Memory is often discussed in the context of dual channel configuration, where two memory modules are used as a pair.
Recently, using a dual channel configuration has become standard for improving computer performance, so it is highly recommended to consider this setup for a personal computer.
This article explains the features of dual channel memory and the requirements for setting up a dual channel configuration.
- Dual channel uses two memory modules as a pair
- Dual channel is now the standard
- Two modules are better than one, even with the same total capacity
- Theoretically, data transfer speed and bandwidth are doubled
- Overall performance improves slightly depending on the workload
- The modules must have the same specifications and capacity
- Both the memory and motherboard must support dual channel
This article also explains basic memory knowledge, how to choose memory from a performance and compatibility perspective.
≫ Related article: How to Choose Memory for a Custom PC [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
Select PC parts and online stores to instantly generate an estimate, check compatibility, and calculate power requirements. You can save up to five different builds, making it easy to try out multiple configurations.
≫ Tool:PC Parts Estimation & Compatibility Check Tool
Table of Contents
What is Dual Channel Memory?
Let’s start with the basics of dual channel memory.
Dual Channel Uses Two Memory Modules as a Pair
Dual channel is a technology that uses two memory modules as a pair to increase memory data transfer speed and bandwidth (the amount of data transferred).
This improves the overall performance of the computer, especially when running heavy applications or games.
Dual channel is not rare, and memory is usually installed in pairs to achieve a dual channel configuration.
Theoretical Memory Speed is Doubled
Dual channel allows two memory modules to read and write data at the same time, which increases data transfer speed.
Normally, memory operates in single channel mode, where one module handles data transfer.
However, in dual channel, two modules work in parallel, so the data transfer speed is theoretically twice as fast as single channel.
Actual Performance Does Not Double
In real-world use, actual performance does not double because of bottlenecks from other components and different usage situations.
- The CPU may not use the full memory bandwidth.
- Other factors like storage speed, CPU processing speed, and cache size can also be bottlenecks.
For these reasons, actual processing speed is not doubled, and may only increase by about 1.1 or 1.2 times.
Benchmark tests may show a slight increase in scores, but it is usually not noticeable in everyday use.
However, dual channel still offers better performance than single channel, so it has become the standard configuration.
3D Games Can See About 10% Performance Improvement
Dual channel can have a noticeable effect in applications that use a lot of memory bandwidth.
Especially, in graphics-heavy 3D games or when multitasking, dual channel configuration shows its benefits.
Depending on the system, 3D games can see about a 10% improvement in FPS (frames per second) compared to single channel.
This is because the increased memory data transfer speed shortens game loading times and improves FPS.
8GB x 2 is Faster Than 16GB x 1
To use dual channel, two modules must be installed as a pair.
So, even with the same total memory capacity, dual channel with two modules performs better than single channel with one module.
For example, even if the total memory is 16GB, it is better to use two 8GB modules in dual channel than one 16GB module.
This doubles the memory data transfer speed and improves data transfer performance.
As a result, the computer runs more smoothly, and applications start up and files read and write faster.
Triple Channel Uses Three Modules as a Set
Usually, dual channel uses two modules as a pair, but there are also triple channel (three modules) and quad channel (four modules) configurations.
While dual channel uses two modules at the same time, triple channel uses three, and quad channel uses four modules in parallel.
This further increases memory data transfer speed and bandwidth.
As explained later, using dual channel or other multi-channel features requires a compatible CPU and motherboard.
However, most recent components do not support triple or quad channel, so aiming for a dual channel setup is recommended.
Requirements and Hardware Conditions for Dual Channel Memory
To use memory in a dual channel configuration, certain hardware requirements must be met.
Memory Must Support Dual Channel
To use dual channel, the memory itself must support dual channel operation.
Most recent memory modules support this, but it is a good idea to check the manufacturer’s specifications.
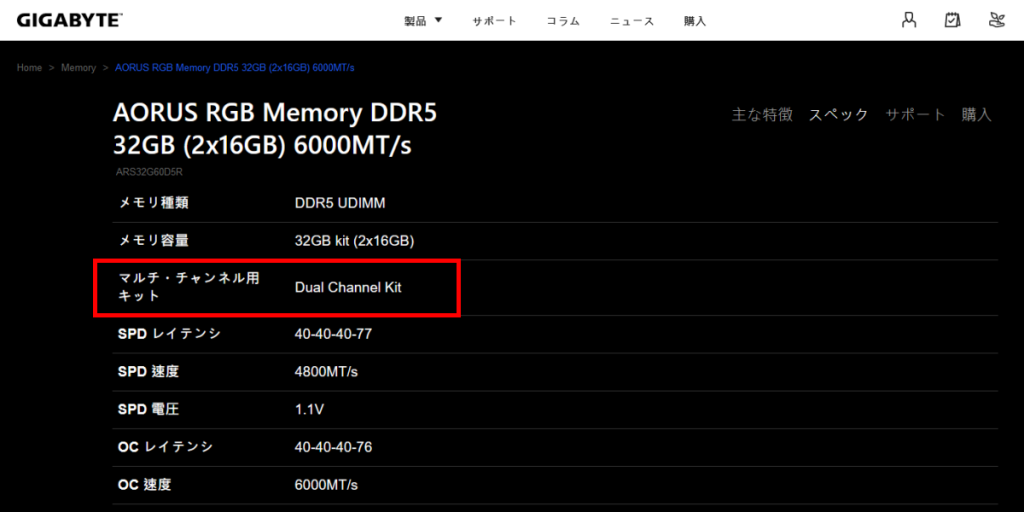
As shown above, it is written that dual channel is supported.
Same Memory Module Type and Capacity
To use dual channel, the two memory modules must have the same module type and the same capacity.
For example, if using DDR4 memory, both modules must be DDR4.
In fact, most motherboards only support one type of memory module, so they must be the same.
Also, the memory capacity must be the same.
Ideally, use the same model from the same manufacturer for better stability and compatibility.
This may sound complicated, but memory is often sold as a set of two or four modules, so buying a set solves this problem.
With a set, all specifications like module type, capacity, speed, and timing are the same, so there is little to worry about.
Use Memory Slots That Support Dual Channel
To use dual channel, install two modules in the slots that support dual channel on the motherboard.
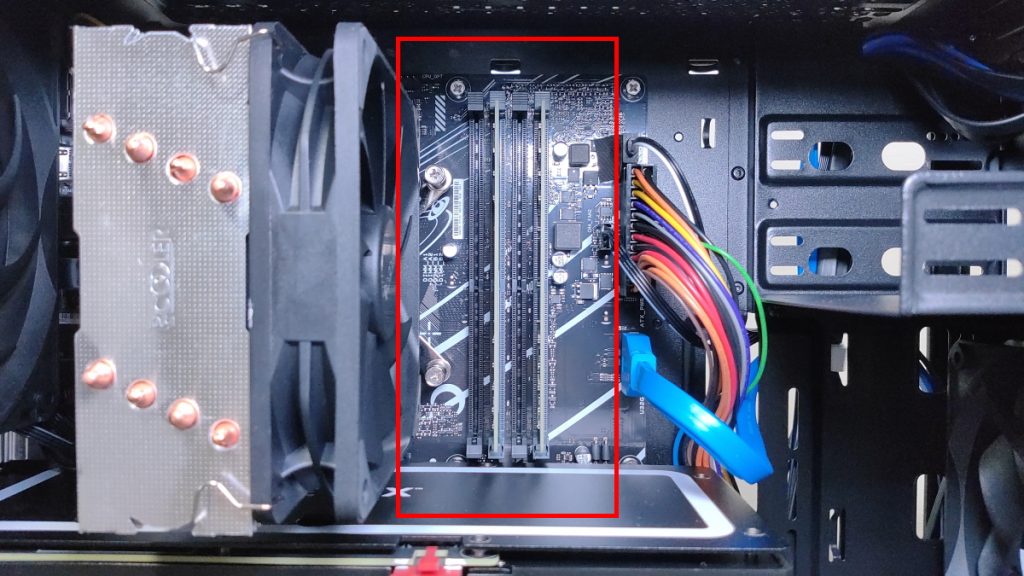

Usually, dual channel slots are color-coded on the motherboard, so follow the color guide when installing memory.
For example, it is common to install modules in the first and third slots, or the second and fourth slots.
![]() Ken
Ken
If the slots are the same color, it can be confusing, so check the motherboard manual if unsure.
Motherboard Must Support Dual Channel
To use dual channel, the motherboard must support dual channel memory.
Most recent motherboards support this, but check the manufacturer’s specifications to be sure.

As shown above, it is written that dual channel memory is supported.
Conditions That Do Not Have to Be Met
For dual channel, not all memory product specifications must be identical.
The same memory module type and capacity are required, but other specifications do not have to be exactly the same, though it is ideal.
So, when adding memory, or using memory from an old computer together with new memory, the products and specifications may differ.
For example, the following differences will still work:
- Different manufacturers or brands
- Data transfer speed
- Operating clock
- Memory timing
Even if memory timing or speed do not match exactly, the system usually adjusts automatically.
However, the system will operate at the lower performance level, so performance may decrease. Matching specifications as much as possible is recommended.
Summary: Dual Channel Configuration is the Basic Choice!
This article explained dual channel memory. If simply using two modules as a pair can improve performance, it is worth doing.
Nowadays, dual channel is standard, and the hardware requirements are not difficult.
Therefore, unless there is a special reason, avoid using only one memory module and use two as a pair.
Here are the key points again.
- Dual channel uses two memory modules as a pair
- Dual channel is now the standard
- Two modules are better than one, even with the same total capacity
- Theoretically, data transfer speed and bandwidth are doubled
- Overall performance improves slightly depending on the workload
- The modules must have the same specifications and capacity
- Both the memory and motherboard must support dual channel
This article also explains basic memory knowledge, how to choose memory from a performance and compatibility perspective.
≫ Related article: How to Choose Memory for a Custom PC [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
Select PC parts and online stores to instantly generate an estimate, check compatibility, and calculate power requirements. You can save up to five different builds, making it easy to try out multiple configurations.
≫ Tool:PC Parts Estimation & Compatibility Check Tool
 ZisaLog: Beginner’s Guide to Building a Custom PC
ZisaLog: Beginner’s Guide to Building a Custom PC