A CPU cooler is an important component that greatly affects the performance and lifespan of a computer.
If the right CPU cooler is not chosen, the computer may overheat, causing performance to drop, and in the worst case, it may break down. Therefore, it is necessary to have correct knowledge when selecting a CPU cooler.
This article explains in detail the types of CPU coolers and their characteristics.
- CPU coolers are parts that affect performance and lifespan
- There are mainly two types: air cooling and water cooling
- Air coolers are affordable, quiet, and suitable for general use
- Water coolers have high cooling performance and are suitable for high-load tasks like 3D games
- It is important to choose a CPU cooler with a TDP higher than the CPU’s TDP
- The current mainstream is side-flow air coolers and all-in-one water coolers
- Fanless and sub-zero coolers are for special purposes and not common
This article also explains how to choose a CPU cooler from the perspective of type, performance, and compatibility.
≫ Related article: How to Choose a CPU Cooler for Custom PCs [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
Select PC parts and online stores to instantly generate an estimate, check compatibility, and calculate power requirements. You can save up to five different builds, making it easy to try out multiple configurations.
≫ Tool:PC Parts Estimation & Compatibility Check Tool
Table of Contents
About CPU Cooler Cooling Methods (Air Cooling / Water Cooling)
This section explains the types of CPU cooler cooling methods (air cooling / water cooling), including a list of cooling methods and typical types.
List of CPU Cooler Cooling Methods (Air Cooling / Water Cooling)
CPU coolers can be broadly divided into two types: air coolers and water coolers.
Furthermore, air coolers include side-flow and top-flow types, while water coolers include all-in-one water cooling and custom water cooling.
In addition, although not commonly used in custom PCs, there are also fanless and sub-zero types.
Let’s summarize the features and other details in a table.
| Type of Cooler | Image | Cooling Method | Features | Usage | Price Range | Size/Height | Cooling Performance | Quietness | Installation Difficulty |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Side-flow Type |  | Air Cooling | ・Efficient cooling ・Good airflow | ・Everyday use ・Business ・Gaming ・High-load tasks | Normal | Normal to Large | Normal to High | Quiet to Normal | Easy |
| Top-flow Type |  | Air Cooling | ・Compact ・Cools the entire motherboard | ・Everyday use ・Business ・Small PCs | Cheap to Normal | Small to Normal | Normal | Noisy under high load | Easy |
| All-in-one Water Cooling |  | Water Cooling | ・High cooling performance ・High quietness | ・Gaming ・High-load tasks | Normal to High | Normal to Large | High | Quiet to Normal | Normal |
| Custom Water Cooling |  | Water Cooling | ・High cooling performance ・High quietness ・Highly customizable ・Expensive parts ・Labor intensive ・Risk of water leakage | ・High-end PCs | Expensive | Large | High | Quiet to Normal | Difficult |
| Fanless |  | Air Cooling | ・Completely silent ・No maintenance required | ・Low performance / Silent PCs | – | Normal | Low | Silent | Easy |
| Sub-zero | – | Cooling Plate | ・Ultra-low temperature cooling | ・For competitions | Very expensive | Large | Very high | – | – |
The Mainstream is Side-flow and All-in-one Water Cooling

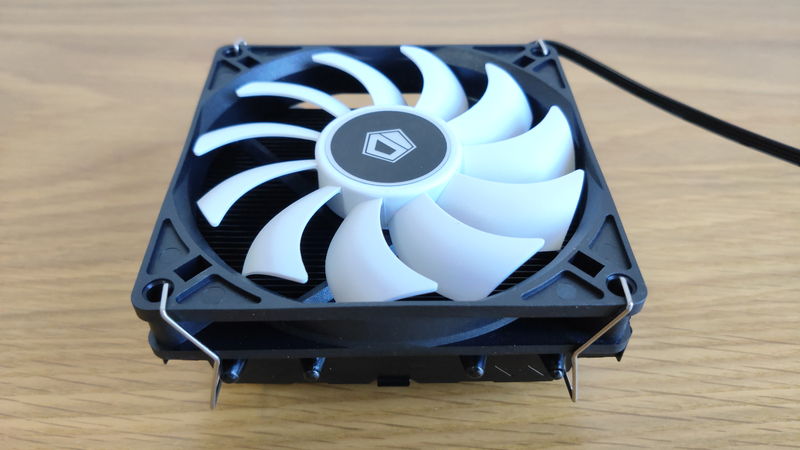
Side-flow Air CPU Cooler

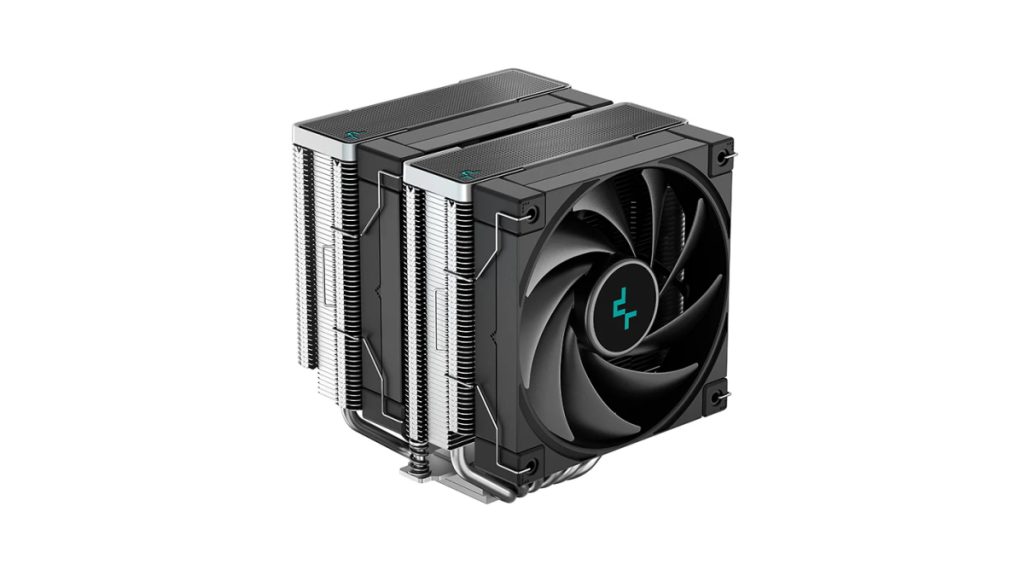
All-in-one Water Cooling CPU Cooler
Currently, the mainstream CPU coolers are side-flow air coolers and all-in-one water coolers.
The features of each will be explained later.
Let’s look at which types users are actually choosing.
Based on the parts selected by users in the Custom PC Tool that allows “estimation“, “compatibility check“, and “power calculation” just by selecting parts, the share was aggregated.
The share of air cooling and water cooling is about half and half.
For water cooling, there are all-in-one and custom water cooling, but this graph only counts all-in-one water cooling.
Among air coolers, there are side-flow and top-flow types, but most users choose the side-flow type.
This data does not include the top-flow type of retail coolers, so the actual ratio of top-flow types may be a little higher.
If you want to see other items such as water cooling fan size and radiator size, please refer to the following.
≫ Related article: Popular CPU Cooler Rankings and Selection Rates by Specification [Statistics]
Check the TDP for Cooling Performance
When checking the cooling performance of a CPU cooler, it is important to check the TDP (Thermal Design Power) of both the CPU cooler and the CPU.
TDP is an indicator of the amount of heat generated by the CPU at maximum load, and it is used to select the appropriate cooler.
For example, if the CPU’s TDP is 95W, it is necessary to choose a CPU cooler with at least 95W TDP.
In other words, a CPU cooler’s TDP means it can cool CPUs up to that TDP. If the CPU cooler’s TDP is lower than the CPU’s TDP, the cooling performance may not be sufficient.
This ensures that the CPU is properly cooled even under high load, preventing performance drops and failures due to overheating.
For gaming or high-load tasks, CPUs with high TDP are often used, so a high-performance cooler that can handle it is necessary.
On the other hand, for light tasks, a CPU with low TDP and a matching cooler is sufficient.
Also, if the CPU has features such as overclocking or temporarily increasing the clock speed (*), the default TDP will be exceeded.
Therefore, it is better to choose a CPU cooler with a margin in TDP, not just barely enough.
*For Intel, this is called Turbo Boost Technology, and for AMD, it is called Precision Boost.
For example, with Intel Core i7-14700F, the base power (TDP at rated clock speed) is 65W, but when the clock speed is temporarily increased by Turbo Boost Technology, it can reach up to 219W.
Intel lists both base power and maximum, but AMD only lists base power, so it is recommended to choose a cooler with about 1.5 to 2 times the CPU’s TDP.
There are air cooling and water cooling types of CPU coolers, but whichever is chosen, it is important to check the TDP and select one that matches the usage environment.
Air Cooling CPU Coolers
This section explains the main types of air cooling CPU coolers and their features.
Side-flow Type

The side-flow type has a heatsink placed horizontally, and the cooling fan blows air from the side to efficiently dissipate heat.
It can cool along the airflow inside the PC created by the case fans, so it provides smooth cooling without disturbing the airflow.
Compared to the top-flow type, the heatsink and fan are larger, so cooling performance is higher.
For mid-range and high-end CPUs such as Core i5 and Ryzen 5 or higher, side-flow types with high cooling performance are often used.
Also, since larger fans such as 120mm and 140mm can be installed, the fan speed can be kept low even under high load, making it quieter.
Top-flow Type
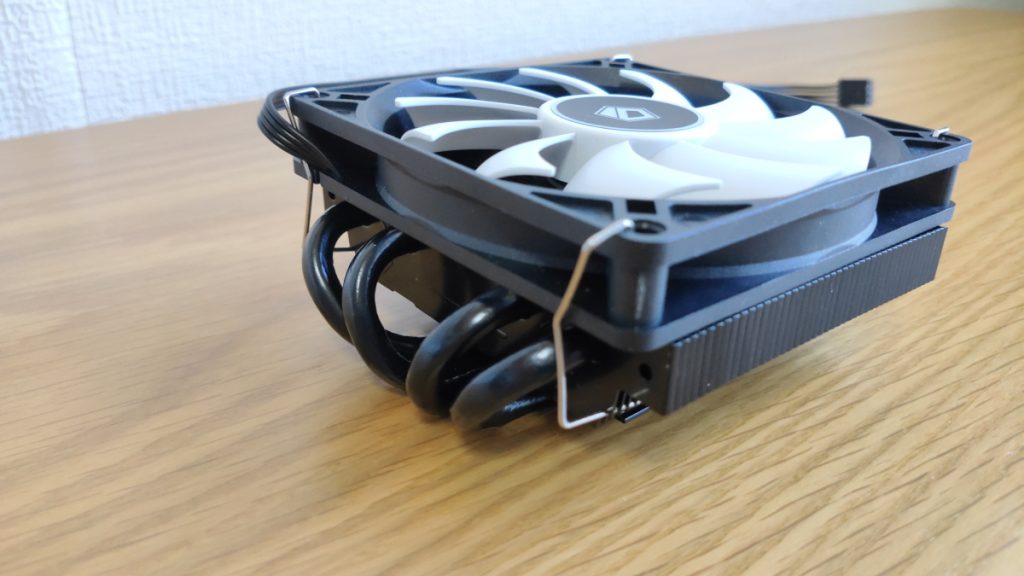

Top-flow CPU coolers have the cooling fan mounted horizontally, blowing air from top to bottom to cool the CPU.
The stock CPU coolers that come with CPUs are usually top-flow types.
This type blows air from above, so it also cools parts and components around the motherboard.
It is especially effective for areas that tend to get hot, such as VRMs (Voltage Regulator Modules) and memory slots.
Compared to side-flow types, they are smaller and lower in height, so they are suitable for compact cases or limited spaces.
However, the maximum cooling performance tends to be lower.
Also, since the fan size is small (92mm), the fan speed increases under high load, making it noisier.
Water Cooling CPU Coolers
This section explains the main types of water cooling CPU coolers and their features.
All-in-one Water Cooling

A water cooling CPU cooler is a cooling system that circulates coolant to efficiently remove heat from the CPU.
It consists of a cooling head (water block) attached to the CPU, a radiator (fan part) for cooling, a pump connecting them, and coolant, all integrated. Cooling is achieved by circulating coolant between the cooling head and radiator.
The cooling head attached to the CPU absorbs heat from the CPU, and the pump circulates the coolant, moving the warm coolant to the radiator.
When the coolant reaches the radiator, the fan and fins spread the heat over a wide area as the coolant flows through the radiator.
As the coolant temperature drops, it is sent back to the cooling head, continuing the cooling cycle.
All-in-one water cooling CPU coolers are relatively easy to install and suitable for beginners.
This makes them an easy option for users who want higher cooling performance than air coolers.
Also, they are often used when installing high-end CPUs.
Since everything is integrated and sold as a product, the risk of coolant leakage and maintenance effort is greatly reduced.
The coolant is sealed at the factory, so users do not need to refill or replace the liquid themselves. Simply attach the cooling head to the CPU and the radiator to the PC case.
Compared to air coolers, all-in-one water coolers have more fans, so the speed of each fan can be lowered, making them quieter.
Especially under high load, they operate quietly, making them suitable for users who value quietness.
Furthermore, all-in-one water cooling can also improve airflow inside the case.
Air coolers tend to trap heat around the CPU, but all-in-one water cooling moves the heat to the radiator, exhausting it directly outside the case, improving overall cooling efficiency.
The part that is cooled by blowing air is called the radiator, and there are several sizes of radiators.
Basically, radiators are fitted with case fans, so the size matches the fan standard.
First, they are roughly divided into 120mm and 140mm types.
120mm types come in three sizes:
- 120mm (1 x 120mm fan)
- 240mm (2 x 120mm fans)
- 360mm (3 x 120mm fans)
140mm types come in three sizes:
- 140mm (1 x 140mm fan)
- 280mm (2 x 140mm fans)
- 420mm (3 x 140mm fans)
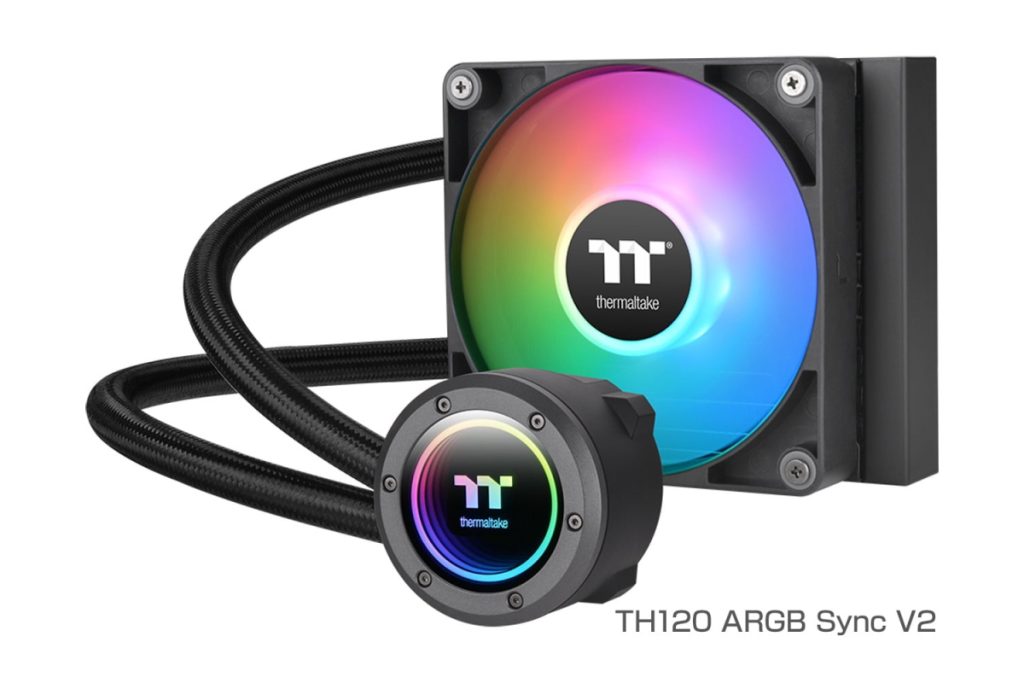

120mm Radiator
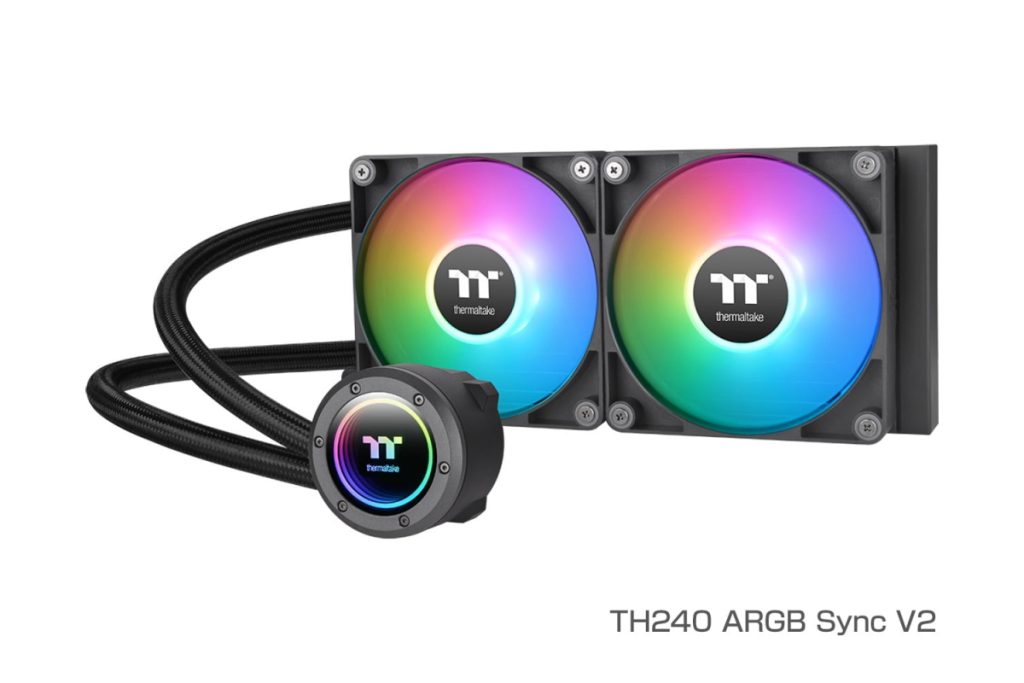

240mm Radiator
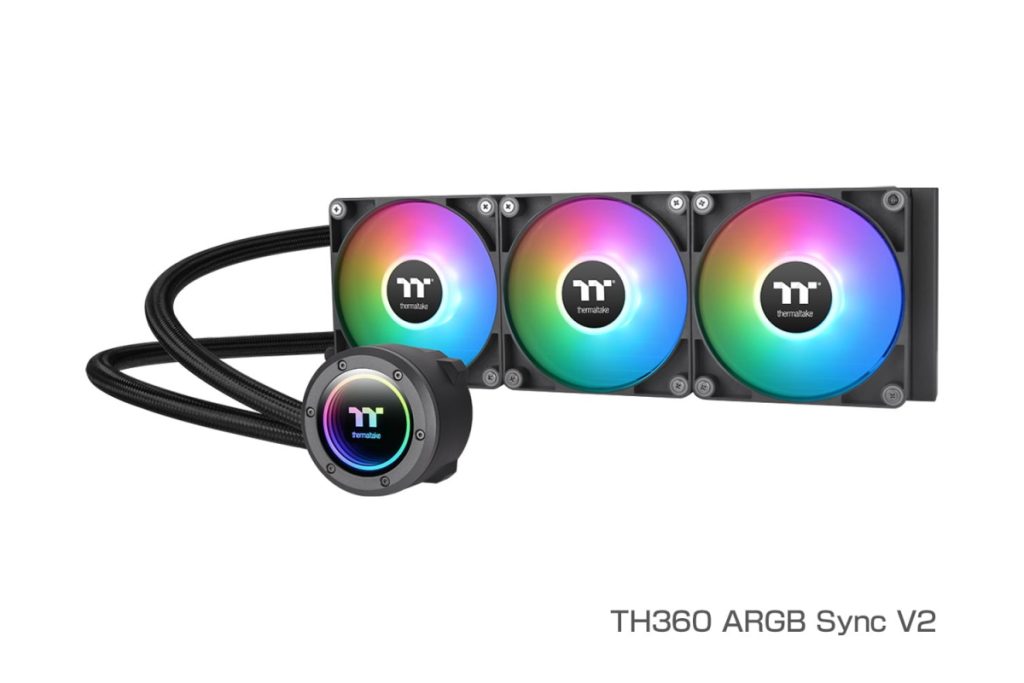

360mm Radiator
Radiators are responsible for dissipating heat from the CPU using coolant, and the larger the size, the more heat can be released.
Also, each PC case supports specific radiator sizes, so it is necessary to check if it can be installed properly.
For small PC cases or mainly light tasks, smaller sizes like 120mm or 140mm are suitable.
On the other hand, for gaming, video editing, or overclocking, sizes of 240mm or larger are recommended.
Custom Water Cooling
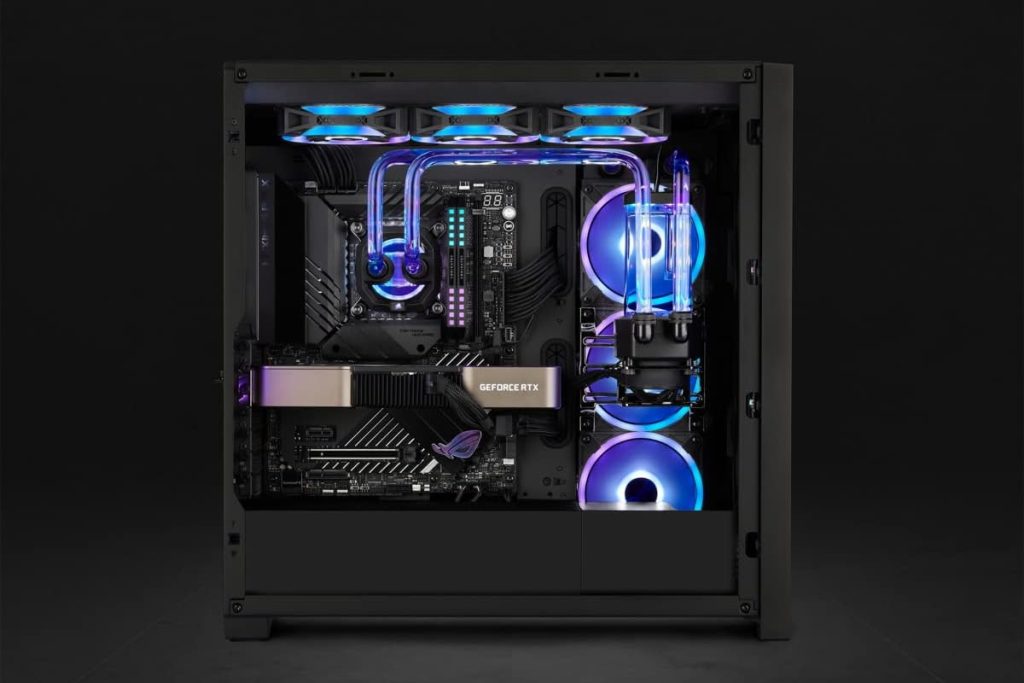
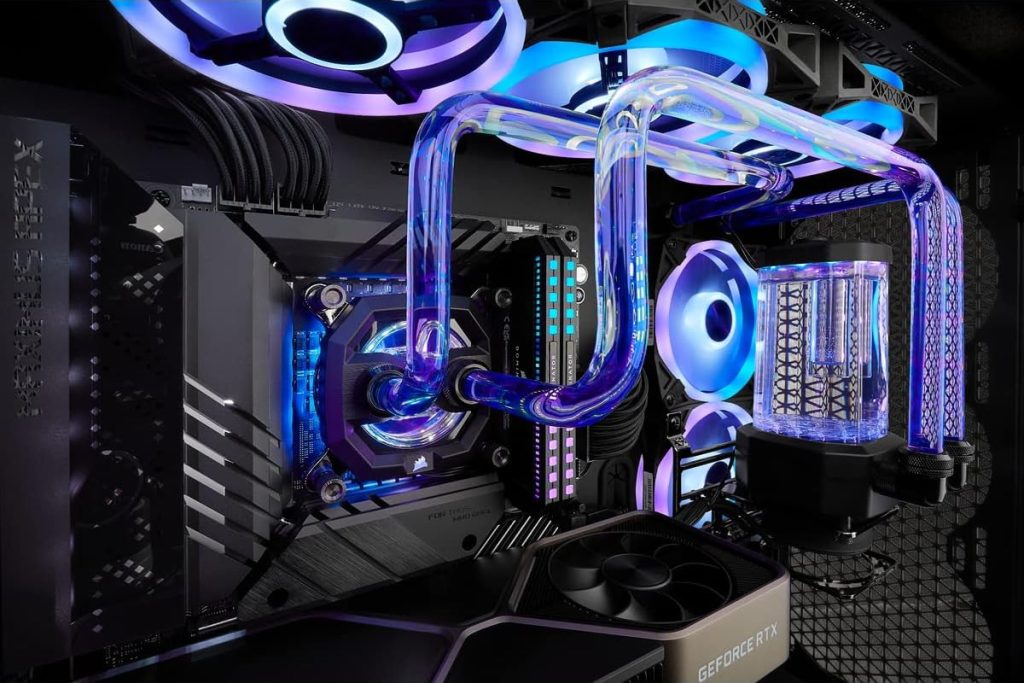


(Source: Corsair iCUE Hydro X Series )
Custom water cooling CPU coolers have the same basic cooling mechanism as all-in-one water coolers, but there are big differences in ease of assembly, customizability, cost, and maintenance.
Custom water cooling is more complex and difficult to assemble than all-in-one, the parts are more expensive, and maintenance such as checking for leaks is necessary.
It is necessary to cut the water pipes to fit the custom PC and be careful about leaks, so the assembly process and maintenance are difficult, making custom PC building much harder.
There is the advantage of being able to choose each part for high customizability, but more knowledge is required and assembly is more complicated, so it is not recommended for those building a custom PC for the first time.
Appearance and performance can be adjusted to personal preference, but the excellent cooling performance comes with high cost and effort as disadvantages.
Unless one enjoys building and customizing PCs, it may be too challenging.
The initial cost is high, and it is necessary to prepare dedicated parts such as pumps, radiators, tubes, and coolant separately.
There are kits available, which make it somewhat easier to gather the necessary parts.
Also, it is necessary to regularly replace the coolant and clean the system, and there is a risk of water leakage.
Especially if installation or regular inspection is neglected, other parts may get wet and break.
Other CPU Coolers
This section explains the features of other types.
These are not popular and are not used in custom PCs, but it is good to know about these special cooling technologies as knowledge.
Fanless CPU Coolers
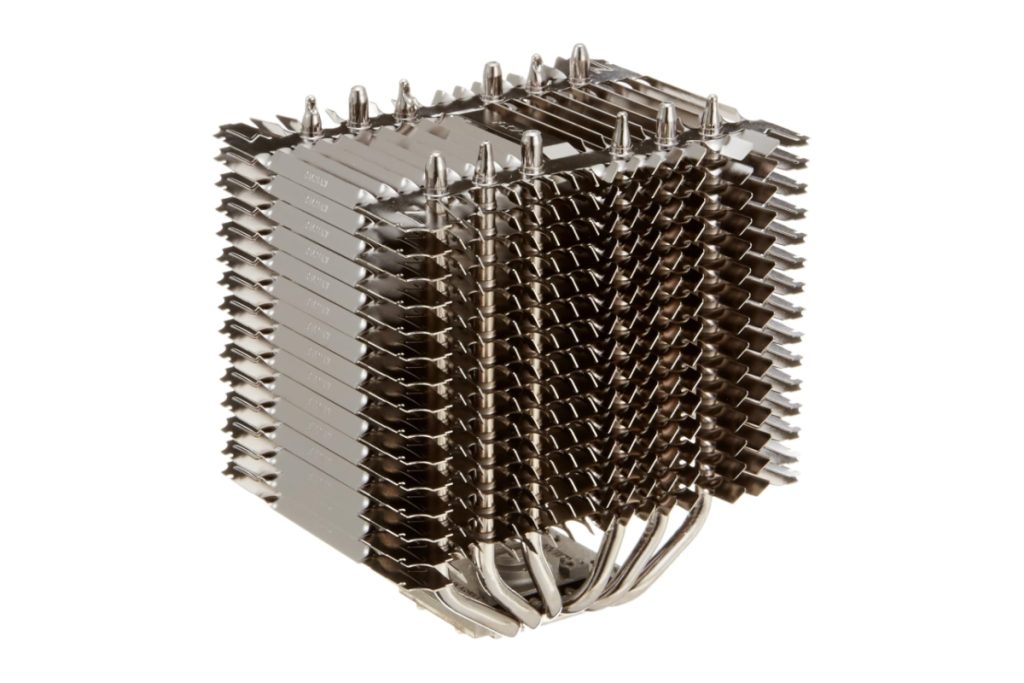
Fanless CPU coolers use a metal heat sink to dissipate heat from the CPU.
The heat sink is made of materials with high thermal conductivity, such as aluminum or copper, which quickly absorb heat and release it over a large surface area.
As the name suggests, there is no fan, so there is no operating noise at all.
However, if a case fan is installed, there will still be fan noise, so this may not be a big advantage.
Also, fanless CPU coolers have low cooling performance, so they can only be used with low-performance (low-heat) CPUs.
They are mainly recommended for low-power CPUs or use in power-saving mode.
To use a fanless CPU cooler effectively, it is necessary to ensure natural airflow inside the case and prevent heat buildup.
However, since custom PCs are often high-performance, fanless CPU coolers with low cooling performance are rarely used.
The small number of products also shows that they are not popular and are rarely used.
Sub-zero CPU Coolers
Sub-zero coolers are special coolers that achieve ultra-low temperature cooling, which is not possible with normal air or water coolers.
Sub-zero means below zero degrees Celsius.
Sub-zero coolers include types that use Peltier elements and types that use liquid nitrogen.
| Cooling Method | Cooling Medium | Temperature Range | Purpose | Usage Period | Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peltier Element | Peltier element Heat sink Liquid cooling | 0°C to -30°C | Long-term cooling Stable operation | Long-term | Medium (Condensation risk) |
| Liquid Nitrogen | Liquid nitrogen Liquid helium | -100°C to -200°C | Temporary record breaking For competitions | Short-term (a few minutes to a few hours) | High (Condensation, freezing) |
Peltier element CPU coolers use the thermoelectric effect, cooling one side and heating the other by applying voltage.
By passing current, one side is cooled and the other is heated, making it a special semiconductor. One side becomes ultra-cold, and the other becomes hot.
There are few products using Peltier elements, and although there were some combined with all-in-one water coolers in the past, they are not widely used.
CPU coolers using liquid nitrogen can cool the CPU to the extreme in a short time due to the very low temperature.
This type is not available as a product, but is often used in overclocking competitions, and is usually homemade.
The structure involves attaching a cup-like object to the CPU cooler part and pouring liquid nitrogen for cooling.
As the liquid nitrogen decreases, it is manually refilled, so it is not designed for long-term operation.
It is only needed for short-term cooling during competitions, and requires specialized knowledge and experience, so it is not something general users can use.
Summary: For High Cooling Performance, Choose Large Side-flow or All-in-one Water Cooling
This article explained in detail the types and features of air and water cooling CPU coolers.
Here are the key points again.
- CPU coolers are parts that affect performance and lifespan
- There are mainly two types: air cooling and water cooling
- Air coolers are affordable, quiet, and suitable for general use
- Water coolers have high cooling performance and are suitable for high-load tasks like 3D games
- It is important to choose a CPU cooler with a TDP higher than the CPU’s TDP
- The current mainstream is side-flow air coolers and all-in-one water coolers
- Fanless and sub-zero coolers are for special purposes and not common
Recently, the mainstream is side-flow air coolers and easy-to-install all-in-one water coolers.
Especially for high-performance CPUs used in high-load situations, all-in-one water coolers with higher cooling performance and quietness are popular.
Whichever is chosen, it is important to select the best one according to the usage environment and purpose. Especially for high-load tasks, it is important to check the TDP and choose an appropriate cooler.
This article also explains how to choose a CPU cooler from the perspective of type, performance, and compatibility.
≫ Related article: How to Choose a CPU Cooler for Custom PCs [Performance / Features / Compatibility]
Select PC parts and online stores to instantly generate an estimate, check compatibility, and calculate power requirements. You can save up to five different builds, making it easy to try out multiple configurations.
≫ Tool:PC Parts Estimation & Compatibility Check Tool
 ZisaLog: Beginner’s Guide to Building a Custom PC
ZisaLog: Beginner’s Guide to Building a Custom PC 



