses for 105°C capacitors are explained in detail.
≫ Related article: What is a 105°C Capacitor in a Power Supply Unit? [High Durability/Stability]
About PFC in Power Supply Units
PFC (Power Factor Correction) is a technology that improves the power efficiency of a power supply unit and reduces unnecessary power consumption.
Power supply units convert AC power to DC power, but some power is wasted in the process. PFC minimizes this waste by allowing the power supply unit to convert power more efficiently.
About 80% of power supply units support PFC, so choosing one with PFC will not limit your options.
Other details about power factor, types of PFC, and how to check PFC specifications are explained in detail.
≫ Related article: What is PFC in Power Supply Units? [Power Efficiency/Electricity Savings]
About ATX/EPS Versions
Power supply unit standards have versions, which are improved over time for better features and performance.
For example, newer versions often have better power efficiency and safety, and combining them with the latest PC parts can provide optimal performance.
However, unless you use a very old version, there is usually no problem in normal use, so you do not need to worry too much about the version. But if you want the latest features or power-saving performance, choose the latest version.
≫ Related article: About ATX and EPS Version Standards for Custom PC Power Supply Units
Summary: Be Sure to Calculate Power Capacity Correctly!
A power supply unit is a part that supplies power to each component such as the CPU, GPU, motherboard, and storage.
It does not directly affect the processing performance of the computer, but it is important to choose with the correct knowledge to keep the PC running stably.
Here is a summary of how to choose a power supply unit again.
- Most power supply units are ATX or SFX standard
- Choose a power supply unit with a depth that fits the supported size of the PC case
- Select a power supply with enough capacity
- As a guideline, total power consumption of all parts × 1.8 times
- Check the types and number of power cables
- Modular (plug-in) types that allow cable removal are recommended
The most important things not to get wrong are the standard, size (depth), power capacity, and the types and number of cables.
If you make a mistake here, you may not be able to assemble the PC, or even if you do, it may be unstable, may not start, or may shut down during use, so be careful.
Also, for better work efficiency, choose modular types, and for quietness at low loads, choose fanless features as needed.
For other PC parts, basic knowledge, roles, and how to choose from the perspective of performance and compatibility are also explained, so please refer to them.
≫ Related article: PC Parts List and Explanation of Each PC Part [A Must-Read for Custom PC Beginners]
Select PC parts and online stores to instantly generate an estimate, check compatibility, and calculate power requirements. You can save up to five different builds, making it easy to try out multiple configurations.
≫ Tool:PC Parts Estimation & Compatibility Check Tool
 ZisaLog: Beginner’s Guide to Building a Custom PC
ZisaLog: Beginner’s Guide to Building a Custom PC